diff --git "a/docs/database/\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\255\246\344\271\240Mysql\346\225\260\346\215\256\345\272\2232\357\274\232\343\200\216\346\265\205\345\205\245\346\265\205\345\207\272\343\200\217MySQL \345\222\214 InnoDB.md" "b/docs/database/\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\255\246\344\271\240Mysql\346\225\260\346\215\256\345\272\2232\357\274\232\343\200\216\346\265\205\345\205\245\346\265\205\345\207\272\343\200\217MySQL \345\222\214 InnoDB.md"
index 40e7408..eba3bad 100644
--- "a/docs/database/\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\255\246\344\271\240Mysql\346\225\260\346\215\256\345\272\2232\357\274\232\343\200\216\346\265\205\345\205\245\346\265\205\345\207\272\343\200\217MySQL \345\222\214 InnoDB.md"
+++ "b/docs/database/\351\207\215\346\226\260\345\255\246\344\271\240Mysql\346\225\260\346\215\256\345\272\2232\357\274\232\343\200\216\346\265\205\345\205\245\346\265\205\345\207\272\343\200\217MySQL \345\222\214 InnoDB.md"
@@ -52,7 +52,7 @@
作为一名开发人员,在日常的工作中会难以避免地接触到数据库,无论是基于文件的 sqlite 还是工程上使用非常广泛的 MySQL、PostgreSQL,但是一直以来也没有对数据库有一个非常清晰并且成体系的认知,所以最近两个月的时间看了几本数据库相关的书籍并且阅读了 MySQL 的官方文档,希望对各位了解数据库的、不了解数据库的有所帮助。
-
+
本文中对于数据库的介绍以及研究都是在 MySQL 上进行的,如果涉及到了其他数据库的内容或者实现会在文中单独指出。
@@ -69,7 +69,7 @@
在 MySQL 中,实例和数据库往往都是一一对应的,而我们也无法直接操作数据库,而是要通过数据库实例来操作数据库文件,可以理解为数据库实例是数据库为上层提供的一个专门用于操作的接口。
-
+
在 Unix 上,启动一个 MySQL 实例往往会产生两个进程,`mysqld` 就是真正的数据库服务守护进程,而 `mysqld_safe` 是一个用于检查和设置 `mysqld` 启动的控制程序,它负责监控 MySQL 进程的执行,当 `mysqld` 发生错误时,`mysqld_safe` 会对其状态进行检查并在合适的条件下重启。
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@
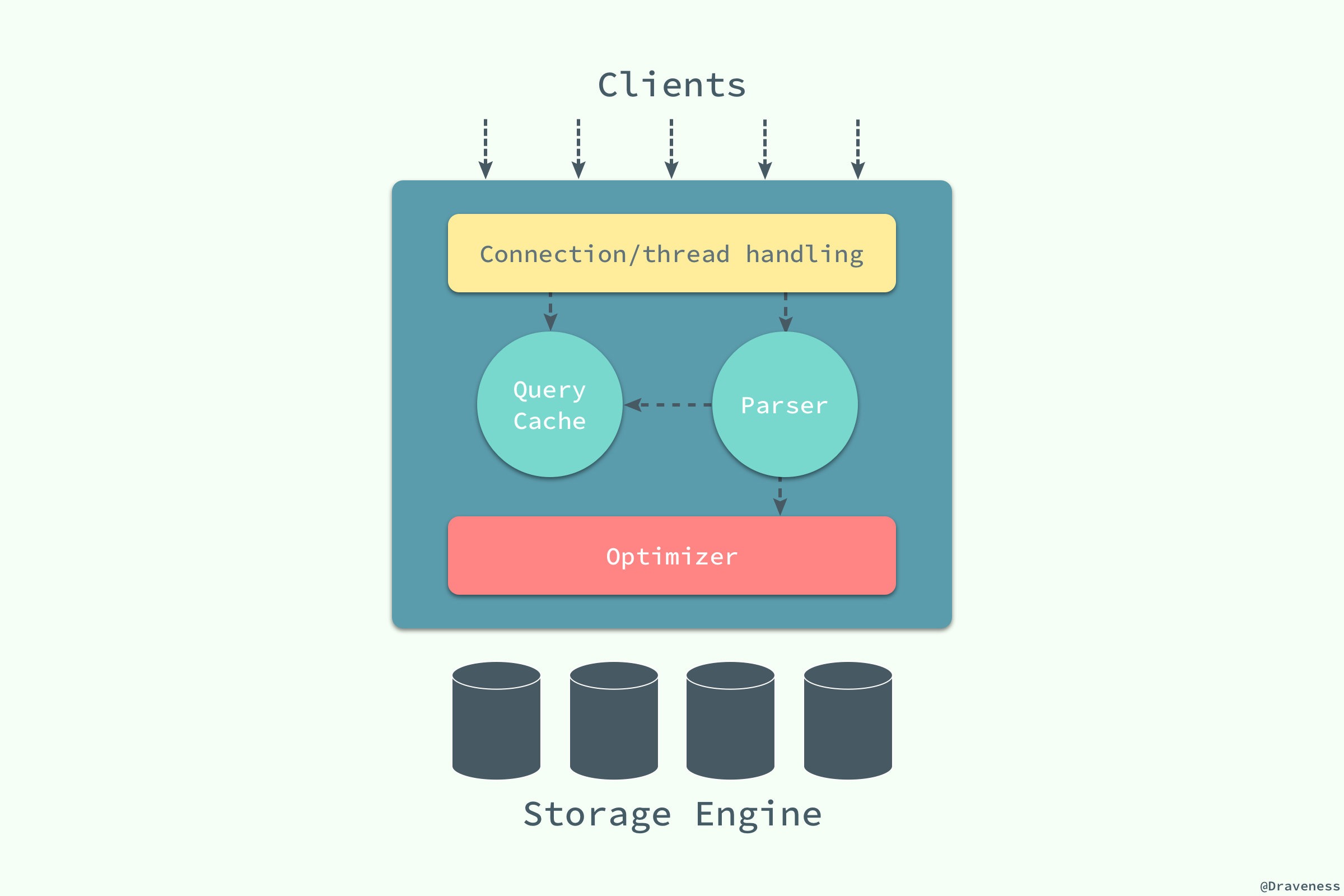
MySQL 从第一个版本发布到现在已经有了 20 多年的历史,在这么多年的发展和演变中,整个应用的体系结构变得越来越复杂:
-
+
最上层用于连接、线程处理的部分并不是 MySQL 『发明』的,很多服务都有类似的组成部分;第二层中包含了大多数 MySQL 的核心服务,包括了对 SQL 的解析、分析、优化和缓存等功能,存储过程、触发器和视图都是在这里实现的;而第三层就是 MySQL 中真正负责数据的存储和提取的存储引擎,例如:[InnoDB](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/InnoDB)、[MyISAM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MyISAM) 等,文中对存储引擎的介绍都是对 InnoDB 实现的分析。
@@ -87,11 +87,11 @@ MySQL 从第一个版本发布到现在已经有了 20 多年的历史,在这
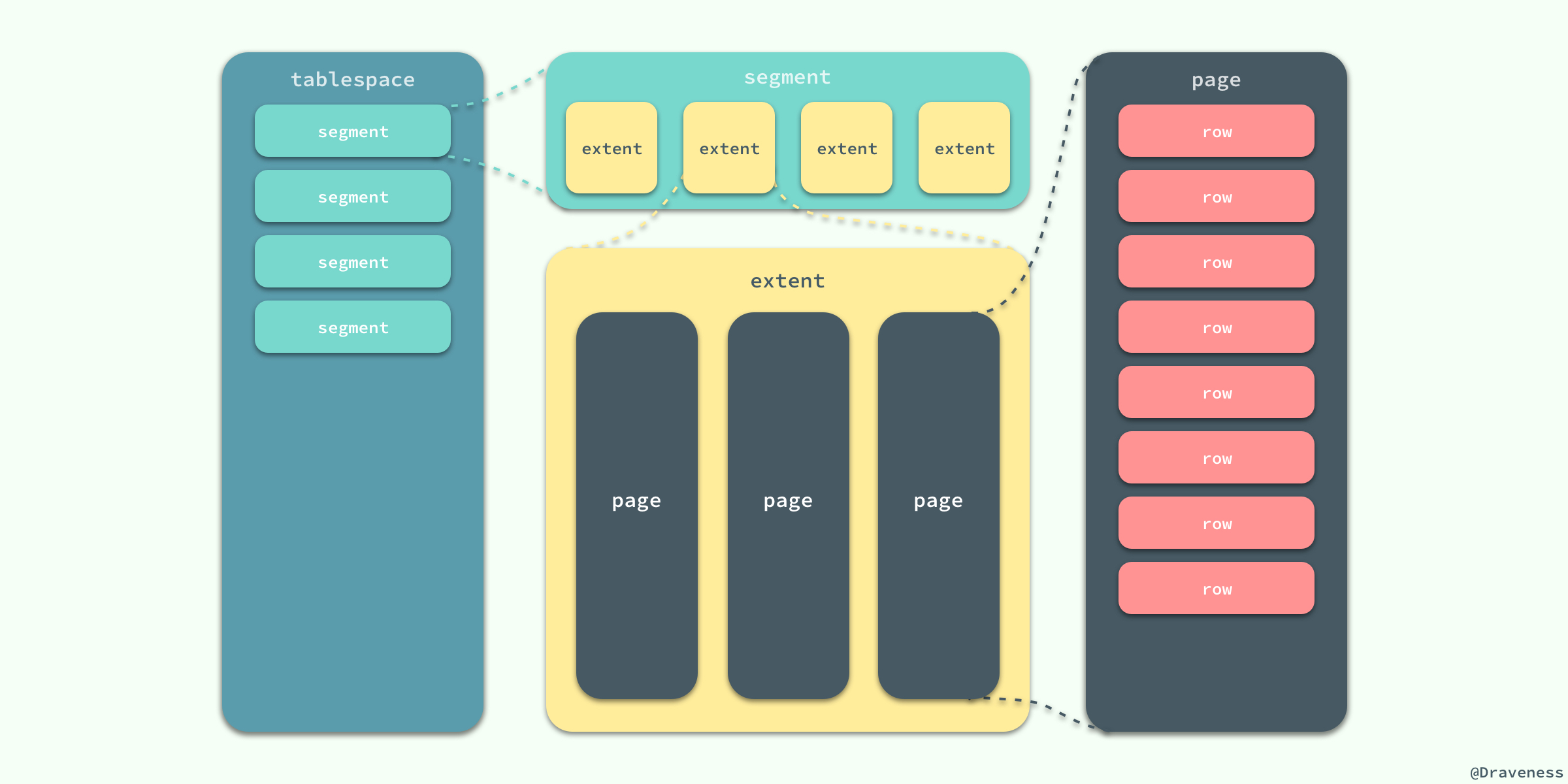
在 InnoDB 存储引擎中,所有的数据都被**逻辑地**存放在表空间中,表空间(tablespace)是存储引擎中最高的存储逻辑单位,在表空间的下面又包括段(segment)、区(extent)、页(page):
-
+
同一个数据库实例的所有表空间都有相同的页大小;默认情况下,表空间中的页大小都为 16KB,当然也可以通过改变 `innodb_page_size` 选项对默认大小进行修改,需要注意的是不同的页大小最终也会导致区大小的不同:
-
+
从图中可以看出,在 InnoDB 存储引擎中,一个区的大小最小为 1MB,页的数量最少为 64 个。
@@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ MySQL 从第一个版本发布到现在已经有了 20 多年的历史,在这
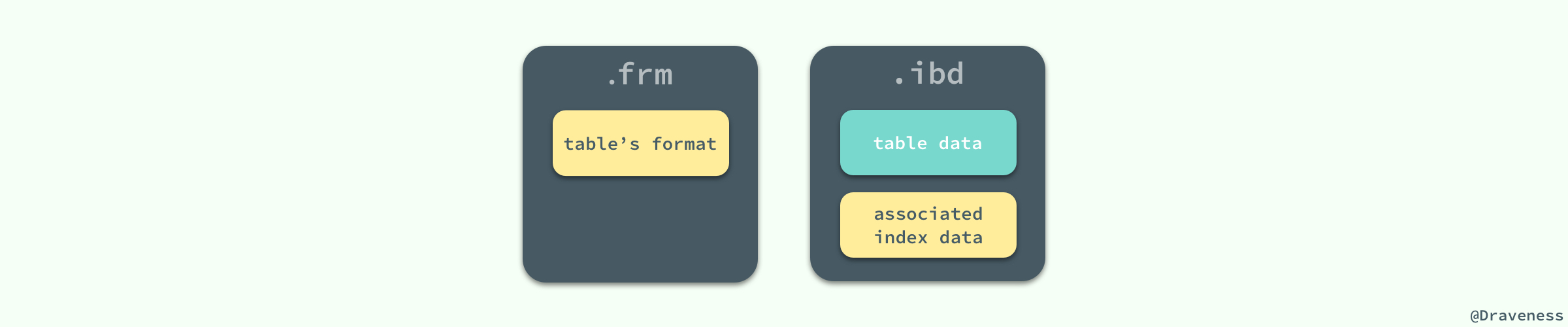
MySQL 使用 InnoDB 存储表时,会将**表的定义**和**数据索引**等信息分开存储,其中前者存储在 `.frm` 文件中,后者存储在 `.ibd` 文件中,这一节就会对这两种不同的文件分别进行介绍。
-
+
.frm 文件
@@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ MySQL 使用 InnoDB 存储表时,会将**表的定义**和**数据索引**等
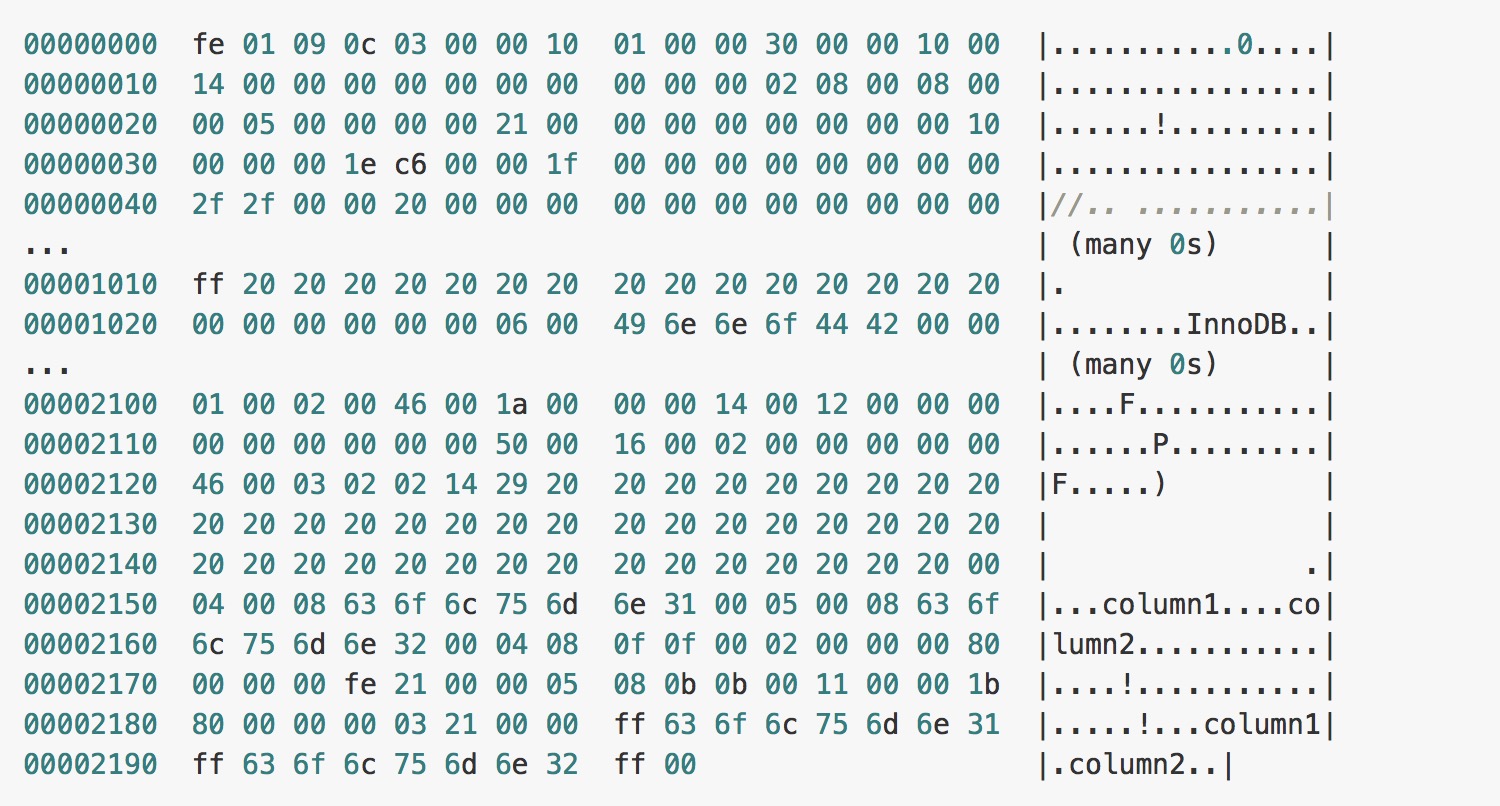
当我们使用上面的代码创建表时,会在磁盘上的 `datadir` 文件夹中生成一个 `test_frm.frm` 的文件,这个文件中就包含了表结构相关的信息:
-
+
> MySQL 官方文档中的 [11.1 MySQL .frm File Format](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/internals/en/frm-file-format.html) 一文对于 `.frm`文件格式中的二进制的内容有着非常详细的表述,在这里就不展开介绍了。
@@ -127,13 +127,13 @@ InnoDB 中用于存储数据的文件总共有两个部分,一是系统表空
当 InnoDB 存储数据时,它可以使用不同的行格式进行存储;MySQL 5.7 版本支持以下格式的行存储方式:
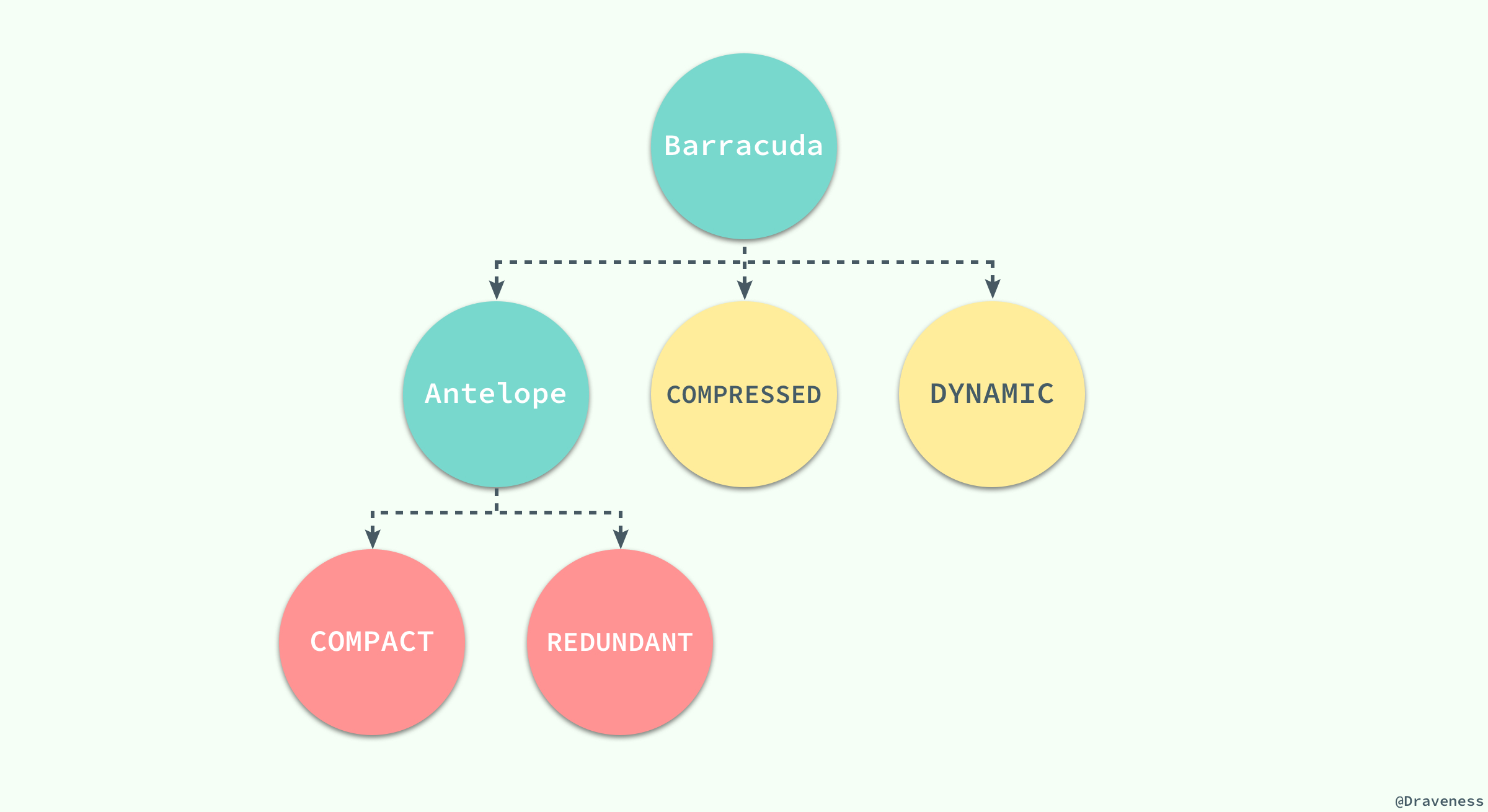
-
+
> Antelope 是 InnoDB 最开始支持的文件格式,它包含两种行格式 Compact 和 Redundant,它最开始并没有名字;Antelope 的名字是在新的文件格式 Barracuda 出现后才起的,Barracuda 的出现引入了两种新的行格式 Compressed 和 Dynamic;InnoDB 对于文件格式都会向前兼容,而官方文档中也对之后会出现的新文件格式预先定义好了名字:Cheetah、Dragon、Elk 等等。
两种行记录格式 Compact 和 Redundant 在磁盘上按照以下方式存储:
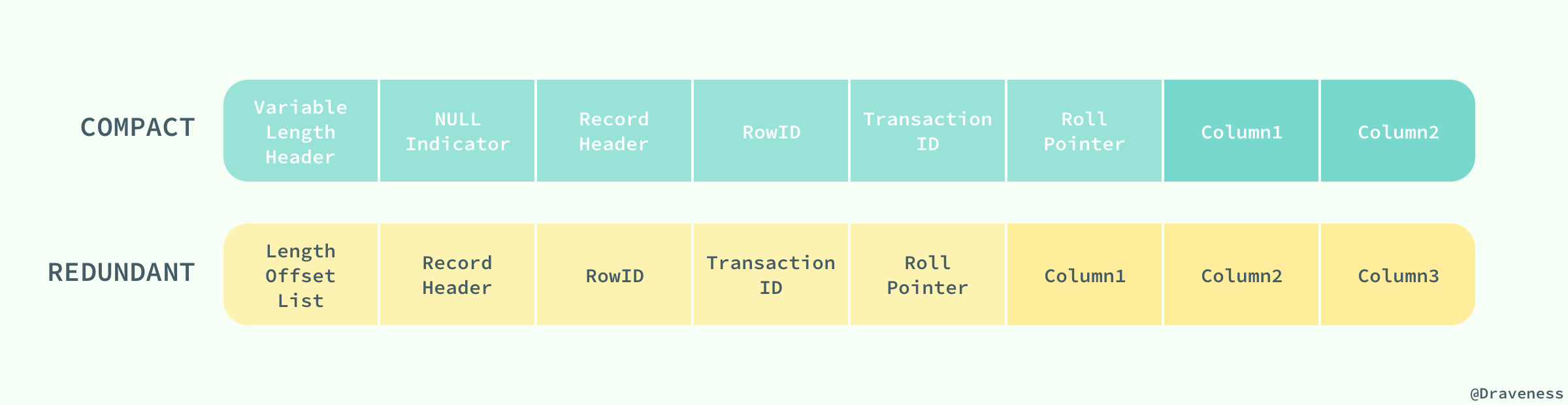
-
+
Compact 和 Redundant 格式最大的不同就是记录格式的第一个部分;在 Compact 中,行记录的第一部分倒序存放了一行数据中列的长度(Length),而 Redundant 中存的是每一列的偏移量(Offset),从总体上上看,Compact 行记录格式相比 Redundant 格式能够减少 20% 的存储空间。
@@ -141,11 +141,11 @@ Compact 和 Redundant 格式最大的不同就是记录格式的第一个部分
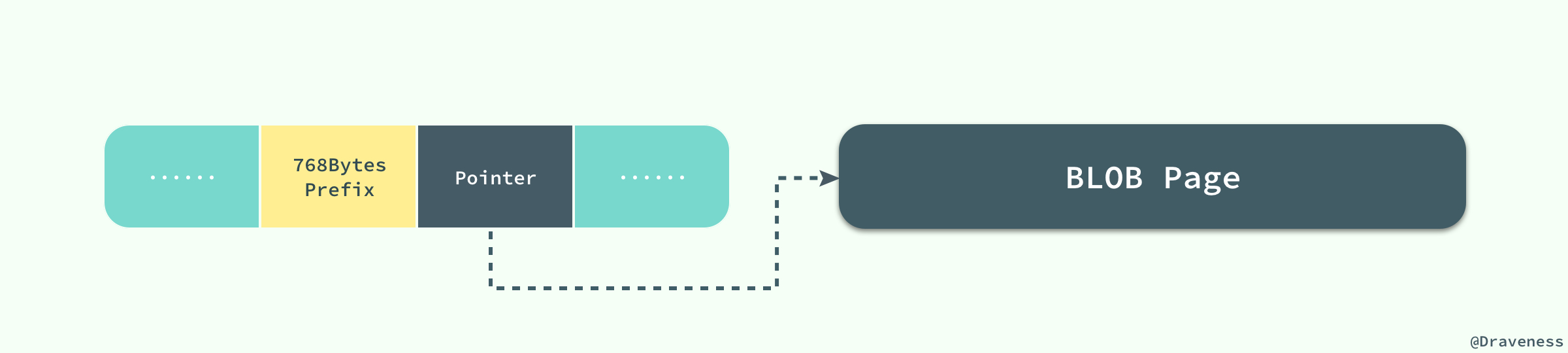
当 InnoDB 使用 Compact 或者 Redundant 格式存储极长的 VARCHAR 或者 BLOB 这类大对象时,我们并不会直接将所有的内容都存放在数据页节点中,而是将行数据中的前 768 个字节存储在数据页中,后面会通过偏移量指向溢出页。
-
+
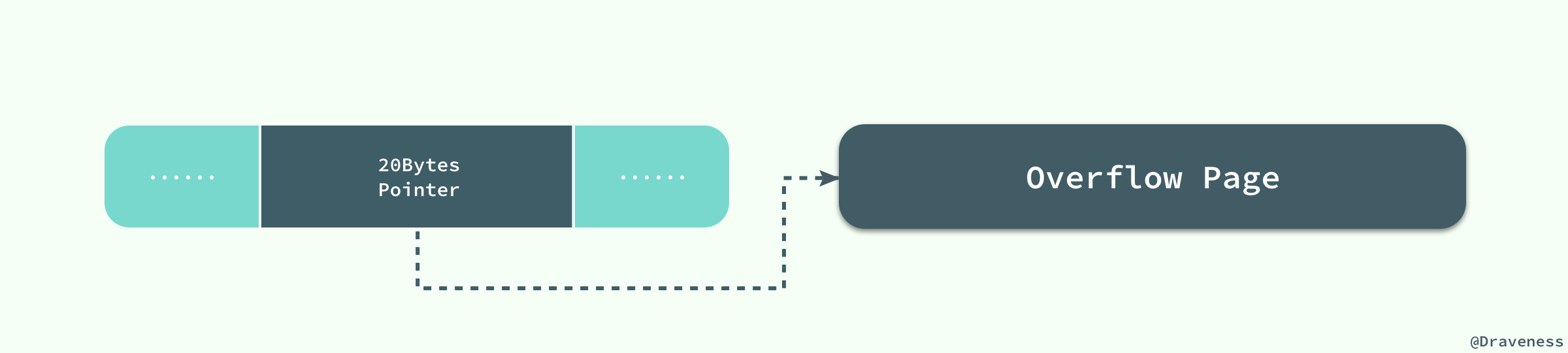
但是当我们使用新的行记录格式 Compressed 或者 Dynamic 时都只会在行记录中保存 20 个字节的指针,实际的数据都会存放在溢出页面中。
-
+
当然在实际存储中,可能会对不同长度的 TEXT 和 BLOB 列进行优化,不过这就不是本文关注的重点了。
@@ -155,13 +155,13 @@ Compact 和 Redundant 格式最大的不同就是记录格式的第一个部分
页是 InnoDB 存储引擎管理数据的最小磁盘单位,而 B-Tree 节点就是实际存放表中数据的页面,我们在这里将要介绍页是如何组织和存储记录的;首先,一个 InnoDB 页有以下七个部分:
-
+
每一个页中包含了两对 header/trailer:内部的 Page Header/Page Directory 关心的是页的状态信息,而 Fil Header/Fil Trailer 关心的是记录页的头信息。
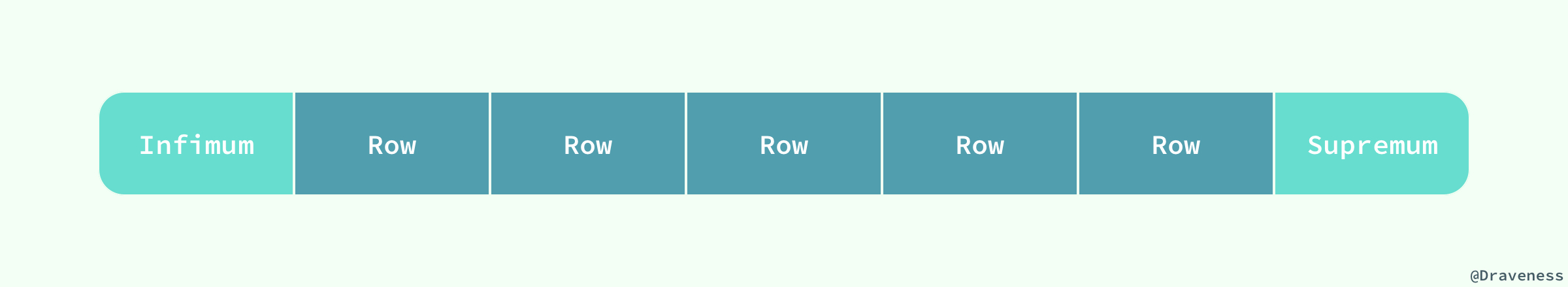
在页的头部和尾部之间就是用户记录和空闲空间了,每一个数据页中都包含 Infimum 和 Supremum 这两个**虚拟**的记录(可以理解为占位符),Infimum 记录是比该页中任何主键值都要小的值,Supremum 是该页中的最大值:
-
+
User Records 就是整个页面中真正用于存放行记录的部分,而 Free Space 就是空余空间了,它是一个链表的数据结构,为了保证插入和删除的效率,整个页面并不会按照主键顺序对所有记录进行排序,它会自动从左侧向右寻找空白节点进行插入,行记录在物理存储上并不是按照顺序的,它们之间的顺序是由 `next_record` 这一指针控制的。
@@ -177,7 +177,7 @@ InnoDB 存储引擎中对数据的存储是一个非常复杂的话题,这一
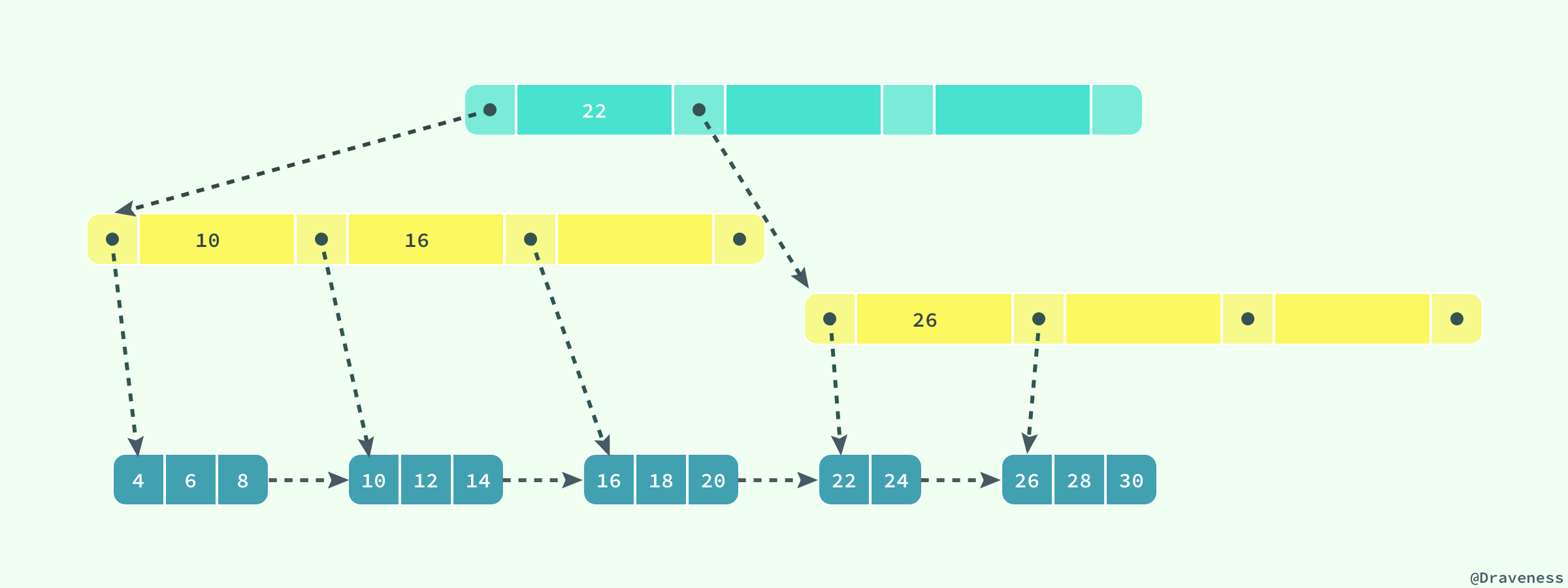
在上一节中,我们谈了行记录的存储和页的存储,在这里我们就要从更高的层面看 InnoDB 中对于数据是如何存储的;InnoDB 存储引擎在绝大多数情况下使用 B+ 树建立索引,这是关系型数据库中查找最为常用和有效的索引,但是 B+ 树索引并不能找到一个给定键对应的具体值,它只能找到数据行对应的页,然后正如上一节所提到的,数据库把整个页读入到内存中,并在内存中查找具体的数据行。
-
+
B+ 树是平衡树,它查找任意节点所耗费的时间都是完全相同的,比较的次数就是 B+ 树的高度;在这里,我们并不会深入分析或者动手实现一个 B+ 树,只是对它的特性进行简单的介绍。
@@ -195,7 +195,7 @@ InnoDB 存储引擎中的表都是使用索引组织的,也就是按照键的
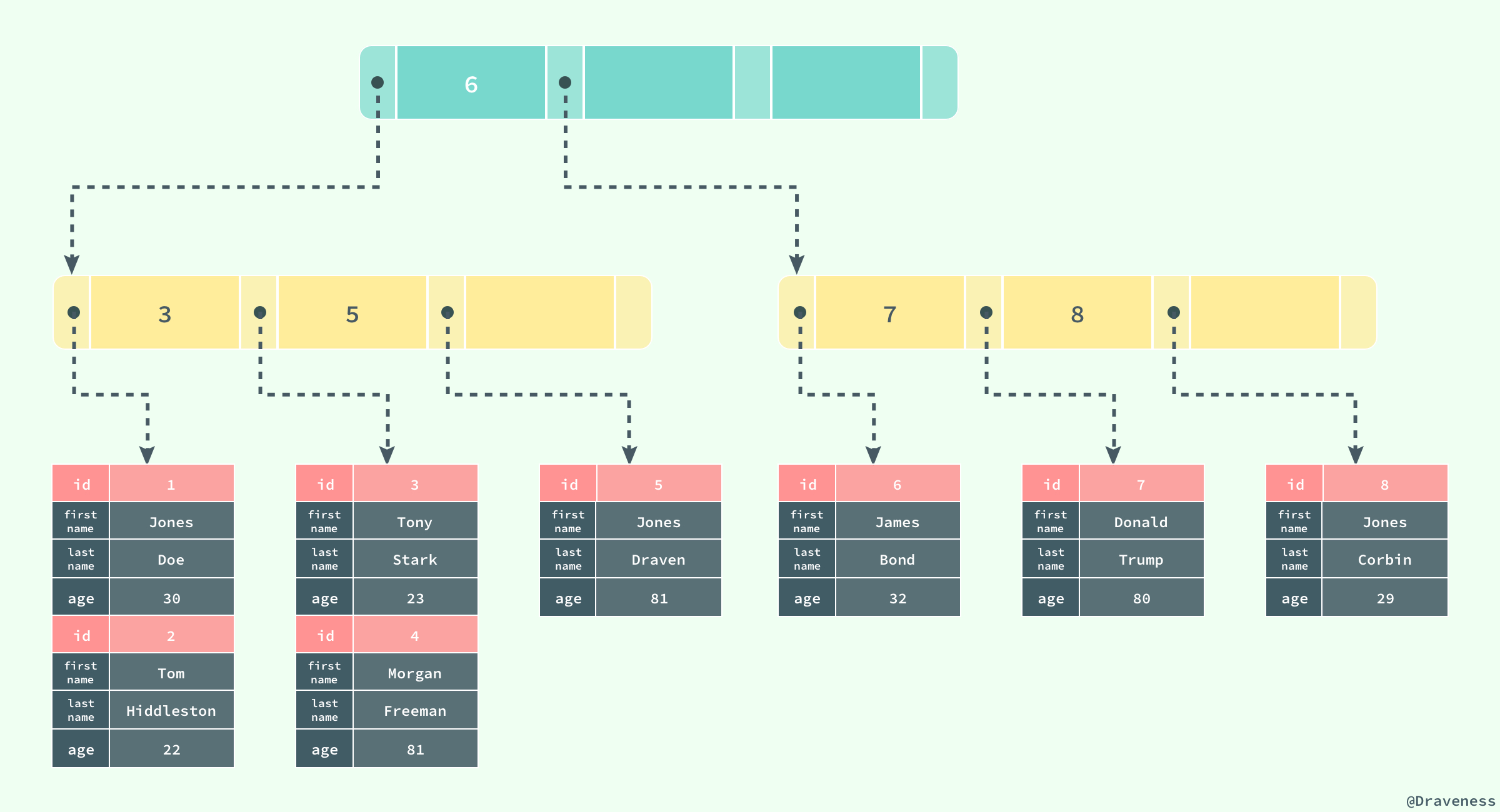
如果使用上面的 SQL 在数据库中创建一张表,B+ 树就会使用 `id` 作为索引的键,并在叶子节点中存储一条记录中的**所有**信息。
-
+
> 图中对 B+ 树的描述与真实情况下 B+ 树中的数据结构有一些差别,不过这里想要表达的主要意思是:聚集索引叶节点中保存的是整条行记录,而不是其中的一部分。
@@ -211,11 +211,11 @@ InnoDB 存储引擎中的表都是使用索引组织的,也就是按照键的
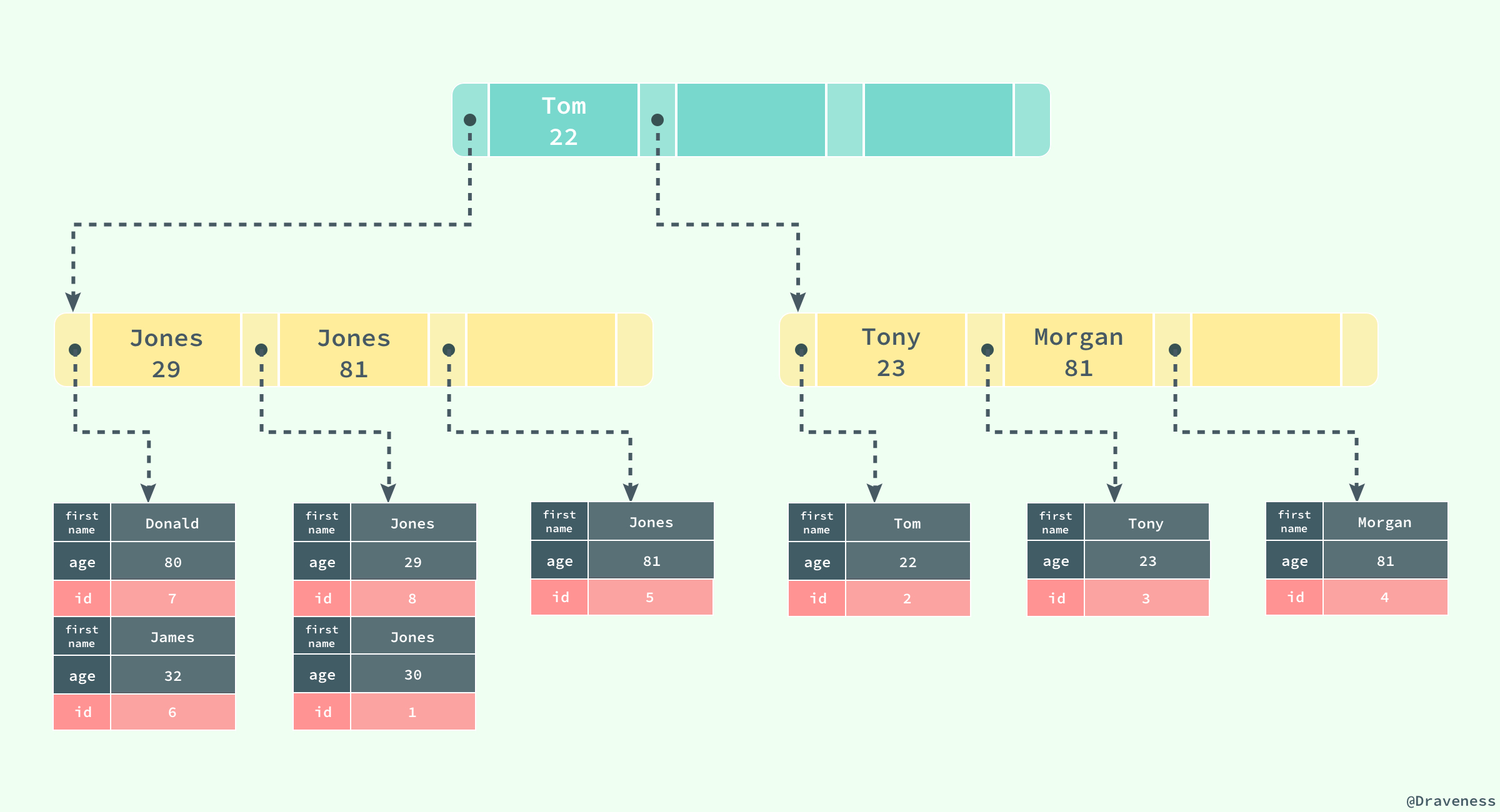
> 一张表一定包含一个聚集索引构成的 B+ 树以及若干辅助索引的构成的 B+ 树。
-
+
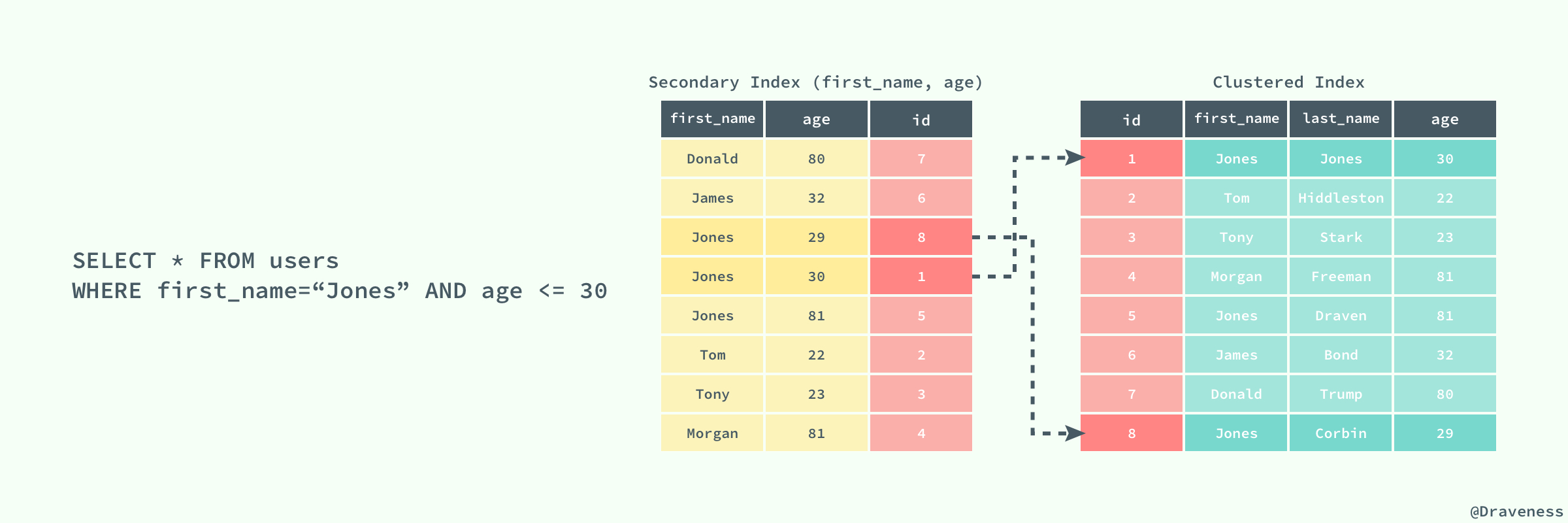
如果在表 `users` 中存在一个辅助索引 `(first_name, age)`,那么它构成的 B+ 树大致就是上图这样,按照 `(first_name, age)` 的字母顺序对表中的数据进行排序,当查找到主键时,再通过聚集索引获取到整条行记录。
-
+
上图展示了一个使用辅助索引查找一条表记录的过程:通过辅助索引查找到对应的主键,最后在聚集索引中使用主键获取对应的行记录,这也是通常情况下行记录的查找方式。
@@ -236,7 +236,7 @@ InnoDB 存储引擎中的表都是使用索引组织的,也就是按照键的
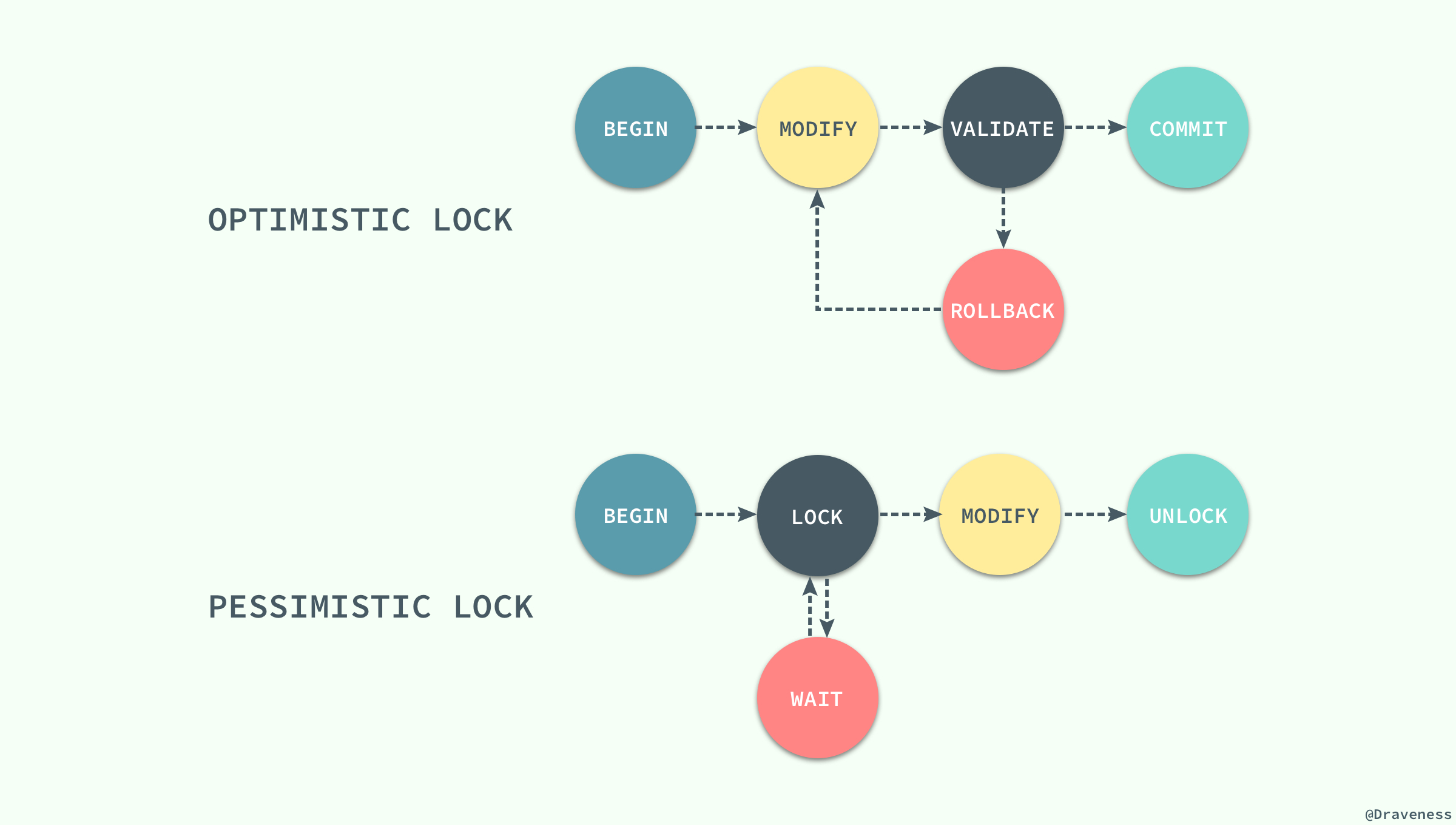
虽然乐观锁和悲观锁在本质上并不是同一种东西,一个是一种思想,另一个是一种真正的锁,但是它们都是一种并发控制机制。
-
+
乐观锁不会存在死锁的问题,但是由于更新后验证,所以当**冲突频率**和**重试成本**较高时更推荐使用悲观锁,而需要非常高的**响应速度**并且**并发量**非常大的时候使用乐观锁就能较好的解决问题,在这时使用悲观锁就可能出现严重的性能问题;在选择并发控制机制时,需要综合考虑上面的四个方面(冲突频率、重试成本、响应速度和并发量)进行选择。
@@ -249,7 +249,7 @@ InnoDB 存储引擎中的表都是使用索引组织的,也就是按照键的
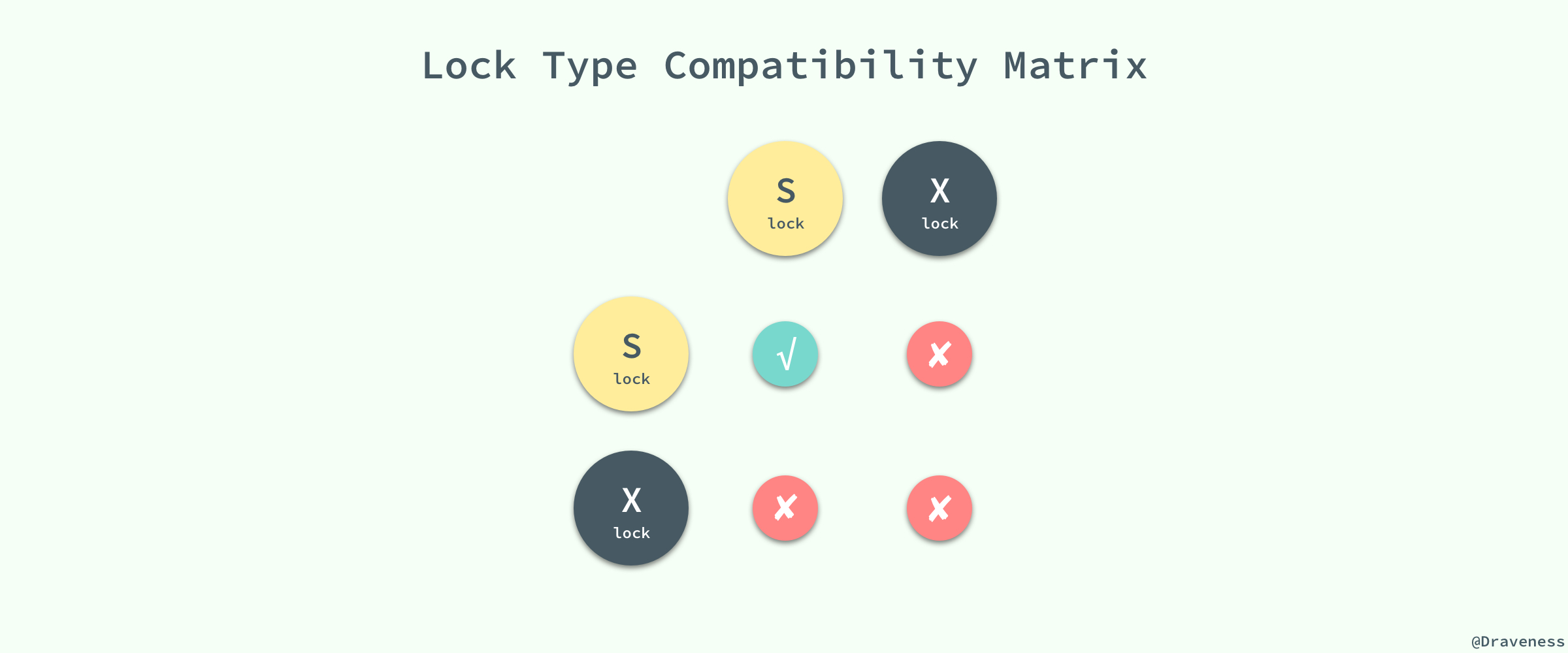
而它们的名字也暗示着各自的另外一个特性,共享锁之间是兼容的,而互斥锁与其他任意锁都不兼容:
-
+
稍微对它们的使用进行思考就能想明白它们为什么要这么设计,因为共享锁代表了读操作、互斥锁代表了写操作,所以我们可以在数据库中**并行读**,但是只能**串行写**,只有这样才能保证不会发生线程竞争,实现线程安全。
@@ -264,7 +264,7 @@ InnoDB 存储引擎中的表都是使用索引组织的,也就是按照键的
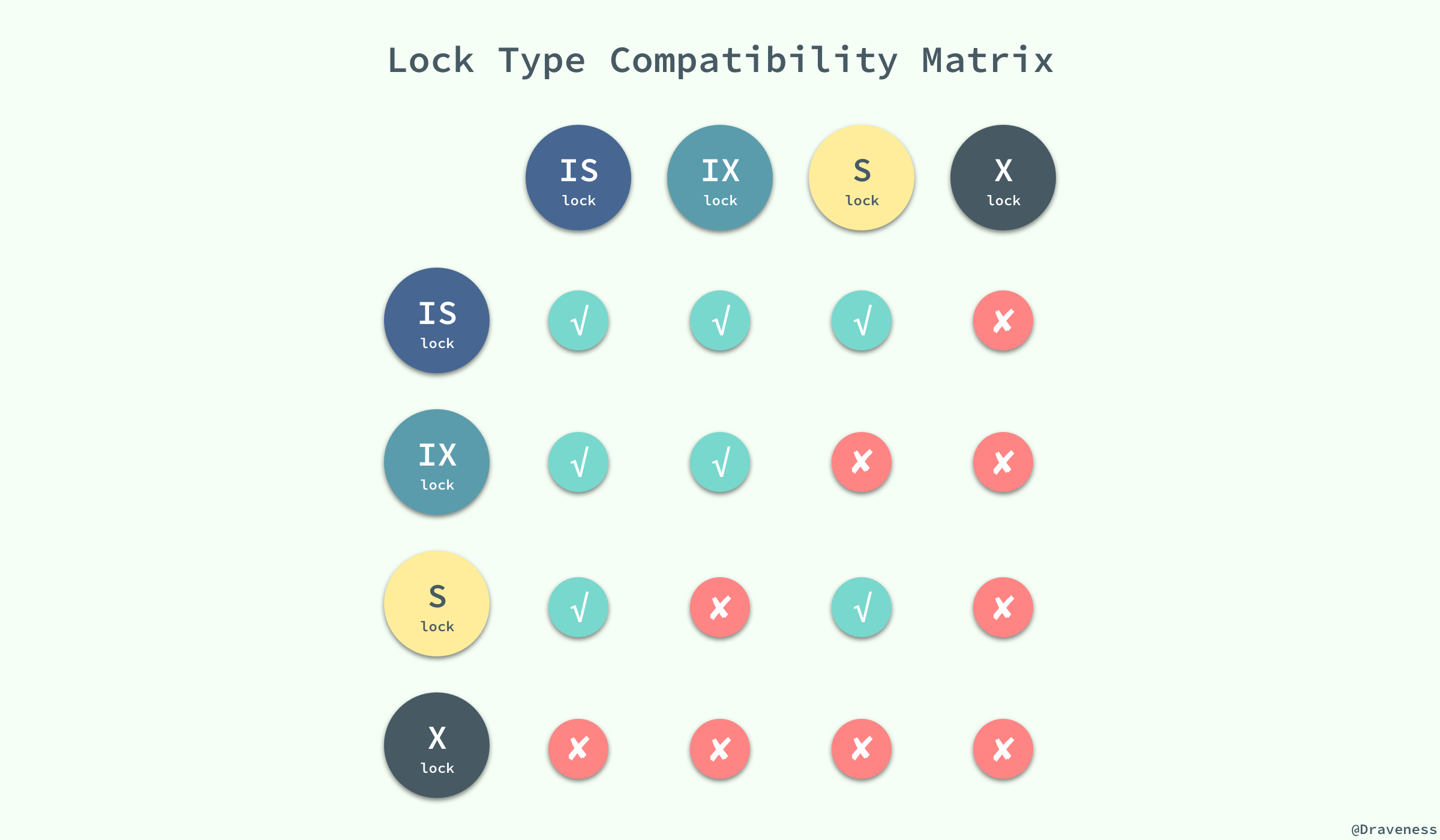
随着意向锁的加入,锁类型之间的兼容矩阵也变得愈加复杂:
-
+
意向锁其实不会阻塞全表扫描之外的任何请求,它们的主要目的是为了表示**是否有人请求锁定表中的某一行数据**。
@@ -316,7 +316,7 @@ Next-Key 锁的作用其实是为了解决幻读的问题,我们会在下一
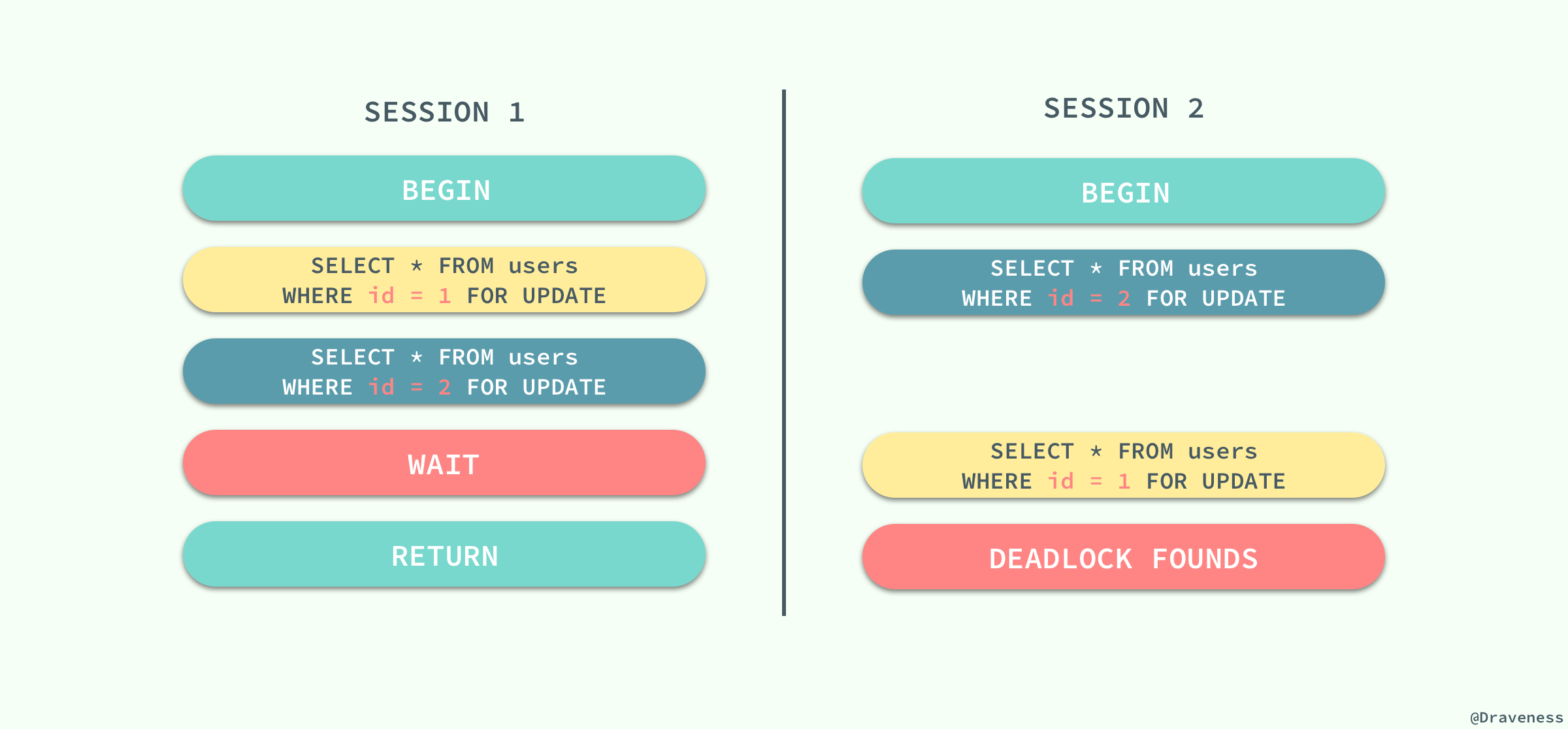
既然 InnoDB 中实现的锁是悲观的,那么不同事务之间就可能会互相等待对方释放锁造成死锁,最终导致事务发生错误;想要在 MySQL 中制造死锁的问题其实非常容易:
-
+
两个会话都持有一个锁,并且尝试获取对方的锁时就会发生死锁,不过 MySQL 也能在发生死锁时及时发现问题,并保证其中的一个事务能够正常工作,这对我们来说也是一个好消息。
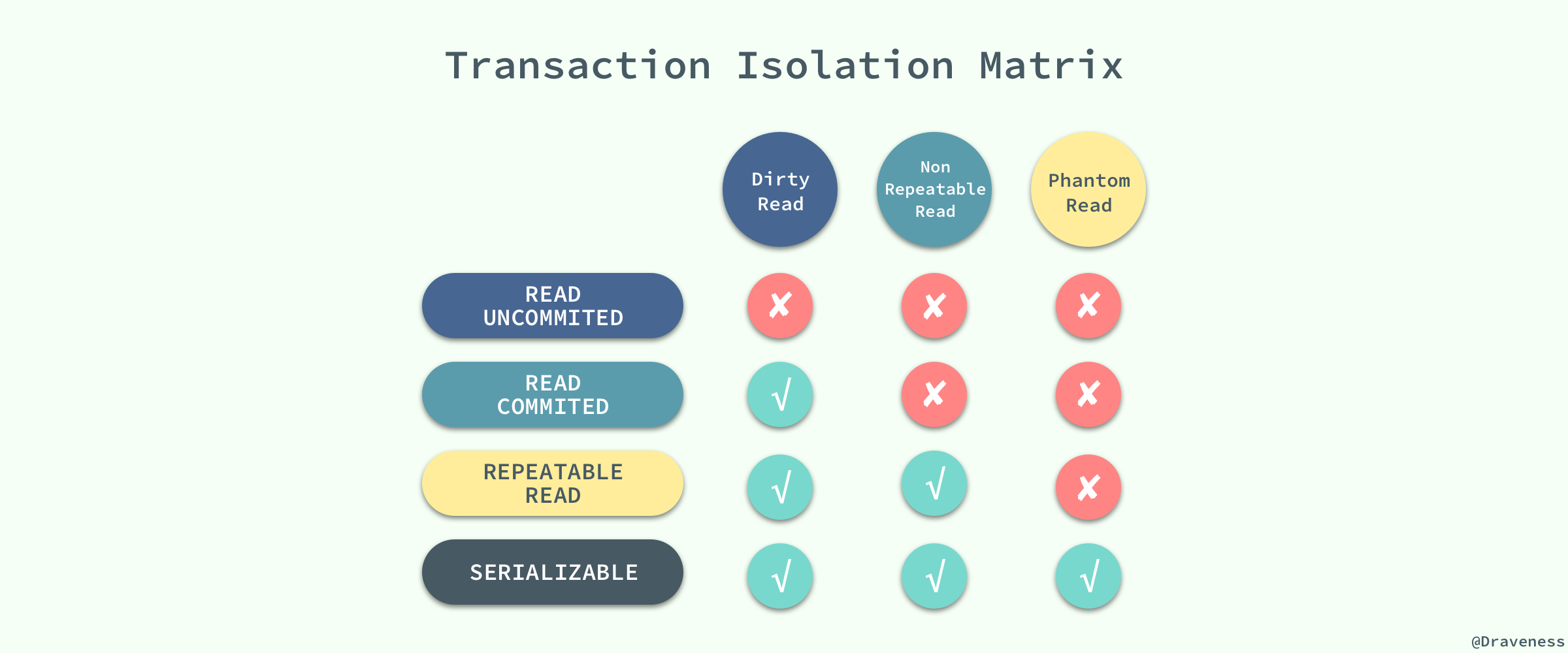
@@ -339,7 +339,7 @@ ISO 和 ANIS SQL 标准制定了四种事务隔离级别,而 InnoDB 遵循了
MySQL 中默认的事务隔离级别就是 `REPEATABLE READ`,但是它通过 Next-Key 锁也能够在某种程度上解决幻读的问题。
-
+
接下来,我们将数据库中创建如下的表并通过个例子来展示在不同的事务隔离级别之下,会发生什么样的问题:
@@ -353,7 +353,7 @@ MySQL 中默认的事务隔离级别就是 `REPEATABLE READ`,但是它通过
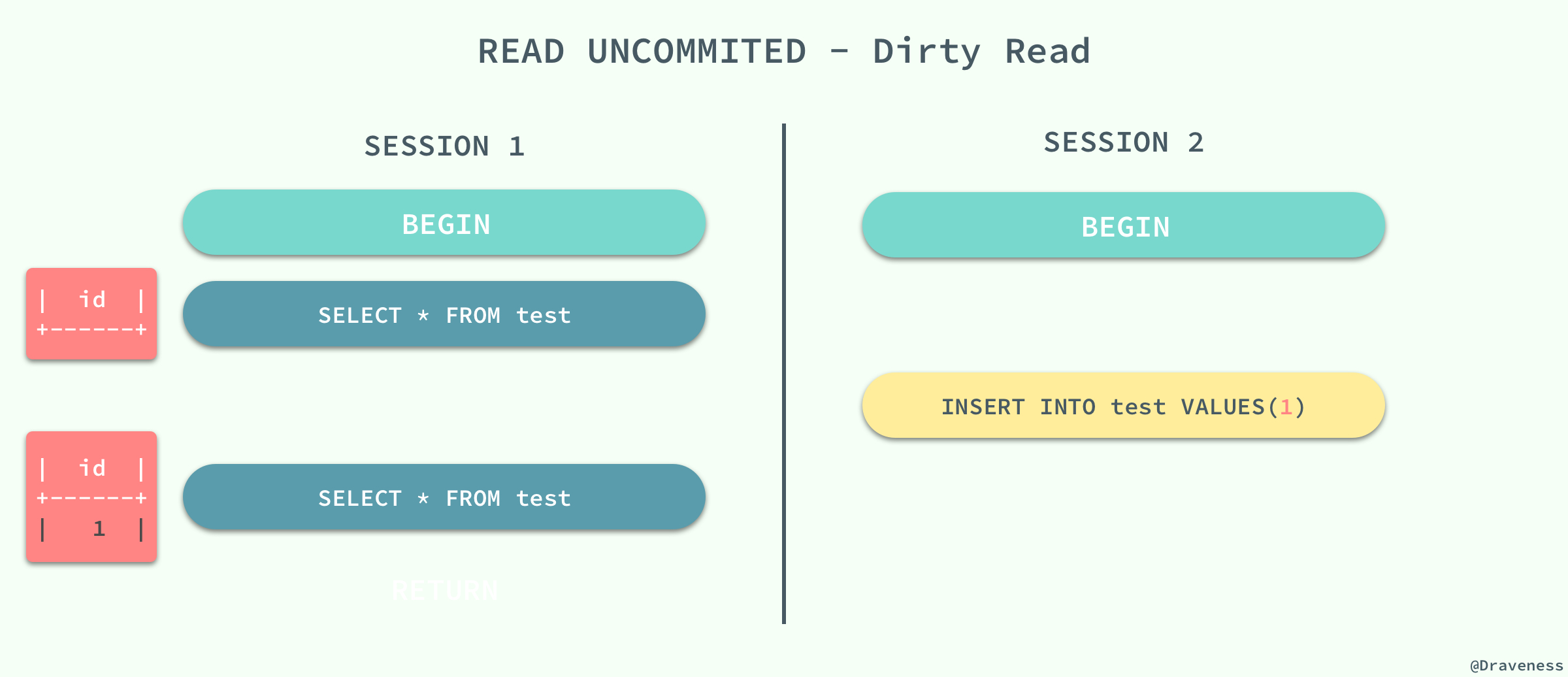
当事务的隔离级别为 `READ UNCOMMITED` 时,我们在 `SESSION 2` 中插入的**未提交**数据在 `SESSION 1` 中是可以访问的。
-
+
### 不可重复读
@@ -361,7 +361,7 @@ MySQL 中默认的事务隔离级别就是 `REPEATABLE READ`,但是它通过
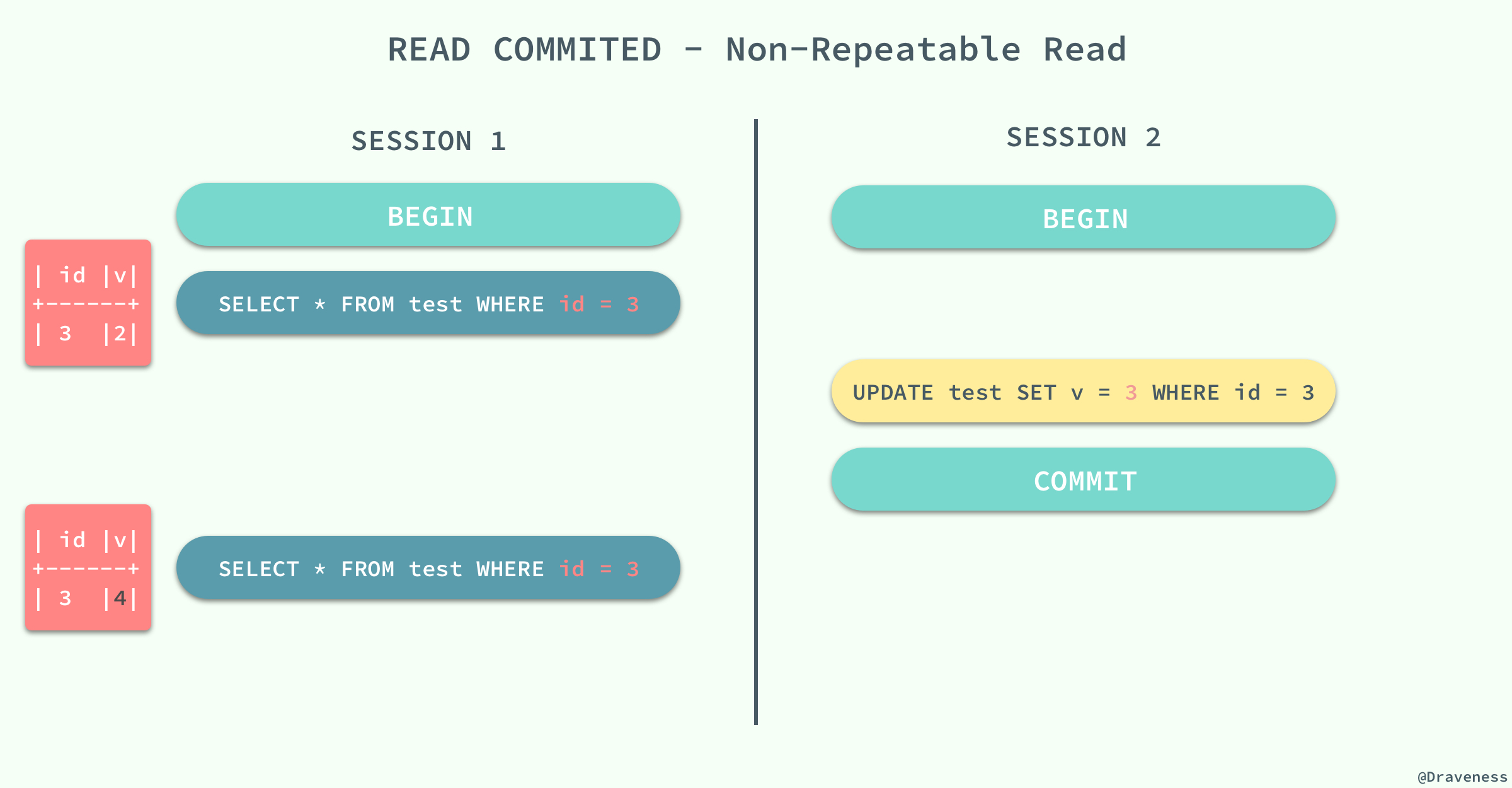
当事务的隔离级别为 `READ COMMITED` 时,虽然解决了脏读的问题,但是如果在 `SESSION 1` 先查询了**一行**数据,在这之后 `SESSION 2` 中修改了同一行数据并且提交了修改,在这时,如果 `SESSION 1` 中再次使用相同的查询语句,就会发现两次查询的结果不一样。
-
+
不可重复读的原因就是,在 `READ COMMITED` 的隔离级别下,存储引擎不会在查询记录时添加行锁,锁定 `id = 3` 这条记录。
@@ -371,13 +371,13 @@ MySQL 中默认的事务隔离级别就是 `REPEATABLE READ`,但是它通过
重新开启了两个会话 `SESSION 1` 和 `SESSION 2`,在 `SESSION 1` 中我们查询全表的信息,没有得到任何记录;在 `SESSION 2` 中向表中插入一条数据并提交;由于 `REPEATABLE READ` 的原因,再次查询全表的数据时,我们获得到的仍然是空集,但是在向表中插入同样的数据却出现了错误。
-
+
这种现象在数据库中就被称作幻读,虽然我们使用查询语句得到了一个空的集合,但是插入数据时却得到了错误,好像之前的查询是幻觉一样。
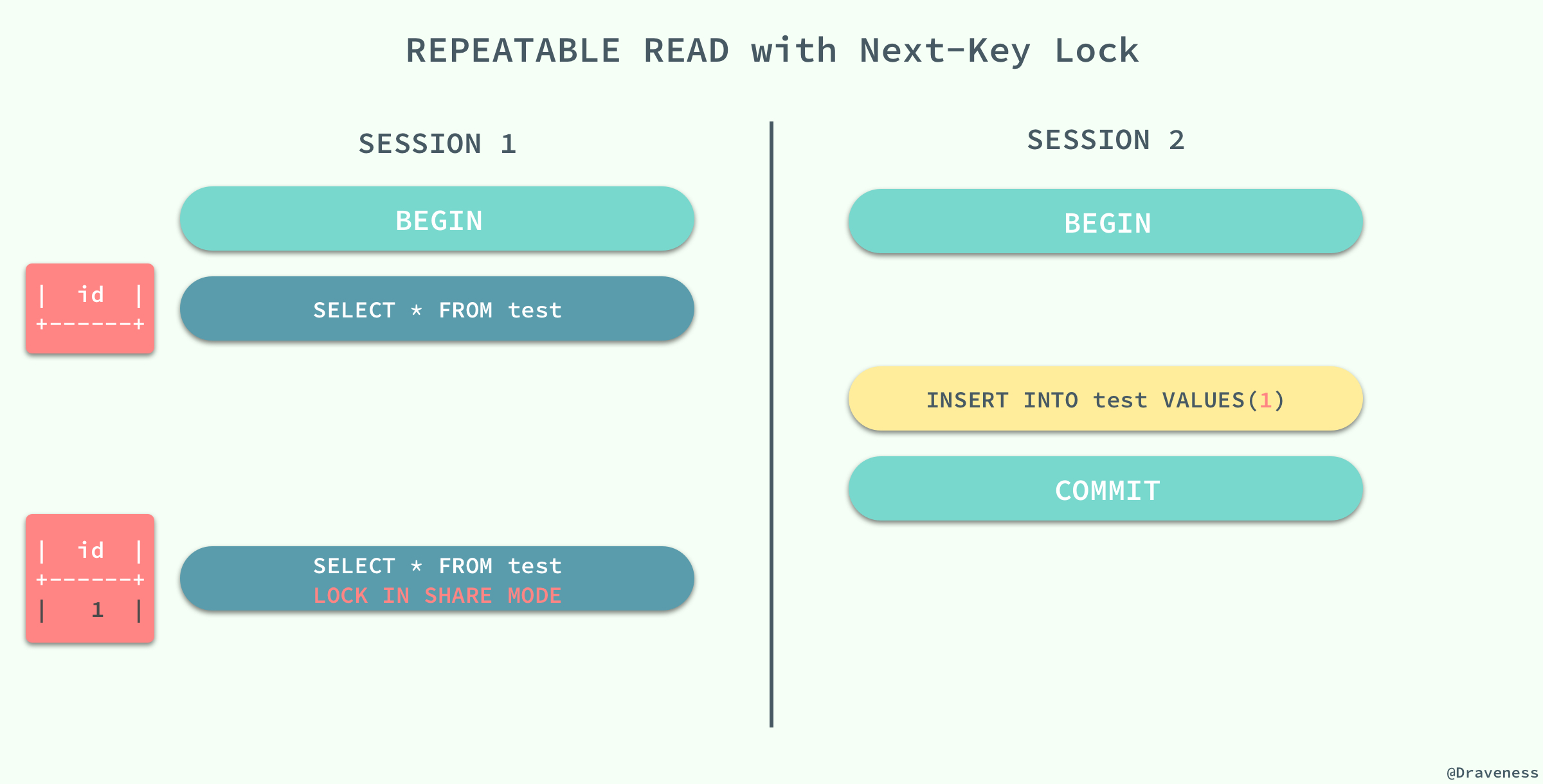
在标准的事务隔离级别中,幻读是由更高的隔离级别 `SERIALIZABLE` 解决的,但是它也可以通过 MySQL 提供的 Next-Key 锁解决:
-
+
`REPERATABLE READ` 和 `READ UNCOMMITED` 其实是矛盾的,如果保证了前者就看不到已经提交的事务,如果保证了后者,就会导致两次查询的结果不同,MySQL 为我们提供了一种折中的方式,能够在 `REPERATABLE READ` 模式下加锁访问已经提交的数据,其本身并不能解决幻读的问题,而是通过文章前面提到的 Next-Key 锁来解决。
diff --git a/pom.xml b/pom.xml
index 2cca927..45b8b97 100644
--- a/pom.xml
+++ b/pom.xml
@@ -7,6 +7,18 @@
groupId
JavaTutorial
1.0-SNAPSHOT
+
+
+
+ org.apache.maven.plugins
+ maven-compiler-plugin
+
+ 8
+ 8
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/resource/img/Antelope-Barracuda-Row-Format.jpg b/resource/img/Antelope-Barracuda-Row-Format.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a4cca7f
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Antelope-Barracuda-Row-Format.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/B+Tree.jpg b/resource/img/B+Tree.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5346601
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/B+Tree.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/COMPACT-And-REDUNDANT-Row-Format.jpg b/resource/img/COMPACT-And-REDUNDANT-Row-Format.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ac01b41
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/COMPACT-And-REDUNDANT-Row-Format.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Clustered-Index.jpg b/resource/img/Clustered-Index.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f313192
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Clustered-Index.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Clustered-Secondary-Index.jpg b/resource/img/Clustered-Secondary-Index.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c34c625
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Clustered-Secondary-Index.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Deadlocks.jpg b/resource/img/Deadlocks.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e2e4845
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Deadlocks.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Infimum-Rows-Supremum.jpg b/resource/img/Infimum-Rows-Supremum.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2894d4b
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Infimum-Rows-Supremum.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/InnoDB-B-Tree-Node.jpg b/resource/img/InnoDB-B-Tree-Node.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..22409df
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/InnoDB-B-Tree-Node.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Lock-Type-Compatibility-Matrix.jpg b/resource/img/Lock-Type-Compatibility-Matrix.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c5098ee
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Lock-Type-Compatibility-Matrix.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Logical-View-of-MySQL-Architecture.jpg b/resource/img/Logical-View-of-MySQL-Architecture.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..be2c1ad
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Logical-View-of-MySQL-Architecture.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Optimistic-Pessimistic-Locks.jpg b/resource/img/Optimistic-Pessimistic-Locks.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6cfff4a
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Optimistic-Pessimistic-Locks.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Read-Commited-Non-Repeatable-Read.jpg b/resource/img/Read-Commited-Non-Repeatable-Read.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7d4b259
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Read-Commited-Non-Repeatable-Read.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Read-Uncommited-Dirty-Read.jpg b/resource/img/Read-Uncommited-Dirty-Read.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..54d913d
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Read-Uncommited-Dirty-Read.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Repeatable-Read-Phantom-Read.jpg b/resource/img/Repeatable-Read-Phantom-Read.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a7633be
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Repeatable-Read-Phantom-Read.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Repeatable-with-Next-Key-Lock.jpg b/resource/img/Repeatable-with-Next-Key-Lock.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..bab3dc4
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Repeatable-with-Next-Key-Lock.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Row-Overflow-in-Barracuda.jpg b/resource/img/Row-Overflow-in-Barracuda.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f702e4e
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Row-Overflow-in-Barracuda.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Row-Overflow.jpg b/resource/img/Row-Overflow.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c743e7a
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Row-Overflow.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Secondary-Index.jpg b/resource/img/Secondary-Index.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..1924223
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Secondary-Index.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Shared-Exclusive-Lock.jpg b/resource/img/Shared-Exclusive-Lock.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9f07746
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Shared-Exclusive-Lock.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Tablespace-segment-extent-page-row.jpg b/resource/img/Tablespace-segment-extent-page-row.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..66db246
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Tablespace-segment-extent-page-row.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/Transaction-Isolation-Matrix.jpg b/resource/img/Transaction-Isolation-Matrix.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c203fca
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/Transaction-Isolation-Matrix.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/frm-and-ibd-file.jpg b/resource/img/frm-and-ibd-file.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..dacb667
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/frm-and-ibd-file.jpg differ
diff --git a/resource/img/frm-file-hex.png b/resource/img/frm-file-hex.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7e4a446
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/frm-file-hex.png differ
diff --git a/resource/img/mysql.png b/resource/img/mysql.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5e57082
Binary files /dev/null and b/resource/img/mysql.png differ
diff --git a/src/main/java/test/Hello.java b/src/main/java/test/Hello.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cd7c568
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/test/Hello.java
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
+package test;
+
+public class Hello implements HelloInterface{
+
+ @Override
+ public void say() {
+ System.out.println("Hello,World.");
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/test/HelloInterface.java b/src/main/java/test/HelloInterface.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..869652b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/test/HelloInterface.java
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
+package test;
+
+public interface HelloInterface {
+ public void say();
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/test/HelloProxy.java b/src/main/java/test/HelloProxy.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9ca6028
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/test/HelloProxy.java
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
+package test;
+
+import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
+import java.lang.reflect.Method;
+
+public class HelloProxy implements InvocationHandler {
+
+ Object subject;
+ public HelloProxy(Object object){
+ this.subject = object;
+ }
+ @Override
+ public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
+ System.out.println("动态代理前 ...");
+ method.invoke(subject,args);
+ System.out.println("动态代理后 ...");
+ return null;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/test/Singleton.java b/src/main/java/test/Singleton.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0b3d6c0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/test/Singleton.java
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+package test;
+
+public class Singleton {
+ private Singleton(){
+
+ }
+ private static class Sin{
+ private static final Singleton singleton = new Singleton();
+ }
+ private enum Single{
+ INSTANCE,
+ SINGLE;
+
+ private final Singleton singleton;
+
+ Single() {
+ singleton = new Singleton();
+ }
+
+ public Singleton getSingleton() {
+ return singleton;
+ }
+ }
+
+ private enum wha{
+ ;
+ private String a;
+ private String b;
+
+
+ public String getA() {
+ return a;
+ }
+
+ public String getB() {
+ return b;
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/test/Test.java b/src/main/java/test/Test.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e523903
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/test/Test.java
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+package test;
+
+import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
+import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
+
+public class Test {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Hello hello = new Hello();
+ InvocationHandler handler = new HelloProxy(hello);
+ HelloInterface helloInterface = (HelloInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(handler.getClass().getClassLoader(),
+ hello.getClass().getInterfaces(),handler);
+ helloInterface.say();
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/test/TestA.java b/src/main/java/test/TestA.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9870096
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/test/TestA.java
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+package test;
+
+public class TestA implements defaultT {
+ @Override
+ public void a() {
+ System.out.println("fdff");
+ }
+
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ TestA a = new TestA();
+ a.a();
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/test/defaultT.java b/src/main/java/test/defaultT.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b11702c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/test/defaultT.java
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
+package test;
+
+public interface defaultT {
+ public default void a(){
+ System.out.println("sf");
+ }
+}