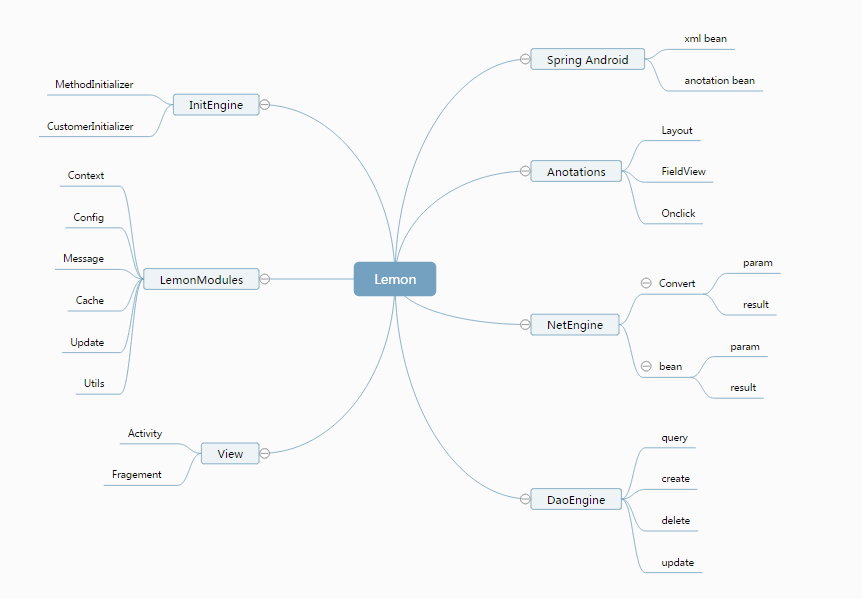
lemon初衷是让android开发更简单,核心实现了一个轻量级别的控制反转(IoC) ,通过配置XML和注解的方式使得代码之间松耦合,当应用了IoC,一个对象依赖的其它对象会通过被动的方式传递进来,而不是这个对象自己创建或者查找依赖对象。构建与IOC核心之上做了如下几个模块:
- 网络模块
- 数据库模块
- 配置模块
- 初始化模块
- 缓存模块
- Annotations模块
- 消息模块
- 更新模块
(Spring Android Lemon)
脑图地址: 戳这里
此模块设计思路是加载xml文件和扫描类,根据xml配置和类注解,将类对象,属性,方法写入上下文缓存。关键类BeanFactory
Xml配置模块是类似于spring中xml配置方式,配置文件位置asserts/config/bean.xml。可支持如下配置:
<bean name="config" class="com.lemon.config.Config"> </bean>
<bean name="config" class="com.lemon.config.Config" init-method="parser"> </bean>
<bean name="config" class="com.lemon.config.Config"> <property name="configPath" value="config/config.json" /> </bean>
<bean name="config" class="com.lemon.config.Config"> <property name="mContext" value-ref="mContext" /> </bean>
<bean name="config" class="com.lemon.config.Config"> <property name="paths"> <list> <entity type="basic" value="config/config.json"/> <entity type="basic" value="config/config.json"/> <entity type="basic" value="config/config.json"/> </list> </property> </bean>
<bean name="config" class="com.lemon.config.Config"> <property name="converts"> <map> <entry key="baseParamConverter" value-ref="baseParamConverter"/> <entry key="baseResultParamConverter" value-ref="baseResultParamConverter"/> </map> </property> </bean>
在类上添加Component注解,相当于配置文件中的。
Component 有个name属性,配置name属性表示在BeanFactory cacheMap里面存此对象的key是配置的name,
若默认不配置则使用该类的首字母小写为关键字
@Component
public class Demo1Model {}
使用在属性上,自动装配属性,默认使用属性的名字
@Autowired
public Context mContext;
使用在属性上,有个name属性,根据名称装配
@RefBean(name = "lemonMessage")
public LemonMessage lemonMessage;
使用在方法上,配置了InitMethod方法,在app启动的时候会被执行
@InitMethod
public void init() {
name = "demo1 model";
}
网络模块使用了EventBus,将请求后的对象发送给订阅的对象
1、请求参数
在请求参数类前配置@Module注解,可参看AppUpdateParam.java
server:服务器地址(config.json中配置)
name:访问的模块名称(服务器控制器)
httpMethod:访问的方式(get,post),不写默认为post
@Module(server = "update_server", name = "app",httpMethod="get") public class AppUpdateParam extends BaseParam { public String param1; public String param2; public String param3; public String param4; }
2、返回数据
AppUpdateResult继承BaseResult,定义一个结果数据对象,如UpdateInfo.java,如下:
public class AppUpdateResult extends BaseResult {
}
BaseParamConverter:将参数的属性转换为接口数据
BaseResultConverter:将返回的json对象转换为返回结果
@Component public class ApiManager { @Autowired public Context mContext; @Autowired public NetEngine netEngine;
@ParamType(value = AppUpdateParam.class)
@ReturnType(value = AppUpdateResult.class)
public void update(BaseParam param) {
netEngine.invoke(param);
}
}
访问方式
AppUpdateParam param = new AppUpdateParam();
LemonContext.getBean(ApiManager.class).update(param);
public void onEventMainThread(AppUpdateResult result){ tvResult.setText(result.getRetData().toString()); }
参考NetActivity.java
1、数据库模块使用的是ormlite,配置方式可以参考CarModel.java
@DatabaseTable(tableName = "tb_car")
public class CarModel {
@DatabaseField(generatedId = true)
private int id;
@DatabaseField(columnName = "name")
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CarModel{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2、抽象出数据库的通用操作类:LemonDaoManager.java。使用如下:
@Layout(id = R.layout.activity_database)
public class DatabaseActivity extends LemonActivity {
@FieldView(id = R.id.tvResult)
public TextView tvResult;
@OnClick(id = R.id.btnAdd)
public void addClick() {
CarModel model = new CarModel();
model.setName("car:" + RandomUtils.getRandom(1000));
daoManager.create(CarModel.class, model);
lemonMessage.sendMessage("添加完成");
queryClick();
}
@OnClick(id = R.id.btnUpdate)
public void updateClick() throws SQLException {
List<CarModel> list = daoManager.queryAllOrderBy(CarModel.class, "id", false);
if (ParamUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
return;
}
for (CarModel model : list) {
model.setName(model.getName()+":update:"+RandomUtils.getRandom(1000));
daoManager.update(CarModel.class,model);
}
lemonMessage.sendMessage("更新完成");
queryClick();
}
@OnClick(id = R.id.btnRemove)
public void removeClick() {
try {
daoManager.deleteAll(CarModel.class);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lemonMessage.sendMessage("删除完成");
queryClick();
}
@OnClick(id = R.id.btnQuery)
public void queryClick() {
clearClick();
List<CarModel> list = daoManager.queryAllOrderBy(CarModel.class, "id", false);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if (ParamUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
return;
}
for (CarModel model : list) {
sb.append(model.toString()).append("\n");
}
tvResult.setText(sb.toString());
}
@OnClick(id = R.id.btnClear)
public void clearClick() {
tvResult.setText("");
}
}
3、在此之前需要将表配置到xml文件中新建出来,如下:
<bean name="lemonDatabaseHelper" class="com.lemon.LemonDatabaseHelper" init-method="createTables">
<property name="tables">
<list>
<entity type="basic" value="com.lemon.example.model.CarModel"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
分两类初始化:
1、APP启动初始化:继承AbstractInitializer,实现initialize方法。并且将类对象配置在assets/config/bean.xml里面
public class DemoInitializer extends AbstractInitializer {
@Override
public Object initialize(Object... objects) throws Exception {
LogUtils.e(getClass().getSimpleName()+" : init");
return null;
}
}
<bean name="initEngine" class="com.lemon.init.InitEngine">
<property name="initializers">
<list>
<entity type="ref" value="preMethodInitializer"/>
<entity type="ref" value="demoInitializer"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean name="demoInitializer" class="com.lemon.example.init.DemoInitializer" />
2、类初始化方法,有两种方式:2.1 通过配置文件的方式 init-method="方法名" 2.2 通过annotation的方式"方法前加上@InitMethod"
<bean name="config" class="com.lemon.config.Config" init-method="parser"/>
@Component
public class Demo1Model {
@Autowired
public Context mContext;
@RefBean(name = "lemonMessage")
public LemonMessage lemonMessage;
private String name;
@InitMethod
public void init() {
name = "demo1 model";
}
}
建议能用缓存存储的尽量不存数据库
Activity传递数据也可以通过共享缓存传递
缓存可以直接通过class存,或者取
put:LemonContext.getBean(LemonCacheManager.class).putBean(CarModel.class,new CarModel());
get:LemonContext.getBean(LemonCacheManager.class).getBean(CarModel.class);
主要是Activity 和 Fragment的注解使用,@Layout @FieldView @OnClick 三个注解用法
@Layout 替代 setContentView(layout)
@FieldView 替代 findViewById(view.id())
@OnClick 替代 setOnClickListener
@Layout(id = R.layout.activity_anotations)
public class AnnotationsActivity extends LemonActivity {
@FieldView(id = R.id.btnShow)
public Button btnShow;
@FieldView(id = R.id.tvValue)
public TextView tvValue;
@Override
protected void initView() {
String message ="主要学习 @Layout @FieldView @OnClick 三个注解用法";
tvValue.setText(message);
}
@OnClick(id = R.id.btnShow)
public void showClick() {
lemonMessage.sendMessage("showClick");
}
}
配置模块是一个通用模块,可以来配置一些常量
配置方式:打开asserts/config/config.json,将需要配置的数据配置到json文件
使用方式:Config.getValue("key"),Config.getIntValue("key"),Config.getBooleanValue("key")
任意位置,想toast消息,不需要考虑线程子线程
LemonContext.getBean(LemonMessage.class).sendMessage("message")
name: Xiaofeng.lu
qq: 454162034
email: 454162034@qq.com
blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/luxiaofeng54/