diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index fa4cf3b3..b0855b9e 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -216,6 +216,7 @@
| 0075 |[Sort Colors](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 198 | 85.66
| 0066 |[Plus One](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0066_plus_one)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math | 303 | 35.18
| 0238 |[Product of Array Except Self](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0238_product_of_array_except_self)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Prefix_Sum | 669 | 48.96
+| 1291 |[Sequential Digits](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1291_sequential_digits)| Medium | Enumeration | 114 | 100.00
| 0448 |[Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0448_find_all_numbers_disappeared_in_an_array)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table | 394 | 100.00
| 0442 |[Find All Duplicates in an Array](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0442_find_all_duplicates_in_an_array)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table | 480 | 73.81
| 0041 |[First Missing Positive](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0041_first_missing_positive)| Hard | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table | 345 | 100.00
@@ -259,6 +260,7 @@
| 0074 |[Search a 2D Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Matrix | 290 | 40.17
| 0054 |[Spiral Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0054_spiral_matrix)| Medium | Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Matrix, Simulation | 224 | 62.50
| 0048 |[Rotate Image](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0048_rotate_image)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Math, Matrix | 287 | 46.50
+| 1572 |[Matrix Diagonal Sum](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1572_matrix_diagonal_sum)| Easy | Array, Matrix | 221 | 67.61
| 0073 |[Set Matrix Zeroes](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Hash_Table, Matrix | 255 | 100.00
| 0056 |[Merge Intervals](src/main/kotlin/g0001_0100/s0056_merge_intervals)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Sorting | 320 | 94.22
@@ -581,6 +583,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0155 |[Min Stack](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0155_min_stack)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Stack, Design | 331 | 84.88
+| 1249 |[Minimum Remove to Make Valid Parentheses](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1249_minimum_remove_to_make_valid_parentheses)| Medium | String, Stack | 218 | 100.00
#### Day 15 Tree
@@ -617,6 +620,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0997 |[Find the Town Judge](src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0997_find_the_town_judge)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Graph | 475 | 58.62
+| 1557 |[Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1557_minimum_number_of_vertices_to_reach_all_nodes)| Medium | Graph | 792 | 99.29
| 0841 |[Keys and Rooms](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0841_keys_and_rooms)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph | 189 | 69.23
#### Day 20 Heap Priority Queue
@@ -932,6 +936,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0441 |[Arranging Coins](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0441_arranging_coins)| Easy | Math, Binary_Search | 150 | 84.21
+| 1539 |[Kth Missing Positive Number](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1539_kth_missing_positive_number)| Easy | Array, Binary_Search | 153 | 100.00
#### Day 7
@@ -998,12 +1003,14 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0875 |[Koko Eating Bananas](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0875_koko_eating_bananas)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search | 267 | 93.85
+| 1552 |[Magnetic Force Between Two Balls](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1552_magnetic_force_between_two_balls)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Binary_Search | 636 | 100.00
#### Day 5
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0287 |[Find the Duplicate Number](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0287_find_the_duplicate_number)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Bit_Manipulation | 656 | 66.21
+| 1283 |[Find the Smallest Divisor Given a Threshold](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1283_find_the_smallest_divisor_given_a_threshold)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search | 255 | 100.00
#### Day 6
@@ -1014,6 +1021,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1482 |[Minimum Number of Days to Make m Bouquets](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1482_minimum_number_of_days_to_make_m_bouquets)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search | 538 | 50.00
#### Day 8
@@ -1059,17 +1067,22 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1508 |[Range Sum of Sorted Subarray Sums](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1508_range_sum_of_sorted_subarray_sums)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers | 378 | 66.67
+| 1574 |[Shortest Subarray to be Removed to Make Array Sorted](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1574_shortest_subarray_to_be_removed_to_make_array_sorted)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Stack, Monotonic_Stack | 477 | 50.00
#### Day 15
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1292 |[Maximum Side Length of a Square with Sum Less than or Equal to Threshold](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1292_maximum_side_length_of_a_square_with_sum_less_than_or_equal_to_threshold)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Matrix, Prefix_Sum | 376 | 100.00
+| 1498 |[Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1498_number_of_subsequences_that_satisfy_the_given_sum_condition)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers | 487 | 97.89
#### Day 16
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0981 |[Time Based Key-Value Store](src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0981_time_based_key_value_store)| Medium | String, Hash_Table, Binary_Search, Design | 1555 | 10.00
+| 1300 |[Sum of Mutated Array Closest to Target](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1300_sum_of_mutated_array_closest_to_target)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Binary_Search | 217 | 100.00
#### Day 17
@@ -1081,16 +1094,19 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 1146 |[Snapshot Array](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1146_snapshot_array)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Binary_Search, Design | 1064 | 57.14
+| 1488 |[Avoid Flood in The City](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1488_avoid_flood_in_the_city)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Greedy, Binary_Search, Heap_Priority_Queue | 823 | 66.67
#### Day 19
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1562 |[Find Latest Group of Size M](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1562_find_latest_group_of_size_m)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Simulation | 534 | 100.00
#### Day 20
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1201 |[Ugly Number III](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1201_ugly_number_iii)| Medium | Math, Binary_Search, Number_Theory | 136 | 100.00
| 0911 |[Online Election](src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0911_online_election)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Binary_Search, Design | 766 | 83.33
### Dynamic Programming I
@@ -1136,6 +1152,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0152 |[Maximum Product Subarray](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0152_maximum_product_subarray)| Medium | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Dynamic_Programming | 253 | 88.42
+| 1567 |[Maximum Length of Subarray With Positive Product](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1567_maximum_length_of_subarray_with_positive_product)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 468 | 33.33
#### Day 7
@@ -1251,12 +1268,15 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1523 |[Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1523_count_odd_numbers_in_an_interval_range)| Easy | Math | 114 | 97.22
+| 1491 |[Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1491_average_salary_excluding_the_minimum_and_maximum_salary)| Easy | Array, Sorting | 165 | 27.87
#### Day 2 Operator
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0191 |[Number of 1 Bits](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0191_number_of_1_bits)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Bit_Manipulation | 237 | 68.44
+| 1281 |[Subtract the Product and Sum of Digits of an Integer](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1281_subtract_the_product_and_sum_of_digits_of_an_integer)| Easy | Math | 128 | 61.82
#### Day 3 Conditional Statements
@@ -1268,6 +1288,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1502 |[Can Make Arithmetic Progression From Sequence](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1502_can_make_arithmetic_progression_from_sequence)| Easy | Array, Sorting | 156 | 94.82
| 0202 |[Happy Number](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0202_happy_number)| Easy | Top_Interview_Questions, Hash_Table, Math, Two_Pointers | 261 | 45.08
#### Day 5 Function
@@ -1276,17 +1297,20 @@
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0589 |[N-ary Tree Preorder Traversal](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0589_n_ary_tree_preorder_traversal)| Easy | Depth_First_Search, Tree, Stack | 233 | 84.02
| 0496 |[Next Greater Element I](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0496_next_greater_element_i)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Stack, Monotonic_Stack | 171 | 100.00
+| 1232 |[Check If It Is a Straight Line](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1232_check_if_it_is_a_straight_line)| Easy | Array, Math, Geometry | 152 | 95.38
#### Day 6 Array
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1588 |[Sum of All Odd Length Subarrays](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1588_sum_of_all_odd_length_subarrays)| Easy | Array, Math, Prefix_Sum | 157 | 64.00
| 0283 |[Move Zeroes](src/main/kotlin/g0201_0300/s0283_move_zeroes)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Array, Two_Pointers | 516 | 79.07
#### Day 7 Array
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1572 |[Matrix Diagonal Sum](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1572_matrix_diagonal_sum)| Easy | Array, Matrix | 221 | 67.61
| 0566 |[Reshape the Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g0501_0600/s0566_reshape_the_matrix)| Easy | Array, Matrix, Simulation | 239 | 99.05
#### Day 8 String
@@ -1307,6 +1331,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1290 |[Convert Binary Number in a Linked List to Integer](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1290_convert_binary_number_in_a_linked_list_to_integer)| Easy | Math, Linked_List | 145 | 25.93
| 0876 |[Middle of the Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0876_middle_of_the_linked_list)| Easy | Two_Pointers, Linked_List | 136 | 76.52
| 0104 |[Maximum Depth of Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0104_maximum_depth_of_binary_tree)| Easy | Top_100_Liked_Questions, Top_Interview_Questions, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 236 | 83.39
| 0404 |[Sum of Left Leaves](src/main/kotlin/g0401_0500/s0404_sum_of_left_leaves)| Easy | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 173 | 86.05
@@ -1324,6 +1349,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1603 |[Design Parking System](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1603_design_parking_system)| Easy | Design, Simulation, Counting | 376 | 31.83
| 0303 |[Range Sum Query - Immutable](src/main/kotlin/g0301_0400/s0303_range_sum_query_immutable)| Easy | Array, Design, Prefix_Sum | 472 | 63.64
### Programming Skills II
@@ -1479,6 +1505,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0695 |[Max Area of Island](src/main/kotlin/g0601_0700/s0695_max_area_of_island)| Medium | Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find | 324 | 24.06
+| 1254 |[Number of Closed Islands](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1254_number_of_closed_islands)| Medium | Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find | 177 | 89.47
#### Day 3 Matrix Related Problems
@@ -1532,6 +1559,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 1129 |[Shortest Path with Alternating Colors](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1129_shortest_path_with_alternating_colors)| Medium | Breadth_First_Search, Graph | 241 | 16.67
+| 1466 |[Reorder Routes to Make All Paths Lead to the City Zero](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1466_reorder_routes_to_make_all_paths_lead_to_the_city_zero)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph | 718 | 100.00
| 0847 |[Shortest Path Visiting All Nodes](src/main/kotlin/g0801_0900/s0847_shortest_path_visiting_all_nodes)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming, Breadth_First_Search, Bit_Manipulation, Graph, Bitmask | 164 | 100.00
#### Day 11 Breadth First Search
@@ -1554,6 +1582,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0997 |[Find the Town Judge](src/main/kotlin/g0901_1000/s0997_find_the_town_judge)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Graph | 475 | 58.62
+| 1557 |[Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1557_minimum_number_of_vertices_to_reach_all_nodes)| Medium | Graph | 792 | 99.29
#### Day 14 Graph Theory
@@ -1583,6 +1612,8 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1484 |[Group Sold Products By The Date](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1484_group_sold_products_by_the_date)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 899 | 40.76
+| 1527 |[Patients With a Condition](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1527_patients_with_a_condition)| Easy | Database | 708 | 48.23
#### Day 4 Union and Select
@@ -1596,6 +1627,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0175 |[Combine Two Tables](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0175_combine_two_tables)| Easy | Database | 473 | 54.97
+| 1581 |[Customer Who Visited but Did Not Make Any Transactions](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1581_customer_who_visited_but_did_not_make_any_transactions)| Easy | Database | 2771 | 54.68
| 1148 |[Article Views I](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1148_article_views_i)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 806 | 54.41
#### Day 6 Union
@@ -1632,6 +1664,7 @@
|-|-|-|-|-|-
| 0182 |[Duplicate Emails](src/main/kotlin/g0101_0200/s0182_duplicate_emails)| Easy | Database | 396 | 68.40
| 1050 |[Actors and Directors Who Cooperated At Least Three Times](src/main/kotlin/g1001_1100/s1050_actors_and_directors_who_cooperated_at_least_three_times)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 629 | 81.02
+| 1587 |[Bank Account Summary II](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1587_bank_account_summary_ii)| Easy | Database | 1582 | 52.96
| 1084 |[Sales Analysis III](src/main/kotlin/g1001_1100/s1084_sales_analysis_iii)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database | 1881 | 79.36
### Level 1
@@ -1640,6 +1673,7 @@
| | | | | |
|-|-|-|-|-|-
+| 1480 |[Running Sum of 1d Array](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1480_running_sum_of_1d_array)| Easy | Array, Prefix_Sum | 195 | 21.52
| 0724 |[Find Pivot Index](src/main/kotlin/g0701_0800/s0724_find_pivot_index)| Easy | Array, Prefix_Sum | 255 | 88.92
#### Day 2 String
@@ -1744,6 +1778,129 @@
| # | Title | Difficulty | Tag | Time, ms | Time, %
|------|----------------|-------------|-------------|----------|--------
+| 1606 |[Find Servers That Handled Most Number of Requests](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1606_find_servers_that_handled_most_number_of_requests)| Hard | Array, Greedy, Heap_Priority_Queue, Ordered_Set | 973 | 33.33
+| 1605 |[Find Valid Matrix Given Row and Column Sums](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1605_find_valid_matrix_given_row_and_column_sums)| Medium | Array, Greedy, Matrix | 574 | 100.00
+| 1604 |[Alert Using Same Key-Card Three or More Times in a One Hour Period](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1604_alert_using_same_key_card_three_or_more_times_in_a_one_hour_period)| Medium | Array, String, Hash_Table, Sorting | 1063 | 20.00
+| 1603 |[Design Parking System](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1603_design_parking_system)| Easy | Design, Simulation, Counting, Programming_Skills_I_Day_12_Class_and_Object | 376 | 31.83
+| 1601 |[Maximum Number of Achievable Transfer Requests](src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1601_maximum_number_of_achievable_transfer_requests)| Hard | Array, Bit_Manipulation, Backtracking, Enumeration | 206 | 100.00
+| 1600 |[Throne Inheritance](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1600_throne_inheritance)| Medium | Hash_Table, Depth_First_Search, Tree, Design | 1847 | 100.00
+| 1599 |[Maximum Profit of Operating a Centennial Wheel](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1599_maximum_profit_of_operating_a_centennial_wheel)| Medium | Array, Simulation | 593 | 100.00
+| 1598 |[Crawler Log Folder](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1598_crawler_log_folder)| Easy | Array, String, Stack | 150 | 92.31
+| 1595 |[Minimum Cost to Connect Two Groups of Points](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1595_minimum_cost_to_connect_two_groups_of_points)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix, Bit_Manipulation, Bitmask | 278 | 100.00
+| 1594 |[Maximum Non Negative Product in a Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1594_maximum_non_negative_product_in_a_matrix)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix | 224 | 100.00
+| 1593 |[Split a String Into the Max Number of Unique Substrings](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1593_split_a_string_into_the_max_number_of_unique_substrings)| Medium | String, Hash_Table, Backtracking | 161 | 100.00
+| 1592 |[Rearrange Spaces Between Words](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1592_rearrange_spaces_between_words)| Easy | String | 182 | 75.00
+| 1591 |[Strange Printer II](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1591_strange_printer_ii)| Hard | Array, Matrix, Graph, Topological_Sort | 321 | 100.00
+| 1590 |[Make Sum Divisible by P](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1590_make_sum_divisible_by_p)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Prefix_Sum | 633 | 20.00
+| 1589 |[Maximum Sum Obtained of Any Permutation](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1589_maximum_sum_obtained_of_any_permutation)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Greedy, Prefix_Sum | 867 | 66.67
+| 1588 |[Sum of All Odd Length Subarrays](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1588_sum_of_all_odd_length_subarrays)| Easy | Array, Math, Prefix_Sum, Programming_Skills_I_Day_6_Array | 157 | 64.00
+| 1587 |[Bank Account Summary II](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1587_bank_account_summary_ii)| Easy | Database, SQL_I_Day_10_Where | 1582 | 52.96
+| 1585 |[Check If String Is Transformable With Substring Sort Operations](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1585_check_if_string_is_transformable_with_substring_sort_operations)| Hard | String, Sorting, Greedy | 271 | 100.00
+| 1584 |[Min Cost to Connect All Points](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1584_min_cost_to_connect_all_points)| Medium | Array, Union_Find, Minimum_Spanning_Tree | 331 | 95.12
+| 1583 |[Count Unhappy Friends](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1583_count_unhappy_friends)| Medium | Array, Simulation | 324 | 100.00
+| 1582 |[Special Positions in a Binary Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1582_special_positions_in_a_binary_matrix)| Easy | Array, Matrix | 212 | 60.00
+| 1581 |[Customer Who Visited but Did Not Make Any Transactions](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1581_customer_who_visited_but_did_not_make_any_transactions)| Easy | Database, SQL_I_Day_5_Union | 2771 | 54.68
+| 1579 |[Remove Max Number of Edges to Keep Graph Fully Traversable](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1579_remove_max_number_of_edges_to_keep_graph_fully_traversable)| Hard | Graph, Union_Find | 942 | 32.52
+| 1578 |[Minimum Time to Make Rope Colorful](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1578_minimum_time_to_make_rope_colorful)| Medium | Array, String, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 577 | 100.00
+| 1577 |[Number of Ways Where Square of Number Is Equal to Product of Two Numbers](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1577_number_of_ways_where_square_of_number_is_equal_to_product_of_two_numbers)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Math, Two_Pointers | 209 | 100.00
+| 1576 |[Replace All ?'s to Avoid Consecutive Repeating Characters](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1576_replace_all_s_to_avoid_consecutive_repeating_characters)| Easy | String | 180 | 37.50
+| 1575 |[Count All Possible Routes](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1575_count_all_possible_routes)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Memoization | 246 | 100.00
+| 1574 |[Shortest Subarray to be Removed to Make Array Sorted](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1574_shortest_subarray_to_be_removed_to_make_array_sorted)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Stack, Monotonic_Stack, Binary_Search_II_Day_14 | 477 | 50.00
+| 1573 |[Number of Ways to Split a String](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1573_number_of_ways_to_split_a_string)| Medium | String, Math | 247 | 100.00
+| 1572 |[Matrix Diagonal Sum](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1572_matrix_diagonal_sum)| Easy | Array, Matrix, Programming_Skills_I_Day_7_Array, Udemy_2D_Arrays/Matrix | 221 | 67.61
+| 1569 |[Number of Ways to Reorder Array to Get Same BST](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1569_number_of_ways_to_reorder_array_to_get_same_bst)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Tree, Binary_Tree, Union_Find, Binary_Search_Tree, Divide_and_Conquer, Memoization, Combinatorics | 256 | 100.00
+| 1568 |[Minimum Number of Days to Disconnect Island](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1568_minimum_number_of_days_to_disconnect_island)| Hard | Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Strongly_Connected_Component | 210 | 100.00
+| 1567 |[Maximum Length of Subarray With Positive Product](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1567_maximum_length_of_subarray_with_positive_product)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy, Dynamic_Programming_I_Day_6 | 468 | 33.33
+| 1566 |[Detect Pattern of Length M Repeated K or More Times](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1566_detect_pattern_of_length_m_repeated_k_or_more_times)| Easy | Array, Enumeration | 168 | 33.33
+| 1563 |[Stone Game V](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1563_stone_game_v)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Game_Theory | 371 | 100.00
+| 1562 |[Find Latest Group of Size M](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1562_find_latest_group_of_size_m)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Simulation, Binary_Search_II_Day_19 | 534 | 100.00
+| 1561 |[Maximum Number of Coins You Can Get](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1561_maximum_number_of_coins_you_can_get)| Medium | Array, Math, Sorting, Greedy, Game_Theory | 515 | 50.00
+| 1560 |[Most Visited Sector in a Circular Track](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1560_most_visited_sector_in_a_circular_track)| Easy | Array, Simulation | 230 | 100.00
+| 1559 |[Detect Cycles in 2D Grid](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1559_detect_cycles_in_2d_grid)| Medium | Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find | 871 | 33.33
+| 1558 |[Minimum Numbers of Function Calls to Make Target Array](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1558_minimum_numbers_of_function_calls_to_make_target_array)| Medium | Array, Greedy | 347 | 50.00
+| 1557 |[Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1557_minimum_number_of_vertices_to_reach_all_nodes)| Medium | Graph, Data_Structure_II_Day_19_Graph, Graph_Theory_I_Day_13_Graph_Theory | 792 | 99.29
+| 1556 |[Thousand Separator](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1556_thousand_separator)| Easy | String | 131 | 100.00
+| 1553 |[Minimum Number of Days to Eat N Oranges](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1553_minimum_number_of_days_to_eat_n_oranges)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming, Memoization | 153 | 100.00
+| 1552 |[Magnetic Force Between Two Balls](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1552_magnetic_force_between_two_balls)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Binary_Search, Binary_Search_II_Day_4 | 636 | 100.00
+| 1551 |[Minimum Operations to Make Array Equal](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1551_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal)| |||
+| 1550 |[Three Consecutive Odds](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1550_three_consecutive_odds)| Easy | Array | 154 | 90.00
+| 1547 |[Minimum Cost to Cut a Stick](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1547_minimum_cost_to_cut_a_stick)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 187 | 92.00
+| 1546 |[Maximum Number of Non-Overlapping Subarrays With Sum Equals Target](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1546_maximum_number_of_non_overlapping_subarrays_with_sum_equals_target)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Greedy, Prefix_Sum | 560 | 100.00
+| 1545 |[Find Kth Bit in Nth Binary String](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1545_find_kth_bit_in_nth_binary_string)| Medium | String, Recursion | 141 | 100.00
+| 1544 |[Make The String Great](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1544_make_the_string_great)| Easy | String, Stack | 164 | 92.16
+| 1542 |[Find Longest Awesome Substring](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1542_find_longest_awesome_substring)| Hard | String, Hash_Table, Bit_Manipulation | 239 | 100.00
+| 1541 |[Minimum Insertions to Balance a Parentheses String](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1541_minimum_insertions_to_balance_a_parentheses_string)| Medium | String, Greedy, Stack | 240 | 80.00
+| 1540 |[Can Convert String in K Moves](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1540_can_convert_string_in_k_moves)| Medium | String, Hash_Table | 272 | 75.00
+| 1539 |[Kth Missing Positive Number](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1539_kth_missing_positive_number)| Easy | Array, Binary_Search, Binary_Search_I_Day_6 | 153 | 100.00
+| 1537 |[Get the Maximum Score](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1537_get_the_maximum_score)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy, Two_Pointers | 453 | 100.00
+| 1536 |[Minimum Swaps to Arrange a Binary Grid](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1536_minimum_swaps_to_arrange_a_binary_grid)| Medium | Array, Greedy, Matrix | 336 | 100.00
+| 1535 |[Find the Winner of an Array Game](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1535_find_the_winner_of_an_array_game)| Medium | Array, Simulation | 460 | 100.00
+| 1534 |[Count Good Triplets](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1534_count_good_triplets)| Easy | Array, Enumeration | 175 | 66.67
+| 1531 |[String Compression II](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1531_string_compression_ii)| Hard | String, Dynamic_Programming | 207 | 100.00
+| 1530 |[Number of Good Leaf Nodes Pairs](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1530_number_of_good_leaf_nodes_pairs)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 242 | 100.00
+| 1529 |[Minimum Suffix Flips](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1529_minimum_suffix_flips)| Medium | String, Greedy | 200 | 100.00
+| 1528 |[Shuffle String](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1528_shuffle_string)| Easy | Array, String | 180 | 89.23
+| 1527 |[Patients With a Condition](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1527_patients_with_a_condition)| Easy | Database, SQL_I_Day_3_String_Processing_Functions | 708 | 48.23
+| 1526 |[Minimum Number of Increments on Subarrays to Form a Target Array](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1526_minimum_number_of_increments_on_subarrays_to_form_a_target_array)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy, Stack, Monotonic_Stack | 466 | 100.00
+| 1525 |[Number of Good Ways to Split a String](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1525_number_of_good_ways_to_split_a_string)| Medium | String, Dynamic_Programming, Bit_Manipulation | 238 | 100.00
+| 1524 |[Number of Sub-arrays With Odd Sum](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1524_number_of_sub_arrays_with_odd_sum)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Prefix_Sum | 584 | 100.00
+| 1523 |[Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1523_count_odd_numbers_in_an_interval_range)| Easy | Math, Programming_Skills_I_Day_1_Basic_Data_Type | 114 | 97.22
+| 1521 |[Find a Value of a Mysterious Function Closest to Target](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1521_find_a_value_of_a_mysterious_function_closest_to_target)| Hard | Array, Binary_Search, Bit_Manipulation, Segment_Tree | 446 | 100.00
+| 1520 |[Maximum Number of Non-Overlapping Substrings](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1520_maximum_number_of_non_overlapping_substrings)| Hard | String, Greedy | 333 | 100.00
+| 1519 |[Number of Nodes in the Sub-Tree With the Same Label](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1519_number_of_nodes_in_the_sub_tree_with_the_same_label)| Medium | Hash_Table, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Counting | 1130 | 87.50
+| 1518 |[Water Bottles](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1518_water_bottles)| Easy | Math, Simulation | 116 | 100.00
+| 1515 |[Best Position for a Service Centre](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1515_best_position_for_a_service_centre)| Hard | Math, Geometry, Randomized | 183 | 100.00
+| 1514 |[Path with Maximum Probability](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1514_path_with_maximum_probability)| Medium | Heap_Priority_Queue, Graph, Shortest_Path | 681 | 100.00
+| 1513 |[Number of Substrings With Only 1s](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1513_number_of_substrings_with_only_1s)| Medium | String, Math | 171 | 100.00
+| 1512 |[Number of Good Pairs](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1512_number_of_good_pairs)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Math, Counting | 138 | 70.65
+| 1510 |[Stone Game IV](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1510_stone_game_iv)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming, Math, Game_Theory | 137 | 100.00
+| 1509 |[Minimum Difference Between Largest and Smallest Value in Three Moves](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1509_minimum_difference_between_largest_and_smallest_value_in_three_moves)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Greedy | 415 | 100.00
+| 1508 |[Range Sum of Sorted Subarray Sums](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1508_range_sum_of_sorted_subarray_sums)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Binary_Search_II_Day_14 | 378 | 66.67
+| 1507 |[Reformat Date](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1507_reformat_date)| Easy | String | 147 | 100.00
+| 1505 |[Minimum Possible Integer After at Most K Adjacent Swaps On Digits](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1505_minimum_possible_integer_after_at_most_k_adjacent_swaps_on_digits)| Hard | String, Greedy, Segment_Tree, Binary_Indexed_Tree | 226 | 100.00
+| 1504 |[Count Submatrices With All Ones](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1504_count_submatrices_with_all_ones)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix, Stack, Monotonic_Stack | 265 | 80.00
+| 1503 |[Last Moment Before All Ants Fall Out of a Plank](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1503_last_moment_before_all_ants_fall_out_of_a_plank)| Medium | Array, Simulation, Brainteaser | 253 | 100.00
+| 1502 |[Can Make Arithmetic Progression From Sequence](src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1502_can_make_arithmetic_progression_from_sequence)| Easy | Array, Sorting, Programming_Skills_I_Day_4_Loop | 156 | 94.82
+| 1499 |[Max Value of Equation](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1499_max_value_of_equation)| Hard | Array, Heap_Priority_Queue, Sliding_Window, Queue, Monotonic_Queue | 708 | 100.00
+| 1498 |[Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1498_number_of_subsequences_that_satisfy_the_given_sum_condition)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Binary_Search_II_Day_15 | 487 | 97.89
+| 1497 |[Check If Array Pairs Are Divisible by k](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1497_check_if_array_pairs_are_divisible_by_k)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Counting | 575 | 83.33
+| 1496 |[Path Crossing](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1496_path_crossing)| Easy | String, Hash_Table | 120 | 100.00
+| 1494 |[Parallel Courses II](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1494_parallel_courses_ii)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming, Bit_Manipulation, Graph, Bitmask | 381 | 100.00
+| 1493 |[Longest Subarray of 1's After Deleting One Element](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1493_longest_subarray_of_1s_after_deleting_one_element)| Medium | Dynamic_Programming, Math, Sliding_Window | 288 | 73.85
+| 1492 |[The kth Factor of n](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1492_the_kth_factor_of_n)| Medium | Math | 133 | 65.12
+| 1491 |[Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1491_average_salary_excluding_the_minimum_and_maximum_salary)| Easy | Array, Sorting, Programming_Skills_I_Day_1_Basic_Data_Type | 165 | 27.87
+| 1489 |[Find Critical and Pseudo-Critical Edges in Minimum Spanning Tree](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1489_find_critical_and_pseudo_critical_edges_in_minimum_spanning_tree)| Hard | Sorting, Graph, Union_Find, Minimum_Spanning_Tree, Strongly_Connected_Component | 342 | 100.00
+| 1488 |[Avoid Flood in The City](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1488_avoid_flood_in_the_city)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Greedy, Binary_Search, Heap_Priority_Queue, Binary_Search_II_Day_18 | 823 | 66.67
+| 1487 |[Making File Names Unique](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1487_making_file_names_unique)| Medium | Array, String, Hash_Table | 553 | 50.00
+| 1486 |[XOR Operation in an Array](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1486_xor_operation_in_an_array)| Easy | Math, Bit_Manipulation | 123 | 81.25
+| 1484 |[Group Sold Products By The Date](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1484_group_sold_products_by_the_date)| Easy | LeetCode_Curated_SQL_70, Database, SQL_I_Day_3_String_Processing_Functions | 899 | 40.76
+| 1483 |[Kth Ancestor of a Tree Node](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1483_kth_ancestor_of_a_tree_node)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Search, Design | 956 | 100.00
+| 1482 |[Minimum Number of Days to Make m Bouquets](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1482_minimum_number_of_days_to_make_m_bouquets)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Binary_Search_II_Day_7 | 538 | 50.00
+| 1481 |[Least Number of Unique Integers after K Removals](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1481_least_number_of_unique_integers_after_k_removals)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Greedy, Counting | 564 | 76.19
+| 1480 |[Running Sum of 1d Array](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1480_running_sum_of_1d_array)| Easy | Array, Prefix_Sum, Level_1_Day_1_Prefix_Sum | 195 | 21.52
+| 1478 |[Allocate Mailboxes](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1478_allocate_mailboxes)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Math, Sorting | 226 | 100.00
+| 1477 |[Find Two Non-overlapping Sub-arrays Each With Target Sum](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1477_find_two_non_overlapping_sub_arrays_each_with_target_sum)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Dynamic_Programming, Binary_Search, Sliding_Window | 746 | 100.00
+| 1476 |[Subrectangle Queries](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1476_subrectangle_queries)| Medium | Array, Matrix, Design | 332 | 81.82
+| 1475 |[Final Prices With a Special Discount in a Shop](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1475_final_prices_with_a_special_discount_in_a_shop)| Easy | Array, Stack, Monotonic_Stack | 182 | 94.12
+| 1473 |[Paint House III](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1473_paint_house_iii)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 235 | 100.00
+| 1472 |[Design Browser History](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1472_design_browser_history)| Medium | Array, Stack, Design, Linked_List, Data_Stream, Doubly_Linked_List | 576 | 42.42
+| 1471 |[The k Strongest Values in an Array](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1471_the_k_strongest_values_in_an_array)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Two_Pointers | 780 | 100.00
+| 1470 |[Shuffle the Array](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1470_shuffle_the_array)| Easy | Array | 220 | 41.96
+| 1467 |[Probability of a Two Boxes Having The Same Number of Distinct Balls](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1467_probability_of_a_two_boxes_having_the_same_number_of_distinct_balls)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming, Math, Backtracking, Combinatorics, Probability_and_Statistics | 150 | 100.00
+| 1466 |[Reorder Routes to Make All Paths Lead to the City Zero](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1466_reorder_routes_to_make_all_paths_lead_to_the_city_zero)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Graph_Theory_I_Day_10_Standard_Traversal | 718 | 100.00
+| 1465 |[Maximum Area of a Piece of Cake After Horizontal and Vertical Cuts](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1465_maximum_area_of_a_piece_of_cake_after_horizontal_and_vertical_cuts)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Greedy | 418 | 50.00
+| 1464 |[Maximum Product of Two Elements in an Array](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1464_maximum_product_of_two_elements_in_an_array)| Easy | Array, Sorting, Heap_Priority_Queue | 190 | 64.71
+| 1463 |[Cherry Pickup II](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1463_cherry_pickup_ii)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix | 198 | 100.00
+| 1462 |[Course Schedule IV](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1462_course_schedule_iv)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph | Sort | Sort
+| 1461 |[Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1461_check_if_a_string_contains_all_binary_codes_of_size_k)| Medium | String, Hash_Table, Bit_Manipulation, Hash_Function, Rolling_Hash | 578 | 20.00
+| 1460 |[Make Two Arrays Equal by Reversing Sub-arrays](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1460_make_two_arrays_equal_by_reversing_subarrays)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting | 231 | 66.67
+| 1458 |[Max Dot Product of Two Subsequences](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1458_max_dot_product_of_two_subsequences)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 215 | 100.00
+| 1457 |[Pseudo-Palindromic Paths in a Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1457_pseudo_palindromic_paths_in_a_binary_tree)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Bit_Manipulation | 583 | 50.00
+| 1456 |[Maximum Number of Vowels in a Substring of Given Length](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1456_maximum_number_of_vowels_in_a_substring_of_given_length)| Medium | String, Sliding_Window | 215 | 97.25
+| 1455 |[Check If a Word Occurs As a Prefix of Any Word in a Sentence](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1455_check_if_a_word_occurs_as_a_prefix_of_any_word_in_a_sentence)| Easy | String, String_Matching | 155 | 42.86
+| 1453 |[Maximum Number of Darts Inside of a Circular Dartboard](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1453_maximum_number_of_darts_inside_of_a_circular_dartboard)| Hard | Array, Math, Geometry | 211 | 100.00
+| 1452 |[People Whose List of Favorite Companies Is Not a Subset of Another List](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1452_people_whose_list_of_favorite_companies_is_not_a_subset_of_another_list)| Medium | Array, String, Hash_Table | 600 | 100.00
+| 1451 |[Rearrange Words in a Sentence](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1451_rearrange_words_in_a_sentence)| Medium | String, Sorting | 263 | 100.00
| 1450 |[Number of Students Doing Homework at a Given Time](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1450_number_of_students_doing_homework_at_a_given_time)| Easy | Array | 180 | 10.00
| 1449 |[Form Largest Integer With Digits That Add up to Target](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1449_form_largest_integer_with_digits_that_add_up_to_target)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 201 | 100.00
| 1448 |[Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1448_count_good_nodes_in_binary_tree)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 384 | 68.52
@@ -1836,6 +1993,7 @@
| 1344 |[Angle Between Hands of a Clock](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1344_angle_between_hands_of_a_clock)| Medium | Math | 118 | 83.33
| 1343 |[Number of Sub-arrays of Size K and Average Greater than or Equal to Threshold](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1343_number_of_sub_arrays_of_size_k_and_average_greater_than_or_equal_to_threshold)| Medium | Array, Sliding_Window | 394 | 84.62
| 1342 |[Number of Steps to Reduce a Number to Zero](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1342_number_of_steps_to_reduce_a_number_to_zero)| Easy | Math, Bit_Manipulation | 124 | 83.18
+| 1341 |[Movie Rating](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1341_movie_rating)| Medium | Database | 2387 | 59.80
| 1340 |[Jump Game V](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1340_jump_game_v)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Sorting | 208 | 100.00
| 1339 |[Maximum Product of Splitted Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1339_maximum_product_of_splitted_binary_tree)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 384 | 100.00
| 1338 |[Reduce Array Size to The Half](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1338_reduce_array_size_to_the_half)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Greedy, Heap_Priority_Queue | 579 | 71.43
@@ -1848,10 +2006,12 @@
| 1330 |[Reverse Subarray To Maximize Array Value](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1330_reverse_subarray_to_maximize_array_value)| Hard | Array, Math, Greedy | 347 | 100.00
| 1329 |[Sort the Matrix Diagonally](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1329_sort_the_matrix_diagonally)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Matrix | 243 | 100.00
| 1328 |[Break a Palindrome](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1328_break_a_palindrome)| Medium | String, Greedy | 137 | 81.82
+| 1327 |[List the Products Ordered in a Period](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1327_list_the_products_ordered_in_a_period)| Easy | Database | 1324 | 61.30
| 1326 |[Minimum Number of Taps to Open to Water a Garden](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1326_minimum_number_of_taps_to_open_to_water_a_garden)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 189 | 100.00
| 1325 |[Delete Leaves With a Given Value](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1325_delete_leaves_with_a_given_value)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 185 | 100.00
| 1324 |[Print Words Vertically](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1324_print_words_vertically)| Medium | Array, String, Simulation | 149 | 66.67
| 1323 |[Maximum 69 Number](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1323_maximum_69_number)| Easy | Math, Greedy | 118 | 90.00
+| 1321 |[Restaurant Growth](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1321_restaurant_growth)| Medium | Database | 630 | 83.05
| 1320 |[Minimum Distance to Type a Word Using Two Fingers](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1320_minimum_distance_to_type_a_word_using_two_fingers)| Hard | String, Dynamic_Programming | 181 | 100.00
| 1319 |[Number of Operations to Make Network Connected](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1319_number_of_operations_to_make_network_connected)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Union_Find, Graph_Theory_I_Day_8_Standard_Traversal | 379 | 83.33
| 1318 |[Minimum Flips to Make a OR b Equal to c](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1318_minimum_flips_to_make_a_or_b_equal_to_c)| Medium | Bit_Manipulation | 123 | 88.89
@@ -1870,8 +2030,77 @@
| 1304 |[Find N Unique Integers Sum up to Zero](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1304_find_n_unique_integers_sum_up_to_zero)| Easy | Array, Math | 142 | 100.00
| 1302 |[Deepest Leaves Sum](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1302_deepest_leaves_sum)| Medium | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree | 325 | 67.39
| 1301 |[Number of Paths with Max Score](src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1301_number_of_paths_with_max_score)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix | 178 | 100.00
+| 1300 |[Sum of Mutated Array Closest to Target](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1300_sum_of_mutated_array_closest_to_target)| Medium | Array, Sorting, Binary_Search, Binary_Search_II_Day_16 | 217 | 100.00
+| 1299 |[Replace Elements with Greatest Element on Right Side](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1299_replace_elements_with_greatest_element_on_right_side)| Easy | Array | 514 | 79.69
+| 1298 |[Maximum Candies You Can Get from Boxes](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1298_maximum_candies_you_can_get_from_boxes)| Hard | Array, Breadth_First_Search | 442 | 80.00
+| 1297 |[Maximum Number of Occurrences of a Substring](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1297_maximum_number_of_occurrences_of_a_substring)| Medium | String, Hash_Table, Sliding_Window | 253 | 75.00
+| 1296 |[Divide Array in Sets of K Consecutive Numbers](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1296_divide_array_in_sets_of_k_consecutive_numbers)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Sorting, Greedy | 488 | 100.00
+| 1295 |[Find Numbers with Even Number of Digits](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1295_find_numbers_with_even_number_of_digits)| Easy | Array | 189 | 35.85
+| 1293 |[Shortest Path in a Grid with Obstacles Elimination](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1293_shortest_path_in_a_grid_with_obstacles_elimination)| Hard | Array, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix | 189 | 100.00
+| 1292 |[Maximum Side Length of a Square with Sum Less than or Equal to Threshold](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1292_maximum_side_length_of_a_square_with_sum_less_than_or_equal_to_threshold)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Matrix, Prefix_Sum, Binary_Search_II_Day_15 | 376 | 100.00
+| 1291 |[Sequential Digits](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1291_sequential_digits)| Medium | Enumeration, Udemy_Arrays | 114 | 100.00
+| 1290 |[Convert Binary Number in a Linked List to Integer](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1290_convert_binary_number_in_a_linked_list_to_integer)| Easy | Math, Linked_List, Programming_Skills_I_Day_10_Linked_List_and_Tree | 145 | 25.93
+| 1289 |[Minimum Falling Path Sum II](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1289_minimum_falling_path_sum_ii)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix | 234 | 100.00
+| 1288 |[Remove Covered Intervals](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1288_remove_covered_intervals)| Medium | Array, Sorting | 184 | 100.00
+| 1287 |[Element Appearing More Than 25% In Sorted Array](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1287_element_appearing_more_than_25_in_sorted_array)| Easy | Array | 199 | 100.00
+| 1286 |[Iterator for Combination](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1286_iterator_for_combination)| Medium | String, Design, Backtracking, Iterator | 236 | 100.00
+| 1284 |[Minimum Number of Flips to Convert Binary Matrix to Zero Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1284_minimum_number_of_flips_to_convert_binary_matrix_to_zero_matrix)| Hard | Array, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Bit_Manipulation | 131 | 100.00
+| 1283 |[Find the Smallest Divisor Given a Threshold](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1283_find_the_smallest_divisor_given_a_threshold)| Medium | Array, Binary_Search, Binary_Search_II_Day_5 | 255 | 100.00
+| 1282 |[Group the People Given the Group Size They Belong To](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1282_group_the_people_given_the_group_size_they_belong_to)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table | 267 | 100.00
+| 1281 |[Subtract the Product and Sum of Digits of an Integer](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1281_subtract_the_product_and_sum_of_digits_of_an_integer)| Easy | Math, Programming_Skills_I_Day_2_Operator | 128 | 61.82
+| 1280 |[Students and Examinations](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1280_students_and_examinations)| Easy | Database | 1552 | 85.96
+| 1278 |[Palindrome Partitioning III](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1278_palindrome_partitioning_iii)| Hard | String, Dynamic_Programming | 137 | 100.00
+| 1277 |[Count Square Submatrices with All Ones](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1277_count_square_submatrices_with_all_ones)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Matrix | 381 | 75.00
+| 1276 |[Number of Burgers with No Waste of Ingredients](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1276_number_of_burgers_with_no_waste_of_ingredients)| Medium | Math | 190 | 50.00
+| 1275 |[Find Winner on a Tic Tac Toe Game](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1275_find_winner_on_a_tic_tac_toe_game)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table, Matrix, Simulation | 125 | 87.50
+| 1269 |[Number of Ways to Stay in the Same Place After Some Steps](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1269_number_of_ways_to_stay_in_the_same_place_after_some_steps)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming | 159 | 50.00
+| 1268 |[Search Suggestions System](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1268_search_suggestions_system)| Medium | Array, String | 331 | 100.00
+| 1267 |[Count Servers that Communicate](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1267_count_servers_that_communicate)| Medium | Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Counting, Union_Find | 295 | 100.00
+| 1266 |[Minimum Time Visiting All Points](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1266_minimum_time_visiting_all_points)| Easy | Array, Math, Geometry | 152 | 100.00
+| 1263 |[Minimum Moves to Move a Box to Their Target Location](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1263_minimum_moves_to_move_a_box_to_their_target_location)| Hard | Array, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Heap_Priority_Queue | 183 | 100.00
+| 1262 |[Greatest Sum Divisible by Three](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1262_greatest_sum_divisible_by_three)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Greedy | 263 | 100.00
+| 1261 |[Find Elements in a Contaminated Binary Tree](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1261_find_elements_in_a_contaminated_binary_tree)| Medium | Hash_Table, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Tree, Binary_Tree, Design | 287 | 100.00
+| 1260 |[Shift 2D Grid](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1260_shift_2d_grid)| Easy | Array, Matrix, Simulation | 302 | 100.00
+| 1255 |[Maximum Score Words Formed by Letters](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1255_maximum_score_words_formed_by_letters)| Hard | Array, String, Dynamic_Programming, Bit_Manipulation, Backtracking, Bitmask | 131 | 100.00
+| 1254 |[Number of Closed Islands](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1254_number_of_closed_islands)| Medium | Array, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix, Union_Find, Graph_Theory_I_Day_2_Matrix_Related_Problems | 177 | 89.47
+| 1253 |[Reconstruct a 2-Row Binary Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1253_reconstruct_a_2_row_binary_matrix)| Medium | Array, Greedy, Matrix | 496 | 75.00
+| 1252 |[Cells with Odd Values in a Matrix](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1252_cells_with_odd_values_in_a_matrix)| Easy | Array, Math, Simulation | 134 | 100.00
+| 1251 |[Average Selling Price](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1251_average_selling_price)| Easy | Database | 1371 | 76.11
+| 1250 |[Check If It Is a Good Array](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1250_check_if_it_is_a_good_array)| Hard | Array, Math, Number_Theory | 334 | 100.00
+| 1249 |[Minimum Remove to Make Valid Parentheses](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1249_minimum_remove_to_make_valid_parentheses)| Medium | String, Stack, Data_Structure_II_Day_14_Stack_Queue | 218 | 100.00
+| 1248 |[Count Number of Nice Subarrays](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1248_count_number_of_nice_subarrays)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Math, Sliding_Window | 431 | 93.33
+| 1247 |[Minimum Swaps to Make Strings Equal](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1247_minimum_swaps_to_make_strings_equal)| Medium | String, Math, Greedy | 134 | 66.67
+| 1240 |[Tiling a Rectangle with the Fewest Squares](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1240_tiling_a_rectangle_with_the_fewest_squares)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming, Backtracking | 134 | 75.00
+| 1239 |[Maximum Length of a Concatenated String with Unique Characters](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1239_maximum_length_of_a_concatenated_string_with_unique_characters)| Medium | Array, String, Bit_Manipulation, Backtracking | 166 | 50.00
+| 1238 |[Circular Permutation in Binary Representation](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1238_circular_permutation_in_binary_representation)| Medium | Math, Bit_Manipulation, Backtracking | 296 | 100.00
+| 1237 |[Find Positive Integer Solution for a Given Equation](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1237_find_positive_integer_solution_for_a_given_equation)| Medium | Math, Binary_Search, Two_Pointers, Interactive | 176 | 36.36
+| 1235 |[Maximum Profit in Job Scheduling](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1235_maximum_profit_in_job_scheduling)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming, Sorting, Binary_Search | 370 | 100.00
+| 1234 |[Replace the Substring for Balanced String](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1234_replace_the_substring_for_balanced_string)| Medium | String, Sliding_Window | 182 | 100.00
+| 1233 |[Remove Sub-Folders from the Filesystem](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1233_remove_sub_folders_from_the_filesystem)| Medium | Array, String, Trie | 459 | 40.00
+| 1232 |[Check If It Is a Straight Line](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1232_check_if_it_is_a_straight_line)| Easy | Array, Math, Geometry, Programming_Skills_I_Day_5_Function | 152 | 95.38
+| 1227 |[Airplane Seat Assignment Probability](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1227_airplane_seat_assignment_probability)| Medium | Dynamic_Programming, Math, Brainteaser, Probability_and_Statistics | 135 | 100.00
+| 1226 |[The Dining Philosophers](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1226_the_dining_philosophers)| Medium | Concurrency | 12 | 95.88
+| 1224 |[Maximum Equal Frequency](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1224_maximum_equal_frequency)| Hard | Array, Hash_Table | 330 | 100.00
+| 1223 |[Dice Roll Simulation](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1223_dice_roll_simulation)| Hard | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 146 | 100.00
+| 1222 |[Queens That Can Attack the King](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1222_queens_that_can_attack_the_king)| Medium | Array, Matrix, Simulation | 189 | 50.00
+| 1221 |[Split a String in Balanced Strings](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1221_split_a_string_in_balanced_strings)| Easy | String, Greedy, Counting | 131 | 67.65
+| 1220 |[Count Vowels Permutation](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1220_count_vowels_permutation)| Hard | Dynamic_Programming | 129 | 100.00
+| 1219 |[Path with Maximum Gold](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1219_path_with_maximum_gold)| Medium | Array, Matrix, Backtracking | 238 | 100.00
+| 1218 |[Longest Arithmetic Subsequence of Given Difference](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1218_longest_arithmetic_subsequence_of_given_difference)| Medium | Array, Hash_Table, Dynamic_Programming | 420 | 100.00
+| 1217 |[Minimum Cost to Move Chips to The Same Position](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1217_minimum_cost_to_move_chips_to_the_same_position)| Easy | Array, Math, Greedy | 119 | 100.00
+| 1211 |[Queries Quality and Percentage](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1211_queries_quality_and_percentage)| Easy | Database | 1176 | 80.10
+| 1210 |[Minimum Moves to Reach Target with Rotations](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1210_minimum_moves_to_reach_target_with_rotations)| Hard | Array, Breadth_First_Search, Matrix | 230 | 100.00
+| 1209 |[Remove All Adjacent Duplicates in String II](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1209_remove_all_adjacent_duplicates_in_string_ii)| Medium | String, Stack | 223 | 100.00
+| 1208 |[Get Equal Substrings Within Budget](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1208_get_equal_substrings_within_budget)| Medium | String, Binary_Search, Prefix_Sum, Sliding_Window | 163 | 100.00
+| 1207 |[Unique Number of Occurrences](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1207_unique_number_of_occurrences)| Easy | Array, Hash_Table | 151 | 83.00
+| 1206 |[Design Skiplist](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1206_design_skiplist)| Hard | Design, Linked_List | 306 | 100.00
+| 1204 |[Last Person to Fit in the Bus](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1204_last_person_to_fit_in_the_bus)| Medium | Database | 1476 | 82.95
+| 1203 |[Sort Items by Groups Respecting Dependencies](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1203_sort_items_by_groups_respecting_dependencies)| Hard | Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Graph, Topological_Sort | 503 | 100.00
+| 1202 |[Smallest String With Swaps](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1202_smallest_string_with_swaps)| Medium | String, Hash_Table, Depth_First_Search, Breadth_First_Search, Union_Find | 562 | 100.00
+| 1201 |[Ugly Number III](src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1201_ugly_number_iii)| Medium | Math, Binary_Search, Number_Theory, Binary_Search_II_Day_20 | 136 | 100.00
| 1200 |[Minimum Absolute Difference](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1200_minimum_absolute_difference)| Easy | Array, Sorting | 507 | 75.00
| 1195 |[Fizz Buzz Multithreaded](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1195_fizz_buzz_multithreaded)| Medium | Concurrency | 6 | 87.26
+| 1193 |[Monthly Transactions I](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1193_monthly_transactions_i)| Medium | Database | 891 | 92.73
| 1192 |[Critical Connections in a Network](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1192_critical_connections_in_a_network)| Hard | Depth_First_Search, Graph, Biconnected_Component | 1696 | 60.00
| 1191 |[K-Concatenation Maximum Sum](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1191_k_concatenation_maximum_sum)| Medium | Array, Dynamic_Programming | 389 | 100.00
| 1190 |[Reverse Substrings Between Each Pair of Parentheses](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1190_reverse_substrings_between_each_pair_of_parentheses)| Medium | String, Stack | 153 | 42.86
@@ -1884,6 +2113,7 @@
| 1178 |[Number of Valid Words for Each Puzzle](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1178_number_of_valid_words_for_each_puzzle)| Hard | Array, String, Hash_Table, Bit_Manipulation, Trie | 675 | 100.00
| 1177 |[Can Make Palindrome from Substring](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1177_can_make_palindrome_from_substring)| Medium | String, Hash_Table, Bit_Manipulation, Prefix_Sum | 937 | 100.00
| 1175 |[Prime Arrangements](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1175_prime_arrangements)| Easy | Math | 129 | 50.00
+| 1174 |[Immediate Food Delivery II](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1174_immediate_food_delivery_ii)| Medium | Database | 981 | 97.51
| 1172 |[Dinner Plate Stacks](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1172_dinner_plate_stacks)| Hard | Hash_Table, Stack, Design, Heap_Priority_Queue | 1160 | 50.00
| 1171 |[Remove Zero Sum Consecutive Nodes from Linked List](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1171_remove_zero_sum_consecutive_nodes_from_linked_list)| Medium | Hash_Table, Linked_List | 194 | 50.00
| 1170 |[Compare Strings by Frequency of the Smallest Character](src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1170_compare_strings_by_frequency_of_the_smallest_character)| Medium | Array, String, Hash_Table, Sorting, Binary_Search | 221 | 50.00
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1174_immediate_food_delivery_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1174_immediate_food_delivery_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3f3c5b2d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1174_immediate_food_delivery_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1174\. Immediate Food Delivery II
+
+Medium
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Delivery`
+
+ +-----------------------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-----------------------------+---------+
+ | delivery_id | int |
+ | customer_id | int |
+ | order_date | date |
+ | customer_pref_delivery_date | date |
+ +-----------------------------+---------+
+
+delivery_id is the primary key of this table. The table holds information about food delivery to customers that make orders at some date and specify a preferred delivery date (on the same order date or after it).
+
+If the customer's preferred delivery date is the same as the order date, then the order is called **immediate;** otherwise, it is called **scheduled**.
+
+The **first order** of a customer is the order with the earliest order date that the customer made. It is guaranteed that a customer has precisely one first order.
+
+Write an SQL query to find the percentage of immediate orders in the first orders of all customers, **rounded to 2 decimal places**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** Delivery table:
+
+ +-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------------------+
+ | delivery_id | customer_id | order_date | customer_pref_delivery_date |
+ +-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------------------+
+ | 1 | 1 | 2019-08-01 | 2019-08-02 |
+ | 2 | 2 | 2019-08-02 | 2019-08-02 |
+ | 3 | 1 | 2019-08-11 | 2019-08-12 |
+ | 4 | 3 | 2019-08-24 | 2019-08-24 |
+ | 5 | 3 | 2019-08-21 | 2019-08-22 |
+ | 6 | 2 | 2019-08-11 | 2019-08-13 |
+ | 7 | 4 | 2019-08-09 | 2019-08-09 |
+ +-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +----------------------+
+ | immediate_percentage |
+ +----------------------+
+ | 50.00 |
+ +----------------------+
+
+**Explanation:** The customer id 1 has a first order with delivery id 1 and it is scheduled. The customer id 2 has a first order with delivery id 2 and it is immediate. The customer id 3 has a first order with delivery id 5 and it is scheduled. The customer id 4 has a first order with delivery id 7 and it is immediate. Hence, half the customers have immediate first orders.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT ROUND(AVG(CASE WHEN customer_pref_delivery_date = order_date THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) * 100, 2) AS immediate_percentage
+FROM (
+ SELECT *,
+ DENSE_RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY customer_id ORDER BY order_date ASC) AS dnsrnk
+ FROM delivery
+) subquery_alias
+WHERE subquery_alias.dnsrnk = 1;
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1193_monthly_transactions_i/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1193_monthly_transactions_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..167056a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1101_1200/s1193_monthly_transactions_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1193\. Monthly Transactions I
+
+Medium
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Transactions`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | id | int |
+ | country | varchar |
+ | state | enum |
+ | amount | int |
+ | trans_date | date |
+ +---------------+---------+
+
+id is the primary key of this table.
+
+The table has information about incoming transactions.
+
+The state column is an enum of type ["approved", "declined"].
+
+Write an SQL query to find for each month and country, the number of transactions and their total amount, the number of approved transactions and their total amount.
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** Transactions table:
+
+ +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+
+ | id | country | state | amount | trans_date |
+ +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+
+ | 121 | US | approved | 1000 | 2018-12-18 |
+ | 122 | US | declined | 2000 | 2018-12-19 |
+ | 123 | US | approved | 2000 | 2019-01-01 |
+ | 124 | DE | approved | 2000 | 2019-01-07 |
+ +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +----------+---------+-------------+----------------+--------------------+-----------------------+
+ | month | country | trans_count | approved_count | trans_total_amount | approved_total_amount |
+ +----------+---------+-------------+----------------+--------------------+-----------------------+
+ | 2018-12 | US | 2 | 1 | 3000 | 1000 |
+ | 2019-01 | US | 1 | 1 | 2000 | 2000 |
+ | 2019-01 | DE | 1 | 1 | 2000 | 2000 |
+ +----------+---------+-------------+----------------+--------------------+-----------------------+
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT
+ FORMATDATETIME(trans_date, 'yyyy-MM') AS trans_month,
+ country,
+ COUNT(*) AS trans_count,
+ SUM(CASE WHEN state = 'approved' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS approved_count,
+ SUM(amount) AS trans_total_amount,
+ SUM(CASE WHEN state = 'approved' THEN amount ELSE 0 END) AS approved_total_amount
+FROM Transactions
+GROUP BY trans_month, country;
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1201_ugly_number_iii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1201_ugly_number_iii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..852730ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1201_ugly_number_iii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1201\. Ugly Number III
+
+Medium
+
+An **ugly number** is a positive integer that is divisible by `a`, `b`, or `c`.
+
+Given four integers `n`, `a`, `b`, and `c`, return the nth **ugly number**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, a = 2, b = 3, c = 5
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The ugly numbers are 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10... The 3rd is 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, a = 2, b = 3, c = 4
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** The ugly numbers are 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12... The 4th is 6.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5, a = 2, b = 11, c = 13
+
+**Output:** 10
+
+**Explanation:** The ugly numbers are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13... The 5th is 10.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n, a, b, c <= 109
+* 1 <= a * b * c <= 1018
+* It is guaranteed that the result will be in range [1, 2 * 109].
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private fun getLcm(a: Long, b: Long): Long {
+ var mx = a
+ var mn = b
+ if (a < b) {
+ mx = b
+ mn = a
+ }
+ while (mn != 0L) {
+ val tmp = mn
+ mn = mx % mn
+ mx = tmp
+ }
+ return a * b / mx
+ }
+
+ fun nthUglyNumber(n: Int, a: Int, b: Int, c: Int): Int {
+ val ab = getLcm(a.toLong(), b.toLong())
+ val ac = getLcm(a.toLong(), c.toLong())
+ val bc = getLcm(b.toLong(), c.toLong())
+ val abc = getLcm(a.toLong(), bc)
+ var left: Long = 1
+ var right: Long = 2000000001
+ if (a != 0 && b != 0 && c != 0 && bc != 0L) {
+ while (left < right) {
+ val mid = left + (right - left) / 2
+ if (mid / a + mid / b + mid / c - mid / ab - mid / ac - mid / bc + mid / abc >= n) {
+ right = mid
+ } else {
+ left = mid + 1
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return left.toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1202_smallest_string_with_swaps/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1202_smallest_string_with_swaps/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2bd856b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1202_smallest_string_with_swaps/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1202\. Smallest String With Swaps
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a string `s`, and an array of pairs of indices in the string `pairs` where `pairs[i] = [a, b]` indicates 2 indices(0-indexed) of the string.
+
+You can swap the characters at any pair of indices in the given `pairs` **any number of times**.
+
+Return the lexicographically smallest string that `s` can be changed to after using the swaps.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "dcab", pairs = \[\[0,3],[1,2]]
+
+**Output:** "bacd" **Explaination:**
+
+Swap s[0] and s[3], s = "bcad"
+
+Swap s[1] and s[2], s = "bacd"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "dcab", pairs = \[\[0,3],[1,2],[0,2]]
+
+**Output:** "abcd" **Explaination:**
+
+Swap s[0] and s[3], s = "bcad"
+
+Swap s[0] and s[2], s = "acbd"
+
+Swap s[1] and s[2], s = "abcd"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "cba", pairs = \[\[0,1],[1,2]]
+
+**Output:** "abc" **Explaination:**
+
+Swap s[0] and s[1], s = "bca"
+
+Swap s[1] and s[2], s = "bac"
+
+Swap s[0] and s[1], s = "abc"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 10^5`
+* `0 <= pairs.length <= 10^5`
+* `0 <= pairs[i][0], pairs[i][1] < s.length`
+* `s` only contains lower case English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun smallestStringWithSwaps(s: String, pairs: List>): String {
+ val uf = UF(s.length)
+ for (p in pairs) {
+ uf.union(p[0], p[1])
+ }
+ val freqMapPerRoot: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ for (i in s.indices) {
+ freqMapPerRoot.computeIfAbsent(uf.find(i)) { IntArray(26) }[s[i].code - 'a'.code]++
+ }
+ val ans = CharArray(s.length)
+ for (i in ans.indices) {
+ val css = freqMapPerRoot[uf.find(i)]
+ for (j in css!!.indices) {
+ if (css[j] > 0) {
+ ans[i] = (j + 'a'.code).toChar()
+ css[j]--
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return String(ans)
+ }
+
+ internal class UF(n: Int) {
+ var root: IntArray
+ var rank: IntArray
+
+ init {
+ root = IntArray(n)
+ rank = IntArray(n)
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ root[i] = i
+ rank[i] = 1
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun find(u: Int): Int {
+ if (u == root[u]) {
+ return u
+ }
+ root[u] = find(root[u])
+ return root[u]
+ }
+
+ fun union(u: Int, v: Int) {
+ val ru = find(root[u])
+ val rv = find(root[v])
+ if (ru != rv) {
+ if (rank[ru] < rank[rv]) {
+ root[ru] = root[rv]
+ } else if (rank[ru] > rank[rv]) {
+ root[rv] = root[ru]
+ } else {
+ root[rv] = root[ru]
+ rank[ru]++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1203_sort_items_by_groups_respecting_dependencies/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1203_sort_items_by_groups_respecting_dependencies/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..19af66f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1203_sort_items_by_groups_respecting_dependencies/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
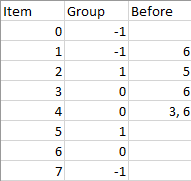
+## 1203\. Sort Items by Groups Respecting Dependencies
+
+Hard
+
+There are `n` items each belonging to zero or one of `m` groups where `group[i]` is the group that the `i`\-th item belongs to and it's equal to `-1` if the `i`\-th item belongs to no group. The items and the groups are zero indexed. A group can have no item belonging to it.
+
+Return a sorted list of the items such that:
+
+* The items that belong to the same group are next to each other in the sorted list.
+* There are some relations between these items where `beforeItems[i]` is a list containing all the items that should come before the `i`\-th item in the sorted array (to the left of the `i`\-th item).
+
+Return any solution if there is more than one solution and return an **empty list** if there is no solution.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = \[\[],[6],[5],[6],[3,6],[],[],[]]
+
+**Output:** [6,3,4,1,5,2,0,7]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = \[\[],[6],[5],[6],[3],[],[4],[]]
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Explanation:** This is the same as example 1 except that 4 needs to be before 6 in the sorted list.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= m <= n <= 3 * 104
+* `group.length == beforeItems.length == n`
+* `-1 <= group[i] <= m - 1`
+* `0 <= beforeItems[i].length <= n - 1`
+* `0 <= beforeItems[i][j] <= n - 1`
+* `i != beforeItems[i][j]`
+* `beforeItems[i] `does not contain duplicates elements.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun sortItems(n: Int, m: Int, group: IntArray, beforeItems: List>): IntArray {
+ var totalGroups = m
+ val indexGroupMap: MutableMap> = HashMap()
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ if (group[i] == -1) {
+ group[i] = totalGroups
+ indexGroupMap[totalGroups] = ArrayList()
+ indexGroupMap[totalGroups]!!.add(i)
+ totalGroups++
+ } else {
+ indexGroupMap.putIfAbsent(group[i], ArrayList())
+ indexGroupMap[group[i]]!!.add(i)
+ }
+ }
+ val externalInMap = IntArray(totalGroups)
+ val internalInMap = IntArray(n)
+ val externalGraph: MutableMap> = HashMap()
+ val internalGraph: MutableMap> = HashMap()
+ for (i in beforeItems.indices) {
+ if (beforeItems[i].isNotEmpty()) {
+ val groupNumber = group[i]
+ for (j in beforeItems[i].indices) {
+ val prevItem = beforeItems[i][j]
+ val prevGroupNumber = group[prevItem]
+ if (groupNumber == prevGroupNumber) {
+ internalGraph.putIfAbsent(prevItem, ArrayList())
+ internalGraph[prevItem]!!.add(i)
+ internalInMap[i]++
+ } else {
+ externalGraph.putIfAbsent(prevGroupNumber, ArrayList())
+ externalGraph[prevGroupNumber]!!.add(groupNumber)
+ externalInMap[groupNumber]++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ val externalQueue: Queue = LinkedList()
+ for (i in 0 until totalGroups) {
+ if (externalInMap[i] == 0) {
+ externalQueue.offer(i)
+ }
+ }
+ val res = IntArray(n)
+ var resIndex = 0
+ while (externalQueue.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val curGroup = externalQueue.poll()
+ val internalQueue: Queue = LinkedList()
+ if (indexGroupMap.containsKey(curGroup)) {
+ for (item in indexGroupMap[curGroup]!!) {
+ if (internalInMap[item] == 0) {
+ internalQueue.offer(item)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ while (internalQueue.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val curItem = internalQueue.poll()
+ res[resIndex] = curItem
+ resIndex++
+ if (internalGraph.containsKey(curItem)) {
+ for (nextItemInGroup in internalGraph[curItem]!!) {
+ internalInMap[nextItemInGroup]--
+ if (internalInMap[nextItemInGroup] == 0) {
+ internalQueue.offer(nextItemInGroup)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (externalGraph.containsKey(curGroup)) {
+ for (nextGroup in externalGraph[curGroup]!!) {
+ externalInMap[nextGroup]--
+ if (externalInMap[nextGroup] == 0) {
+ externalQueue.offer(nextGroup)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return if (resIndex == n) res else intArrayOf()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1204_last_person_to_fit_in_the_bus/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1204_last_person_to_fit_in_the_bus/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..74476f58
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1204_last_person_to_fit_in_the_bus/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1204\. Last Person to Fit in the Bus
+
+Medium
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Queue`
+
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | person_id | int |
+ | person_name | varchar |
+ | weight | int |
+ | turn | int |
+ +-------------+---------+
+
+person_id is the primary key column for this table. This table has the information about all people waiting for a bus. The person_id and turn columns will contain all numbers from 1 to n, where n is the number of rows in the table. turn determines the order of which the people will board the bus, where turn=1 denotes the first person to board and turn=n denotes the last person to board. weight is the weight of the person in kilograms.
+
+There is a queue of people waiting to board a bus. However, the bus has a weight limit of `1000` **kilograms**, so there may be some people who cannot board.
+
+Write an SQL query to find the `person_name` of the **last person** that can fit on the bus without exceeding the weight limit. The test cases are generated such that the first person does not exceed the weight limit.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** Queue table:
+
+ +-----------+-------------+--------+------+
+ | person_id | person_name | weight | turn |
+ +-----------+-------------+--------+------+
+ | 5 | Alice | 250 | 1 |
+ | 4 | Bob | 175 | 5 |
+ | 3 | Alex | 350 | 2 |
+ | 6 | John Cena | 400 | 3 |
+ | 1 | Winston | 500 | 6 |
+ | 2 | Marie | 200 | 4 |
+ +-----------+-------------+--------+------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +-------------+
+ | person_name |
+ +-------------+
+ | John Cena |
+ +-------------+
+
+**Explanation:** The folowing table is ordered by the turn for simplicity.
+
+ +------+----+-----------+--------+--------------+
+ | Turn | ID | Name | Weight | Total Weight |
+ +------+----+-----------+--------+--------------+
+ | 1 | 5 | Alice | 250 | 250 |
+ | 2 | 3 | Alex | 350 | 600 |
+ | 3 | 6 | John Cena | 400 | 1000 | (last person to board)
+ | 4 | 2 | Marie | 200 | 1200 | (cannot board)
+ | 5 | 4 | Bob | 175 | ___ |
+ | 6 | 1 | Winston | 500 | ___ |
+ +------+----+-----------+--------+--------------+
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+WITH ctx AS(
+SELECT person_name, SUM(weight) OVER(ORDER BY turn ASC) AS running_sum
+FROM queue
+)
+
+SELECT person_name
+FROM ctx
+WHERE running_sum <= 1000
+ORDER BY running_sum DESC
+LIMIT 1;
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1206_design_skiplist/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1206_design_skiplist/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..faf7b6ac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1206_design_skiplist/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1206\. Design Skiplist
+
+Hard
+
+Design a **Skiplist** without using any built-in libraries.
+
+A **skiplist** is a data structure that takes `O(log(n))` time to add, erase and search. Comparing with treap and red-black tree which has the same function and performance, the code length of Skiplist can be comparatively short and the idea behind Skiplists is just simple linked lists.
+
+For example, we have a Skiplist containing `[30,40,50,60,70,90]` and we want to add `80` and `45` into it. The Skiplist works this way:
+
+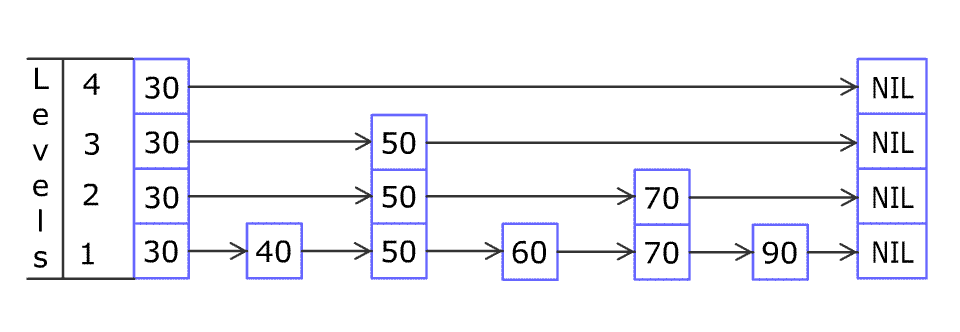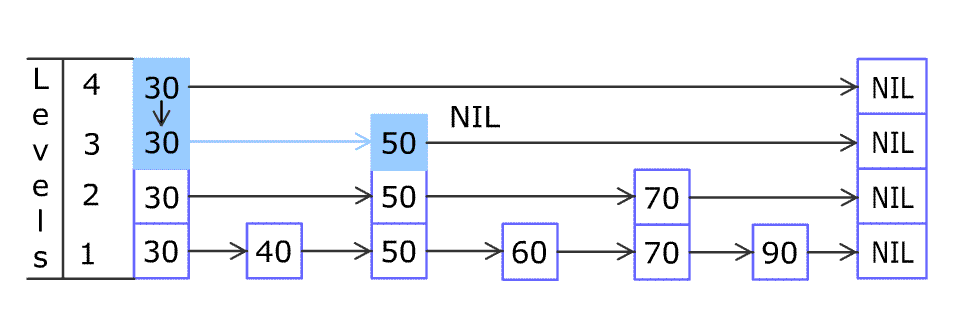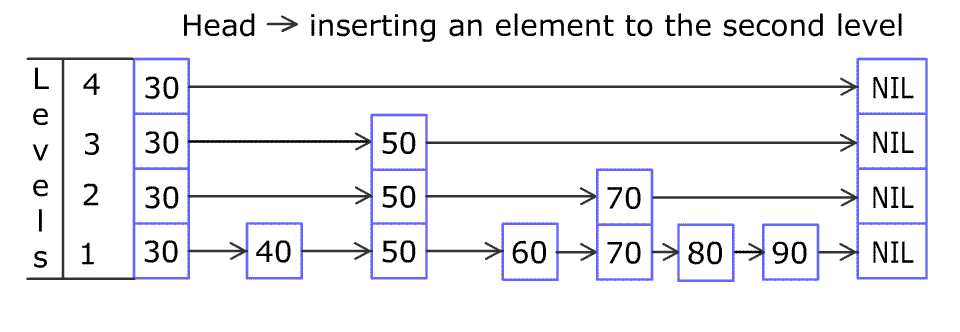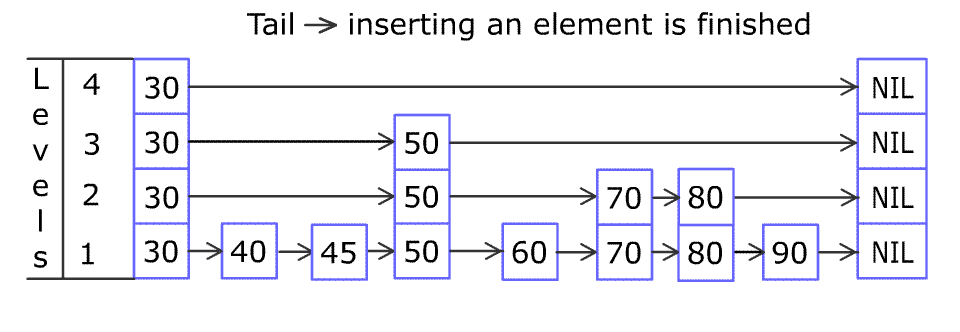
+Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via [Wikimedia Commons](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Skip_list_add_element-en.gif "Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons")
+
+You can see there are many layers in the Skiplist. Each layer is a sorted linked list. With the help of the top layers, add, erase and search can be faster than `O(n)`. It can be proven that the average time complexity for each operation is `O(log(n))` and space complexity is `O(n)`.
+
+See more about Skiplist: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip\_list](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list)
+
+Implement the `Skiplist` class:
+
+* `Skiplist()` Initializes the object of the skiplist.
+* `bool search(int target)` Returns `true` if the integer `target` exists in the Skiplist or `false` otherwise.
+* `void add(int num)` Inserts the value `num` into the SkipList.
+* `bool erase(int num)` Removes the value `num` from the Skiplist and returns `true`. If `num` does not exist in the Skiplist, do nothing and return `false`. If there exist multiple `num` values, removing any one of them is fine.
+
+Note that duplicates may exist in the Skiplist, your code needs to handle this situation.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input**
+
+["Skiplist", "add", "add", "add", "search", "add", "search", "erase", "erase", "search"]
+
+[[], [1], [2], [3], [0], [4], [1], [0], [1], [1]]
+
+**Output:** [null, null, null, null, false, null, true, false, true, false]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist();
+ skiplist.add(1);
+ skiplist.add(2);
+ skiplist.add(3);
+ skiplist.search(0); // return False
+ skiplist.add(4);
+ skiplist.search(1); // return True
+ skiplist.erase(0); // return False, 0 is not in skiplist.
+ skiplist.erase(1); // return True
+ skiplist.search(1); // return False, 1 has already been erased.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= num, target <= 2 * 104
+* At most 5 * 104 calls will be made to `search`, `add`, and `erase`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING", "kotlin:S2245")
+class Skiplist @JvmOverloads constructor(size: Int = INIT_CAPACITY) {
+ private val minBoundary: Int
+ private val head: Node
+ private var headCapacity: Int
+ private var headLevel = 0
+
+ class Node internal constructor(val `val`: Int, level: Int) {
+ var next: Array
+
+ init {
+ next = arrayOfNulls(level)
+ }
+ }
+
+ init {
+ var size = size
+ require(size != 0) { "size should be greater than 0" }
+ if (size < INIT_CAPACITY) {
+ size = INIT_CAPACITY
+ }
+ minBoundary = size / 2
+ headCapacity = size
+ head = Node(0, size)
+ }
+
+ fun search(target: Int): Boolean {
+ var curr: Node? = head
+ for (i in headLevel - 1 downTo 0) {
+ while (curr!!.next[i] != null) {
+ val cmp = target - curr.next[i]!!.`val`
+ curr = if (cmp < 0) {
+ break
+ } else if (cmp > 0) {
+ curr.next[i]
+ } else {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ fun add(num: Int) {
+ val update = arrayOfNulls(headLevel + 1)
+ update[headLevel] = head
+ buildUpdate(num, update)
+ val level = randomLevel
+ if (level > headLevel) {
+ if (headLevel == headCapacity) {
+ resizeHead(2 * headCapacity)
+ }
+ headLevel++
+ }
+ val x = Node(num, level)
+ for (i in 0 until level) {
+ val n = update[i]!!.next[i]
+ update[i]!!.next[i] = x
+ x.next[i] = n
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun erase(num: Int): Boolean {
+ if (headLevel == 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ val update = arrayOfNulls(headLevel)
+ buildUpdate(num, update)
+ if (update[0]!!.next[0] == null || update[0]!!.next[0]!!.`val` != num) {
+ return false
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until headLevel) {
+ if (update[i]!!.next[i] == null || update[i]!!.next[i]!!.`val` != num) {
+ break
+ }
+ update[i]!!.next[i] = update[i]!!.next[i]!!.next[i]
+ }
+ if (head.next[headLevel - 1] == null && --headLevel >= minBoundary && headLevel == headCapacity / 4) {
+ resizeHead(headCapacity / 2)
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private fun buildUpdate(x: Int, update: Array) {
+ var curr: Node? = head
+ for (i in headLevel - 1 downTo 0) {
+ while (curr!!.next[i] != null && curr.next[i]!!.`val` < x) {
+ curr = curr.next[i]
+ }
+ update[i] = curr
+ }
+ }
+
+ private val randomLevel: Int
+ get() {
+ val maxLevel = 14
+ var level = 1
+ val limit = maxLevel.coerceAtMost(headLevel + 1)
+ val p = 0.5
+ while (Math.random() < p && level < limit) {
+ level++
+ }
+ return level
+ }
+
+ private fun resizeHead(size: Int) {
+ val copy = arrayOfNulls(size)
+ System.arraycopy(head.next, 0, copy, 0, headLevel)
+ head.next = copy
+ headCapacity = size
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val INIT_CAPACITY = 8
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1207_unique_number_of_occurrences/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1207_unique_number_of_occurrences/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a7a08bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1207_unique_number_of_occurrences/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1207\. Unique Number of Occurrences
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array of integers `arr`, return `true` if the number of occurrences of each value in the array is **unique**, or `false` otherwise.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,2,1,1,3]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** The value 1 has 3 occurrences, 2 has 2 and 3 has 1. No two values have the same number of occurrences.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [-3,0,1,-3,1,1,1,-3,10,0]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= arr.length <= 1000`
+* `-1000 <= arr[i] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun uniqueOccurrences(arr: IntArray): Boolean {
+ val map: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ for (j in arr) {
+ if (map.containsKey(j)) {
+ map[j] = map[j]!! + 1
+ } else {
+ map[j] = 1
+ }
+ }
+ // map for check unique number of count
+ val uni: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ for (`val` in map.values) {
+ if (uni.containsKey(`val`)) {
+ return false
+ } else {
+ uni[`val`] = 1
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1208_get_equal_substrings_within_budget/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1208_get_equal_substrings_within_budget/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fcff4dde
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1208_get_equal_substrings_within_budget/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1208\. Get Equal Substrings Within Budget
+
+Medium
+
+You are given two strings `s` and `t` of the same length and an integer `maxCost`.
+
+You want to change `s` to `t`. Changing the ith character of `s` to ith character of `t` costs `|s[i] - t[i]|` (i.e., the absolute difference between the ASCII values of the characters).
+
+Return _the maximum length of a substring of_ `s` _that can be changed to be the same as the corresponding substring of_ `t` _with a cost less than or equal to_ `maxCost`. If there is no substring from `s` that can be changed to its corresponding substring from `t`, return `0`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abcd", t = "bcdf", maxCost = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** "abc" of s can change to "bcd". That costs 3, so the maximum length is 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abcd", t = "cdef", maxCost = 3
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** Each character in s costs 2 to change to character in t, so the maximum length is 1.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abcd", t = "acde", maxCost = 0
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** You cannot make any change, so the maximum length is 1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `t.length == s.length`
+* 0 <= maxCost <= 106
+* `s` and `t` consist of only lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import kotlin.math.abs
+
+class Solution {
+ fun equalSubstring(s: String, t: String, maxCost: Int): Int {
+ var start = 0
+ var end = 0
+ var currCost = 0
+ var maxLength = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ while (end < s.length) {
+ currCost += abs(s[end].code - t[end].code)
+ while (currCost > maxCost) {
+ currCost -= abs(s[start].code - t[start].code)
+ start++
+ }
+ if (end - start + 1 > maxLength) {
+ maxLength = (end - start + 1).coerceAtLeast(maxLength)
+ }
+ end++
+ }
+ return maxLength
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1209_remove_all_adjacent_duplicates_in_string_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1209_remove_all_adjacent_duplicates_in_string_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3273e251
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1209_remove_all_adjacent_duplicates_in_string_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1209\. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates in String II
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a string `s` and an integer `k`, a `k` **duplicate removal** consists of choosing `k` adjacent and equal letters from `s` and removing them, causing the left and the right side of the deleted substring to concatenate together.
+
+We repeatedly make `k` **duplicate removals** on `s` until we no longer can.
+
+Return the final string after all such duplicate removals have been made. It is guaranteed that the answer is unique.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abcd", k = 2
+
+**Output:** "abcd"
+
+**Explanation:** There's nothing to delete.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "deeedbbcccbdaa", k = 3
+
+**Output:** "aa"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+First delete "eee" and "ccc", get "ddbbbdaa"
+
+Then delete "bbb", get "dddaa"
+
+Finally delete "ddd", get "aa"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "pbbcggttciiippooaais", k = 2
+
+**Output:** "ps"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* 2 <= k <= 104
+* `s` only contains lower case English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun removeDuplicates(s: String, k: Int): String {
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ var dupCount = 0
+ for (i in s.indices) {
+ if (sb.isNotEmpty() && sb[sb.length - 1] == s[i]) {
+ dupCount++
+ } else {
+ dupCount = 1
+ }
+ sb.append(s[i])
+ if (dupCount == k) {
+ sb.setLength(sb.length - k)
+ if (i + 1 < s.length) {
+ dupCount = 0
+ for (j in sb.length - 1 downTo 0) {
+ if (sb[j] == s[i + 1]) {
+ dupCount++
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return sb.toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1210_minimum_moves_to_reach_target_with_rotations/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1210_minimum_moves_to_reach_target_with_rotations/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d0ea345a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1210_minimum_moves_to_reach_target_with_rotations/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1210\. Minimum Moves to Reach Target with Rotations
+
+Hard
+
+In an `n*n` grid, there is a snake that spans 2 cells and starts moving from the top left corner at `(0, 0)` and `(0, 1)`. The grid has empty cells represented by zeros and blocked cells represented by ones. The snake wants to reach the lower right corner at `(n-1, n-2)` and `(n-1, n-1)`.
+
+In one move the snake can:
+
+* Move one cell to the right if there are no blocked cells there. This move keeps the horizontal/vertical position of the snake as it is.
+* Move down one cell if there are no blocked cells there. This move keeps the horizontal/vertical position of the snake as it is.
+* Rotate clockwise if it's in a horizontal position and the two cells under it are both empty. In that case the snake moves from `(r, c)` and `(r, c+1)` to `(r, c)` and `(r+1, c)`.
+ 
+* Rotate counterclockwise if it's in a vertical position and the two cells to its right are both empty. In that case the snake moves from `(r, c)` and `(r+1, c)` to `(r, c)` and `(r, c+1)`.
+ 
+
+Return the minimum number of moves to reach the target.
+
+If there is no way to reach the target, return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:**
+
+ grid = [ [0,0,0,0,0,1],
+ [1,1,0,0,1,0],
+ [0,0,0,0,1,1],
+ [0,0,1,0,1,0],
+ [0,1,1,0,0,0],
+ [0,1,1,0,0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 11
+
+**Explanation:** One possible solution is [right, right, rotate clockwise, right, down, down, down, down, rotate counterclockwise, right, down].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ grid = [ [0,0,1,1,1,1],
+ [0,0,0,0,1,1],
+ [1,1,0,0,0,1],
+ [1,1,1,0,0,1],
+ [1,1,1,0,0,1],
+ [1,1,1,0,0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n <= 100`
+* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 1`
+* It is guaranteed that the snake starts at empty cells.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Objects
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumMoves(grid: Array): Int {
+ val n = grid.size
+ val visited = Array(n) { IntArray(n) }
+ val bq: Queue = LinkedList()
+ bq.offer(intArrayOf(0, 0, 1))
+ visited[0][0] = visited[0][0] or 1
+ var level = 0
+ while (bq.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val levelSize = bq.size
+ for (l in 0 until levelSize) {
+ val cur = bq.poll()
+ val xtail = Objects.requireNonNull(cur)[0]
+ val ytail = cur[1]
+ val dir = cur[2]
+ if (xtail == n - 1 && ytail == n - 2 && dir == 1) {
+ return level
+ }
+ val xhead = xtail + if (dir == 1) 0 else 1
+ val yhead = ytail + if (dir == 1) 1 else 0
+ if (dir == 2) {
+ if (ytail + 1 < n && grid[xtail][ytail + 1] != 1 && grid[xtail + 1][ytail + 1] != 1) {
+ if (visited[xtail][ytail] and 1 == 0) {
+ bq.offer(intArrayOf(xtail, ytail, 1))
+ visited[xtail][ytail] = visited[xtail][ytail] or 1
+ }
+ if (visited[xtail][ytail + 1] and 2 == 0) {
+ bq.offer(intArrayOf(xtail, ytail + 1, 2))
+ visited[xtail][ytail + 1] = visited[xtail][ytail + 1] or 2
+ }
+ }
+ if (xhead + 1 < n && grid[xhead + 1][yhead] != 1 && visited[xhead][yhead] and 2 == 0) {
+ bq.offer(intArrayOf(xhead, yhead, 2))
+ visited[xhead][yhead] = visited[xhead][yhead] or 2
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (xtail + 1 < n && grid[xtail + 1][ytail] != 1 && grid[xtail + 1][ytail + 1] != 1) {
+ if (visited[xtail][ytail] and 2 == 0) {
+ bq.offer(intArrayOf(xtail, ytail, 2))
+ visited[xtail][ytail] = visited[xtail][ytail] or 2
+ }
+ if (visited[xtail + 1][ytail] and 1 == 0) {
+ bq.offer(intArrayOf(xtail + 1, ytail, 1))
+ visited[xtail + 1][ytail] = visited[xtail + 1][ytail] or 1
+ }
+ }
+ if (yhead + 1 < n && grid[xhead][yhead + 1] != 1 && visited[xhead][yhead] and 1 == 0) {
+ bq.offer(intArrayOf(xhead, yhead, 1))
+ visited[xhead][yhead] = visited[xhead][yhead] or 1
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ level += 1
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1211_queries_quality_and_percentage/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1211_queries_quality_and_percentage/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fc9879ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1211_queries_quality_and_percentage/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1211\. Queries Quality and Percentage
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Queries`
+
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | query_name | varchar |
+ | result | varchar |
+ | position | int |
+ | rating | int |
+ +-------------+---------+
+
+There is no primary key for this table, it may have duplicate rows. This table contains information collected from some queries on a database. The `position` column has a value from **1** to **500**. The `rating` column has a value from **1** to **5**. Query with `rating` less than 3 is a poor query.
+
+We define query `quality` as:
+
+> The average of the ratio between query rating and its position.
+
+We also define `poor query percentage` as:
+
+> The percentage of all queries with rating less than 3.
+
+Write an SQL query to find each `query_name`, the `quality` and `poor_query_percentage`.
+
+Both `quality` and `poor_query_percentage` should be **rounded to 2 decimal places**.
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** Queries table:
+
+ +------------+-------------------+----------+--------+
+ | query_name | result | position | rating |
+ +------------+-------------------+----------+--------+
+ | Dog | Golden Retriever | 1 | 5 |
+ | Dog | German Shepherd | 2 | 5 |
+ | Dog | Mule | 200 | 1 |
+ | Cat | Shirazi | 5 | 2 |
+ | Cat | Siamese | 3 | 3 |
+ | Cat | Sphynx | 7 | 4 |
+ +------------+-------------------+----------+--------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +------------+---------+-----------------------+
+ | query_name | quality | poor_query_percentage |
+ +------------+---------+-----------------------+
+ | Dog | 2.50 | 33.33 |
+ | Cat | 0.66 | 33.33 |
+ +------------+---------+-----------------------+
+
+**Explanation:** Dog queries quality is ((5 / 1) + (5 / 2) + (1 / 200)) / 3 = 2.50 Dog queries poor_ query_percentage is (1 / 3) * 100 = 33.33 Cat queries quality equals ((2 / 5) + (3 / 3) + (4 / 7)) / 3 = 0.66 Cat queries poor_ query_percentage is (1 / 3) * 100 = 33.33
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+select query_name,
+ROUND(AVG(rating / position), 2) AS quality,
+round(SUM(rating<3)/count(query_name)*100,2) as poor_query_percentage
+from queries
+group by query_name;
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1217_minimum_cost_to_move_chips_to_the_same_position/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1217_minimum_cost_to_move_chips_to_the_same_position/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d2547437
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1217_minimum_cost_to_move_chips_to_the_same_position/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1217\. Minimum Cost to Move Chips to The Same Position
+
+Easy
+
+We have `n` chips, where the position of the ith chip is `position[i]`.
+
+We need to move all the chips to **the same position**. In one step, we can change the position of the ith chip from `position[i]` to:
+
+* `position[i] + 2` or `position[i] - 2` with `cost = 0`.
+* `position[i] + 1` or `position[i] - 1` with `cost = 1`.
+
+Return _the minimum cost_ needed to move all the chips to the same position.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** position = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** First step: Move the chip at position 3 to position 1 with cost = 0. Second step: Move the chip at position 2 to position 1 with cost = 1. Total cost is 1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** position = [2,2,2,3,3]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** We can move the two chips at position 3 to position 2. Each move has cost = 1. The total cost = 2.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** position = [1,1000000000]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= position.length <= 100`
+* `1 <= position[i] <= 10^9`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minCostToMoveChips(position: IntArray): Int {
+ var chipsAtOddPosition = 0
+ var chipsAtEvenPosition = 0
+ for (j in position) {
+ if (j % 2 == 0) {
+ chipsAtEvenPosition++
+ } else {
+ chipsAtOddPosition++
+ }
+ }
+ return Math.min(chipsAtEvenPosition, chipsAtOddPosition)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1218_longest_arithmetic_subsequence_of_given_difference/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1218_longest_arithmetic_subsequence_of_given_difference/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..77072752
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1218_longest_arithmetic_subsequence_of_given_difference/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1218\. Longest Arithmetic Subsequence of Given Difference
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `arr` and an integer `difference`, return the length of the longest subsequence in `arr` which is an arithmetic sequence such that the difference between adjacent elements in the subsequence equals `difference`.
+
+A **subsequence** is a sequence that can be derived from `arr` by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3,4], difference = 1
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The longest arithmetic subsequence is [1,2,3,4].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,3,5,7], difference = 1
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The longest arithmetic subsequence is any single element.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,5,7,8,5,3,4,2,1], difference = -2
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The longest arithmetic subsequence is [7,5,3,1].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= arr.length <= 105
+* -104 <= arr[i], difference <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun longestSubsequence(arr: IntArray, difference: Int): Int {
+ var res = 0
+ val dp = IntArray(20001)
+ for (j in arr) {
+ val cur = j + 10000
+ val last = j - difference + 10000
+ if (last < 0 || last > 20000) {
+ dp[cur] = Math.max(dp[cur], 1)
+ } else {
+ dp[cur] = Math.max(dp[cur], dp[last] + 1)
+ }
+ res = Math.max(res, dp[cur])
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1219_path_with_maximum_gold/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1219_path_with_maximum_gold/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f0853fb6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1219_path_with_maximum_gold/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1219\. Path with Maximum Gold
+
+Medium
+
+In a gold mine `grid` of size `m x n`, each cell in this mine has an integer representing the amount of gold in that cell, `0` if it is empty.
+
+Return the maximum amount of gold you can collect under the conditions:
+
+* Every time you are located in a cell you will collect all the gold in that cell.
+* From your position, you can walk one step to the left, right, up, or down.
+* You can't visit the same cell more than once.
+* Never visit a cell with `0` gold.
+* You can start and stop collecting gold from **any** position in the grid that has some gold.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[0,6,0],[5,8,7],[0,9,0]]
+
+**Output:** 24
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ [[0,6,0],
+ [5,8,7],
+ [0,9,0]]
+ Path to get the maximum gold, 9 -> 8 -> 7.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,0,7],[2,0,6],[3,4,5],[0,3,0],[9,0,20]]
+
+**Output:** 28
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ [[1,0,7],
+ [2,0,6],
+ [3,4,5],
+ [0,3,0],
+ [9,0,20]]
+ Path to get the maximum gold, 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 15`
+* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 100`
+* There are at most **25** cells containing gold.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private var maxGold = 0
+ fun getMaximumGold(grid: Array): Int {
+ for (i in grid.indices) {
+ for (j in grid[0].indices) {
+ if (grid[i][j] != 0) {
+ val g = grid[i][j]
+ grid[i][j] = 0
+ gold(grid, i, j, g)
+ grid[i][j] = g
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return maxGold
+ }
+
+ private fun gold(grid: Array, row: Int, col: Int, gold: Int) {
+ if (gold > maxGold) {
+ maxGold = gold
+ }
+ if (row > 0 && grid[row - 1][col] != 0) {
+ val currGold = grid[row - 1][col]
+ grid[row - 1][col] = 0
+ gold(grid, row - 1, col, gold + currGold)
+ grid[row - 1][col] = currGold
+ }
+ if (col > 0 && grid[row][col - 1] != 0) {
+ val currGold = grid[row][col - 1]
+ grid[row][col - 1] = 0
+ gold(grid, row, col - 1, gold + currGold)
+ grid[row][col - 1] = currGold
+ }
+ if (row < grid.size - 1 && grid[row + 1][col] != 0) {
+ // flag=false;
+ val currGold = grid[row + 1][col]
+ grid[row + 1][col] = 0
+ gold(grid, row + 1, col, gold + currGold)
+ grid[row + 1][col] = currGold
+ }
+ if (col < grid[0].size - 1 && grid[row][col + 1] != 0) {
+ val currGold = grid[row][col + 1]
+ grid[row][col + 1] = 0
+ gold(grid, row, col + 1, gold + currGold)
+ grid[row][col + 1] = currGold
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1220_count_vowels_permutation/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1220_count_vowels_permutation/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dba325d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1220_count_vowels_permutation/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1220\. Count Vowels Permutation
+
+Hard
+
+Given an integer `n`, your task is to count how many strings of length `n` can be formed under the following rules:
+
+* Each character is a lower case vowel (`'a'`, `'e'`, `'i'`, `'o'`, `'u'`)
+* Each vowel `'a'` may only be followed by an `'e'`.
+* Each vowel `'e'` may only be followed by an `'a'` or an `'i'`.
+* Each vowel `'i'` **may not** be followed by another `'i'`.
+* Each vowel `'o'` may only be followed by an `'i'` or a `'u'`.
+* Each vowel `'u'` may only be followed by an `'a'.`
+
+Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo `10^9 + 7.`
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** All possible strings are: "a", "e", "i" , "o" and "u".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2
+
+**Output:** 10
+
+**Explanation:** All possible strings are: "ae", "ea", "ei", "ia", "ie", "io", "iu", "oi", "ou" and "ua".
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5
+
+**Output:** 68
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 2 * 10^4`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun countVowelPermutation(n: Int): Int {
+ var n = n
+ val mod = 1e9.toInt() + 7
+ var prevA = 1
+ var prevE = 1
+ var prevI = 1
+ var prevO = 1
+ var prevU = 1
+ while (n-- > 1) {
+ val a = ((prevE + prevI) % mod + prevU) % mod
+ val e = (prevA + prevI) % mod
+ val i = (prevE + prevO) % mod
+ val o = prevI
+ val u = (prevI + prevO) % mod
+ prevA = a
+ prevE = e
+ prevI = i
+ prevO = o
+ prevU = u
+ }
+ return ((((prevA + prevE) % mod + prevI) % mod + prevO) % mod + prevU) % mod
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1221_split_a_string_in_balanced_strings/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1221_split_a_string_in_balanced_strings/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..05463f14
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1221_split_a_string_in_balanced_strings/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1221\. Split a String in Balanced Strings
+
+Easy
+
+**Balanced** strings are those that have an equal quantity of `'L'` and `'R'` characters.
+
+Given a **balanced** string `s`, split it in the maximum amount of balanced strings.
+
+Return _the maximum amount of split **balanced** strings_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "RLRRLLRLRL"
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** s can be split into "RL", "RRLL", "RL", "RL", each substring contains same number of 'L' and 'R'.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "RLLLLRRRLR"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** s can be split into "RL", "LLLRRR", "LR", each substring contains same number of 'L' and 'R'.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "LLLLRRRR"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** s can be split into "LLLLRRRR".
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 1000`
+* `s[i]` is either `'L'` or `'R'`.
+* `s` is a **balanced** string.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun balancedStringSplit(s: String): Int {
+ var i = 0
+ var balancedCount = 0
+ var lCount = 0
+ var rCount = 0
+ while (i < s.length) {
+ if (s[i] == 'L') {
+ lCount++
+ } else {
+ rCount++
+ }
+ i++
+ if (lCount != 0 && lCount == rCount) {
+ lCount = 0
+ rCount = 0
+ balancedCount++
+ }
+ }
+ return balancedCount
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1222_queens_that_can_attack_the_king/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1222_queens_that_can_attack_the_king/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8fc84a82
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1222_queens_that_can_attack_the_king/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1222\. Queens That Can Attack the King
+
+Medium
+
+On an **8x8** chessboard, there can be multiple Black Queens and one White King.
+
+Given an array of integer coordinates `queens` that represents the positions of the Black Queens, and a pair of coordinates `king` that represent the position of the White King, return the coordinates of all the queens (in any order) that can attack the King.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** queens = \[\[0,1],[1,0],[4,0],[0,4],[3,3],[2,4]], king = [0,0]
+
+**Output:** [[0,1],[1,0],[3,3]]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The queen at [0,1] can attack the king cause they're in the same row.
+
+The queen at [1,0] can attack the king cause they're in the same column.
+
+The queen at [3,3] can attack the king cause they're in the same diagnal.
+
+The queen at [0,4] can't attack the king cause it's blocked by the queen at [0,1].
+
+The queen at [4,0] can't attack the king cause it's blocked by the queen at [1,0].
+
+The queen at [2,4] can't attack the king cause it's not in the same row/column/diagnal as the king.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** queens = \[\[0,0],[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[3,5],[4,4],[4,5]], king = [3,3]
+
+**Output:** [[2,2],[3,4],[4,4]]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** queens = \[\[5,6],[7,7],[2,1],[0,7],[1,6],[5,1],[3,7],[0,3],[4,0],[1,2],[6,3],[5,0],[0,4],[2,2],[1,1],[6,4],[5,4],[0,0],[2,6],[4,5],[5,2],[1,4],[7,5],[2,3],[0,5],[4,2],[1,0],[2,7],[0,1],[4,6],[6,1],[0,6],[4,3],[1,7]], king = [3,4]
+
+**Output:** [[2,3],[1,4],[1,6],[3,7],[4,3],[5,4],[4,5]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= queens.length <= 63`
+* `queens[i].length == 2`
+* `0 <= queens[i][j] < 8`
+* `king.length == 2`
+* `0 <= king[0], king[1] < 8`
+* At most one piece is allowed in a cell.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun queensAttacktheKing(queens: Array, king: IntArray): List> {
+ val result: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ val queensLoc: MutableMap> = HashMap()
+ for (queen in queens) {
+ val queensY = queensLoc.getOrDefault(queen[0], HashSet())
+ queensY.add(queen[1])
+ queensLoc[queen[0]] = queensY
+ }
+ dfs(queensLoc, king[0] - 1, king[1], result, "n")
+ dfs(queensLoc, king[0] + 1, king[1], result, "s")
+ dfs(queensLoc, king[0], king[1] + 1, result, "e")
+ dfs(queensLoc, king[0], king[1] - 1, result, "w")
+ dfs(queensLoc, king[0] - 1, king[1] - 1, result, "nw")
+ dfs(queensLoc, king[0] - 1, king[1] + 1, result, "ne")
+ dfs(queensLoc, king[0] + 1, king[1] - 1, result, "sw")
+ dfs(queensLoc, king[0] + 1, king[1] + 1, result, "se")
+ return result
+ }
+
+ fun dfs(
+ queens: Map>,
+ x: Int,
+ y: Int,
+ result: MutableList>,
+ direction: String?
+ ) {
+ if (x < 0 || x >= 8 || y < 0 || y >= 8) {
+ return
+ }
+ if (queens.containsKey(x) && queens[x]!!.contains(y)) {
+ result.add(ArrayList(listOf(x, y)))
+ return
+ }
+ when (direction) {
+ "n" -> dfs(queens, x - 1, y, result, direction)
+ "s" -> dfs(queens, x + 1, y, result, direction)
+ "e" -> dfs(queens, x, y + 1, result, direction)
+ "w" -> dfs(queens, x, y - 1, result, direction)
+ "ne" -> dfs(queens, x - 1, y + 1, result, direction)
+ "nw" -> dfs(queens, x - 1, y - 1, result, direction)
+ "se" -> dfs(queens, x + 1, y + 1, result, direction)
+ "sw" -> dfs(queens, x + 1, y - 1, result, direction)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1223_dice_roll_simulation/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1223_dice_roll_simulation/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8dbe3bb1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1223_dice_roll_simulation/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1223\. Dice Roll Simulation
+
+Hard
+
+A die simulator generates a random number from `1` to `6` for each roll. You introduced a constraint to the generator such that it cannot roll the number `i` more than `rollMax[i]` (**1-indexed**) consecutive times.
+
+Given an array of integers `rollMax` and an integer `n`, return _the number of distinct sequences that can be obtained with exact_ `n` _rolls_. Since the answer may be too large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+Two sequences are considered different if at least one element differs from each other.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2, rollMax = [1,1,2,2,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 34
+
+**Explanation:** There will be 2 rolls of die, if there are no constraints on the die, there are 6 \* 6 = 36 possible combinations. In this case, looking at rollMax array, the numbers 1 and 2 appear at most once consecutively, therefore sequences (1,1) and (2,2) cannot occur, so the final answer is 36-2 = 34.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2, rollMax = [1,1,1,1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** 30
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, rollMax = [1,1,1,2,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 181
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 5000`
+* `rollMax.length == 6`
+* `1 <= rollMax[i] <= 15`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun dieSimulator(n: Int, rollMax: IntArray): Int {
+ val all = Array(6) { LongArray(15 + 1) }
+ val countsBySide = LongArray(6)
+ var total: Long = 0
+ var newTotal: Long
+ var max: Int
+ for (j in all.indices) {
+ all[j][1] = 1
+ countsBySide[j] = 1
+ total = 6
+ }
+ for (i in 1 until n) {
+ newTotal = total
+ for (j in all.indices) {
+ all[j][0] = (total - countsBySide[j]) % MOD
+ max = rollMax[j]
+ newTotal = newTotal - all[j][max] + all[j][0]
+ countsBySide[j] = (total - all[j][max]) % MOD
+ System.arraycopy(all[j], 0, all[j], 1, max)
+ }
+ total = newTotal
+ }
+ return (total % MOD).toInt()
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val MOD: Long = 1000000007
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1224_maximum_equal_frequency/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1224_maximum_equal_frequency/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7c07324f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1224_maximum_equal_frequency/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1224\. Maximum Equal Frequency
+
+Hard
+
+Given an array `nums` of positive integers, return the longest possible length of an array prefix of `nums`, such that it is possible to remove **exactly one** element from this prefix so that every number that has appeared in it will have the same number of occurrences.
+
+If after removing one element there are no remaining elements, it's still considered that every appeared number has the same number of ocurrences (0).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,2,1,1,5,3,3,5]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:** For the subarray [2,2,1,1,5,3,3] of length 7, if we remove nums[4] = 5, we will get [2,2,1,1,3,3], so that each number will appear exactly twice.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,4,5]
+
+**Output:** 13
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxEqualFreq(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val count = IntArray(100001)
+ val freq = IntArray(100001)
+ val n = nums.size
+ for (num in nums) {
+ count[num]++
+ freq[count[num]]++
+ }
+ for (i in n - 1 downTo 1) {
+ if (freq[count[nums[i]]] * count[nums[i]] == i) {
+ return i + 1
+ }
+ freq[count[nums[i]]]--
+ count[nums[i]]--
+ if (freq[count[nums[i - 1]]] * count[nums[i - 1]] == i) {
+ return i + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return 1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1226_the_dining_philosophers/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1226_the_dining_philosophers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c1b9d220
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1226_the_dining_philosophers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1226\. The Dining Philosophers
+
+Medium
+
+Five silent philosophers sit at a round table with bowls of spaghetti. Forks are placed between each pair of adjacent philosophers.
+
+Each philosopher must alternately think and eat. However, a philosopher can only eat spaghetti when they have both left and right forks. Each fork can be held by only one philosopher and so a philosopher can use the fork only if it is not being used by another philosopher. After an individual philosopher finishes eating, they need to put down both forks so that the forks become available to others. A philosopher can take the fork on their right or the one on their left as they become available, but cannot start eating before getting both forks.
+
+Eating is not limited by the remaining amounts of spaghetti or stomach space; an infinite supply and an infinite demand are assumed.
+
+Design a discipline of behaviour (a concurrent algorithm) such that no philosopher will starve; _i.e._, each can forever continue to alternate between eating and thinking, assuming that no philosopher can know when others may want to eat or think.
+
+
+
+_The problem statement and the image above are taken from [wikipedia.org](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dining_philosophers_problem)_
+
+The philosophers' ids are numbered from **0** to **4** in a **clockwise** order. Implement the function `void wantsToEat(philosopher, pickLeftFork, pickRightFork, eat, putLeftFork, putRightFork)` where:
+
+* `philosopher` is the id of the philosopher who wants to eat.
+* `pickLeftFork` and `pickRightFork` are functions you can call to pick the corresponding forks of that philosopher.
+* `eat` is a function you can call to let the philosopher eat once he has picked both forks.
+* `putLeftFork` and `putRightFork` are functions you can call to put down the corresponding forks of that philosopher.
+* The philosophers are assumed to be thinking as long as they are not asking to eat (the function is not being called with their number).
+
+Five threads, each representing a philosopher, will simultaneously use one object of your class to simulate the process. The function may be called for the same philosopher more than once, even before the last call ends.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** [[4,2,1],[4,1,1],[0,1,1],[2,2,1],[2,1,1],[2,0,3],[2,1,2],[2,2,2],[4,0,3],[4,1,2],[0,2,1],[4,2,2],[3,2,1],[3,1,1],[0,0,3],[0,1,2],[0,2,2],[1,2,1],[1,1,1],[3,0,3],[3,1,2],[3,2,2],[1,0,3],[1,1,2],[1,2,2]]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+n is the number of times each philosopher will call the function. The output array describes the calls you made to the functions controlling the forks and the eat function, its format is:
+
+output[i] = [a, b, c] (three integers)
+- a is the id of a philosopher.
+- b specifies the fork: {1 : left, 2 : right}.
+- c specifies the operation: {1 : pick, 2 : put, 3 : eat}.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 60`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("UNUSED_PARAMETER")
+class DiningPhilosophers {
+ private var leftFork = Any()
+ private var rightFork = Any()
+
+ // call the run() method of any runnable to execute its code
+ @Throws(InterruptedException::class)
+ fun wantsToEat(
+ philosopher: Int,
+ pickLeftFork: Runnable,
+ pickRightFork: Runnable,
+ eat: Runnable,
+ putLeftFork: Runnable,
+ putRightFork: Runnable
+ ) {
+ synchronized(leftFork) {
+ synchronized(rightFork) {
+ pickLeftFork.run()
+ pickRightFork.run()
+ eat.run()
+ putRightFork.run()
+ putLeftFork.run()
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1227_airplane_seat_assignment_probability/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1227_airplane_seat_assignment_probability/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7d621a87
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1227_airplane_seat_assignment_probability/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1227\. Airplane Seat Assignment Probability
+
+Medium
+
+`n` passengers board an airplane with exactly `n` seats. The first passenger has lost the ticket and picks a seat randomly. But after that, the rest of the passengers will:
+
+* Take their own seat if it is still available, and
+* Pick other seats randomly when they find their seat occupied
+
+Return _the probability that the_ nth _person gets his own seat_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** 1.00000
+
+**Explanation:** The first person can only get the first seat.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2
+
+**Output:** 0.50000
+
+**Explanation:** The second person has a probability of 0.5 to get the second seat (when first person gets the first seat).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun nthPersonGetsNthSeat(n: Int): Double {
+ return if (n == 1) {
+ 1.0
+ } else 0.5
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1232_check_if_it_is_a_straight_line/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1232_check_if_it_is_a_straight_line/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b912f2a6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1232_check_if_it_is_a_straight_line/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1232\. Check If It Is a Straight Line
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an array `coordinates`, `coordinates[i] = [x, y]`, where `[x, y]` represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** coordinates = \[\[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,7]]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** coordinates = \[\[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[7,7]]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= coordinates.length <= 1000`
+* `coordinates[i].length == 2`
+* `-10^4 <= coordinates[i][0], coordinates[i][1] <= 10^4`
+* `coordinates` contains no duplicate point.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun checkStraightLine(coordinates: Array): Boolean {
+ val deltaX1 = coordinates[0][0] - coordinates[1][0]
+ val deltaY1 = coordinates[0][1] - coordinates[1][1]
+ val prev = coordinates[1]
+ for (i in 2 until coordinates.size) {
+ val point = coordinates[i]
+ val deltaX2 = point[0] - prev[0]
+ val deltaY2 = point[1] - prev[1]
+ if (deltaX1 * deltaY2 != deltaX2 * deltaY1) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1233_remove_sub_folders_from_the_filesystem/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1233_remove_sub_folders_from_the_filesystem/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a44e78b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1233_remove_sub_folders_from_the_filesystem/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1233\. Remove Sub-Folders from the Filesystem
+
+Medium
+
+Given a list of folders `folder`, return _the folders after removing all **sub-folders** in those folders_. You may return the answer in **any order**.
+
+If a `folder[i]` is located within another `folder[j]`, it is called a **sub-folder** of it.
+
+The format of a path is one or more concatenated strings of the form: `'/'` followed by one or more lowercase English letters.
+
+* For example, `"/leetcode"` and `"/leetcode/problems"` are valid paths while an empty string and `"/"` are not.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** folder = ["/a","/a/b","/c/d","/c/d/e","/c/f"]
+
+**Output:** ["/a","/c/d","/c/f"]
+
+**Explanation:** Folders "/a/b" is a subfolder of "/a" and "/c/d/e" is inside of folder "/c/d" in our filesystem.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** folder = ["/a","/a/b/c","/a/b/d"]
+
+**Output:** ["/a"]
+
+**Explanation:** Folders "/a/b/c" and "/a/b/d" will be removed because they are subfolders of "/a".
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** folder = ["/a/b/c","/a/b/ca","/a/b/d"]
+
+**Output:** ["/a/b/c","/a/b/ca","/a/b/d"]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= folder.length <= 4 * 104
+* `2 <= folder[i].length <= 100`
+* `folder[i]` contains only lowercase letters and `'/'`.
+* `folder[i]` always starts with the character `'/'`.
+* Each folder name is **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun removeSubfolders(folder: Array): List {
+ val paths: MutableSet = HashSet()
+ paths.addAll(folder)
+ val res: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (f in folder) {
+ var lastSlash = f.lastIndexOf("/")
+ var isSub = false
+ while (lastSlash > 0) {
+ val upperDir = f.substring(0, lastSlash)
+ if (paths.contains(upperDir)) {
+ isSub = true
+ break
+ }
+ lastSlash = upperDir.lastIndexOf("/")
+ }
+ if (!isSub) {
+ res.add(f)
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1234_replace_the_substring_for_balanced_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1234_replace_the_substring_for_balanced_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bee3fed0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1234_replace_the_substring_for_balanced_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1234\. Replace the Substring for Balanced String
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a string s of length `n` containing only four kinds of characters: `'Q'`, `'W'`, `'E'`, and `'R'`.
+
+A string is said to be **balanced** if each of its characters appears `n / 4` times where `n` is the length of the string.
+
+Return _the minimum length of the substring that can be replaced with **any** other string of the same length to make_ `s` _**balanced**_. If s is already **balanced**, return `0`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "QWER"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** s is already balanced.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "QQWE"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** We need to replace a 'Q' to 'R', so that "RQWE" (or "QRWE") is balanced.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "QQQW"
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** We can replace the first "QQ" to "ER".
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == s.length`
+* 4 <= n <= 105
+* `n` is a multiple of `4`.
+* `s` contains only `'Q'`, `'W'`, `'E'`, and `'R'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun balancedString(s: String): Int {
+ val n = s.length
+ var ans = n
+ var excess = 0
+ val cnt = IntArray(128)
+ cnt['R'.code] = -n / 4
+ cnt['E'.code] = cnt['R'.code]
+ cnt['W'.code] = cnt['E'.code]
+ cnt['Q'.code] = cnt['W'.code]
+ for (ch in s.toCharArray()) {
+ if (++cnt[ch.code] == 1) {
+ excess++
+ }
+ }
+ if (excess == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var i = 0
+ var j = 0
+ while (i < n) {
+ if (--cnt[s[i].code] == 0) {
+ excess--
+ }
+ while (excess == 0) {
+ if (++cnt[s[j].code] == 1) {
+ excess++
+ }
+ ans = Math.min(i - j + 1, ans)
+ j++
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1235_maximum_profit_in_job_scheduling/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1235_maximum_profit_in_job_scheduling/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ee7229d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1235_maximum_profit_in_job_scheduling/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1235\. Maximum Profit in Job Scheduling
+
+Hard
+
+We have `n` jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from `startTime[i]` to `endTime[i]`, obtaining a profit of `profit[i]`.
+
+You're given the `startTime`, `endTime` and `profit` arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
+
+If you choose a job that ends at time `X` you will be able to start another job that starts at time `X`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70]
+
+**Output:** 120
+
+**Explanation:** The subset chosen is the first and fourth job. Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**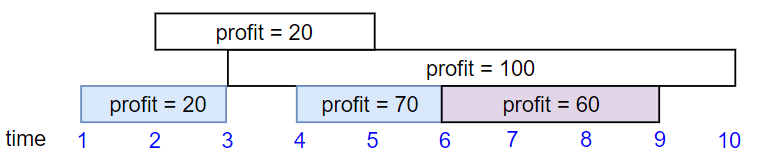**
+
+**Input:** startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60]
+
+**Output:** 150
+
+**Explanation:** The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job. Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**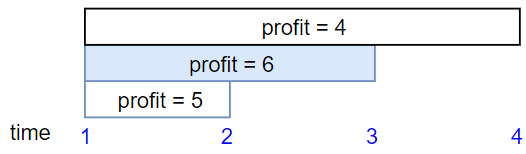**
+
+**Input:** startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 104
+* 1 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 109
+* 1 <= profit[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun jobScheduling(startTime: IntArray, endTime: IntArray, profit: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = startTime.size
+ val time = Array(n) { IntArray(3) }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ time[i][0] = startTime[i]
+ time[i][1] = endTime[i]
+ time[i][2] = profit[i]
+ }
+ Arrays.sort(time, { a: IntArray, b: IntArray -> a[1].compareTo(b[1]) })
+ val maxP = Array(n) { IntArray(2) }
+ var lastPos = -1
+ var currProfit: Int
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ currProfit = time[i][2]
+ for (j in lastPos downTo 0) {
+ if (maxP[j][1] <= time[i][0]) {
+ currProfit += maxP[j][0]
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ if (lastPos == -1 || currProfit > maxP[lastPos][0]) {
+ lastPos++
+ maxP[lastPos][0] = currProfit
+ maxP[lastPos][1] = time[i][1]
+ }
+ }
+ return maxP[lastPos][0]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1237_find_positive_integer_solution_for_a_given_equation/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1237_find_positive_integer_solution_for_a_given_equation/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b167b8f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1237_find_positive_integer_solution_for_a_given_equation/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1237\. Find Positive Integer Solution for a Given Equation
+
+Medium
+
+Given a callable function `f(x, y)` **with a hidden formula** and a value `z`, reverse engineer the formula and return _all positive integer pairs_ `x` _and_ `y` _where_ `f(x,y) == z`. You may return the pairs in any order.
+
+While the exact formula is hidden, the function is monotonically increasing, i.e.:
+
+* `f(x, y) < f(x + 1, y)`
+* `f(x, y) < f(x, y + 1)`
+
+The function interface is defined like this:
+
+interface CustomFunction { public: // Returns some positive integer f(x, y) for two positive integers x and y based on a formula. int f(int x, int y); };
+
+We will judge your solution as follows:
+
+* The judge has a list of `9` hidden implementations of `CustomFunction`, along with a way to generate an **answer key** of all valid pairs for a specific `z`.
+* The judge will receive two inputs: a `function_id` (to determine which implementation to test your code with), and the target `z`.
+* The judge will call your `findSolution` and compare your results with the **answer key**.
+* If your results match the **answer key**, your solution will be `
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+/*
+ * // This is the custom function interface.
+ * // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
+ * class CustomFunction {
+ * // Returns f(x, y) for any given positive integers x and y.
+ * // Note that f(x, y) is increasing with respect to both x and y.
+ * // i.e. f(x, y) < f(x + 1, y), f(x, y) < f(x, y + 1)
+ * fun f(x:Int, y:Int):Int {}
+ * };
+ */
+class Solution {
+ // This is the custom function interface.
+ // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
+ fun interface CustomFunction {
+ // Returns f(x, y) for any given positive integers x and y.
+ // Note that f(x, y) is increasing with respect to both x and y.
+ // i.e. f(x, y) < f(x + 1, y), f(x, y) < f(x, y + 1)
+ fun f(x: Int, y: Int): Int
+ }
+
+ fun findSolution(customfunction: CustomFunction, z: Int): List> {
+ val result: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ var x = 1
+ var y = 1000
+ while (x < 1001 && y > 0) {
+ val functionResult = customfunction.f(x, y)
+ if (functionResult < z) {
+ x++
+ } else if (functionResult > z) {
+ y--
+ } else {
+ result.add(listOf(x++, y--))
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1238_circular_permutation_in_binary_representation/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1238_circular_permutation_in_binary_representation/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2e969066
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1238_circular_permutation_in_binary_representation/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1238\. Circular Permutation in Binary Representation
+
+Medium
+
+Given 2 integers `n` and `start`. Your task is return **any** permutation `p` of `(0,1,2.....,2^n -1)` such that :
+
+* `p[0] = start`
+* `p[i]` and `p[i+1]` differ by only one bit in their binary representation.
+* `p[0]` and `p[2^n -1]` must also differ by only one bit in their binary representation.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2, start = 3
+
+**Output:** [3,2,0,1]
+
+**Explanation:** The binary representation of the permutation is (11,10,00,01). All the adjacent element differ by one bit. Another valid permutation is [3,1,0,2]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, start = 2
+
+**Output:** [2,6,7,5,4,0,1,3]
+
+**Explanation:** The binary representation of the permutation is (010,110,111,101,100,000,001,011).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 16`
+* `0 <= start < 2 ^ n`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun circularPermutation(n: Int, start: Int): List {
+ val l1: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (i in 0 until (1 shl n)) {
+ l1.add(start xor (i xor (i shr 1)))
+ }
+ return l1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1239_maximum_length_of_a_concatenated_string_with_unique_characters/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1239_maximum_length_of_a_concatenated_string_with_unique_characters/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..032561d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1239_maximum_length_of_a_concatenated_string_with_unique_characters/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1239\. Maximum Length of a Concatenated String with Unique Characters
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an array of strings `arr`. A string `s` is formed by the **concatenation** of a **subsequence** of `arr` that has **unique characters**.
+
+Return _the **maximum** possible length_ of `s`.
+
+A **subsequence** is an array that can be derived from another array by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = ["un","iq","ue"]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** All the valid concatenations are:
+- ""
+- "un"
+- "iq"
+- "ue"
+- "uniq" ("un" + "iq")
+- "ique" ("iq" + "ue")
+
+Maximum length is 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = ["cha","r","act","ers"]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** Possible longest valid concatenations are "chaers" ("cha" + "ers") and "acters" ("act" + "ers").
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = ["abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"]
+
+**Output:** 26
+
+**Explanation:** The only string in arr has all 26 characters.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= arr.length <= 16`
+* `1 <= arr[i].length <= 26`
+* `arr[i]` contains only lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun maxLength(arr: List): Int {
+ return find(0, 0, arr)
+ }
+
+ private fun find(index: Int, visChar: Int, arr: List): Int {
+ var visChar = visChar
+ if (index == arr.size) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var ans = 0
+ ans = Math.max(ans, find(index + 1, visChar, arr))
+ if (checkCurrStringValidOrNot(visChar, arr[index])) {
+ visChar = updateState(visChar, arr[index])
+ ans = Math.max(ans, arr[index].length + find(index + 1, visChar, arr))
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun checkCurrStringValidOrNot(vis: Int, s: String): Boolean {
+ var vis = vis
+ for (c in s.toCharArray()) {
+ if (vis and (1 shl c.code - 'a'.code) != 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ vis = vis or (1 shl c.code - 'a'.code)
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private fun updateState(vis: Int, s: String): Int {
+ var vis = vis
+ for (c in s.toCharArray()) {
+ vis = vis or (1 shl c.code - 'a'.code)
+ }
+ return vis
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1240_tiling_a_rectangle_with_the_fewest_squares/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1240_tiling_a_rectangle_with_the_fewest_squares/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..19bad368
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1240_tiling_a_rectangle_with_the_fewest_squares/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1240\. Tiling a Rectangle with the Fewest Squares
+
+Hard
+
+Given a rectangle of size `n` x `m`, return _the minimum number of integer-sided squares that tile the rectangle_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 2, m = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** `3` squares are necessary to cover the rectangle.
+
+`2` (squares of `1x1`)
+
+`1` (square of `2x2`)
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 5, m = 8
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 11, m = 13
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n, m <= 13`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private var n = 0
+ private var m = 0
+ private lateinit var covered: Array
+ private var res = 0
+
+ fun tilingRectangle(n: Int, m: Int): Int {
+ this.n = n
+ this.m = m
+ covered = Array(n) { BooleanArray(m) }
+ res = m * n
+ backtrack(0)
+ return res
+ }
+
+ private fun backtrack(count: Int) {
+ if (count >= res) {
+ return
+ }
+ var find = false
+ for (r in 0 until n) {
+ for (c in 0 until m) {
+ if (!covered[r][c]) {
+ find = true
+ var len = findMaxWidth(r, c)
+ while (len > 0) {
+ cover(r, c, len, true)
+ backtrack(count + 1)
+ cover(r, c, len, false)
+ len--
+ }
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ if (find) {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ if (!find) {
+ res = count
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun cover(r: Int, c: Int, len: Int, flag: Boolean) {
+ for (i in r until r + len) {
+ for (j in c until c + len) {
+ covered[i][j] = flag
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun findMaxWidth(r: Int, c: Int): Int {
+ var len = Math.min(n - r, m - c)
+ while (true) {
+ var find = false
+ for (i in r until r + len) {
+ for (j in c until c + len) {
+ if (covered[i][j]) {
+ find = true
+ len = Math.min(i - r, j - c)
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ if (find) {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ if (!find) {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return len
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1247_minimum_swaps_to_make_strings_equal/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1247_minimum_swaps_to_make_strings_equal/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..027ea215
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1247_minimum_swaps_to_make_strings_equal/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1247\. Minimum Swaps to Make Strings Equal
+
+Medium
+
+You are given two strings `s1` and `s2` of equal length consisting of letters `"x"` and `"y"` **only**. Your task is to make these two strings equal to each other. You can swap any two characters that belong to **different** strings, which means: swap `s1[i]` and `s2[j]`.
+
+Return the minimum number of swaps required to make `s1` and `s2` equal, or return `-1` if it is impossible to do so.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s1 = "xx", s2 = "yy"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** Swap s1[0] and s2[1], s1 = "yx", s2 = "yx".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s1 = "xy", s2 = "yx"
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Swap s1[0] and s2[0], s1 = "yy", s2 = "xx".
+
+Swap s1[0] and s2[1], s1 = "xy", s2 = "xy".
+
+Note that you cannot swap s1[0] and s1[1] to make s1 equal to "yx", cause we can only swap chars in different strings.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s1 = "xx", s2 = "xy"
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s1.length, s2.length <= 1000`
+* `s1, s2` only contain `'x'` or `'y'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minimumSwap(s1: String, s2: String): Int {
+ val len = s1.length
+ var countX1 = 0
+ var countY1 = 0
+ var countX2 = 0
+ var countY2 = 0
+ for (i in 0 until len) {
+ if (s1[i] != s2[i]) {
+ if (s1[i] == 'x') {
+ countX1++
+ } else {
+ countY1++
+ }
+ if (s2[i] == 'x') {
+ countX2++
+ } else {
+ countY2++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if ((countX1 + countX2) % 2 == 1) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ return if (countX1 + countX2 > countY1 + countY2) {
+ Math.ceil(countY1 * 1.0 / 2).toInt() + Math.ceil(countY2 * 1.0 / 2).toInt()
+ } else {
+ Math.ceil(countX1 * 1.0 / 2).toInt() + Math.ceil(countX2 * 1.0 / 2).toInt()
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1248_count_number_of_nice_subarrays/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1248_count_number_of_nice_subarrays/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..af3cc88e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1248_count_number_of_nice_subarrays/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1248\. Count Number of Nice Subarrays
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `k`. A continuous subarray is called **nice** if there are `k` odd numbers on it.
+
+Return _the number of **nice** sub-arrays_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,2,1,1], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The only sub-arrays with 3 odd numbers are [1,1,2,1] and [1,2,1,1].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,4,6], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** There is no odd numbers in the array.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,2,2,1,2,2,1,2,2,2], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 16
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 50000`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 10^5`
+* `1 <= k <= nums.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numberOfSubarrays(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ var oddLen = 0
+ var startIndex = 0
+ var num = 0
+ var endIndex: Int
+ var res = 0
+ var hasK: Boolean
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ hasK = false
+ endIndex = i
+ if (nums[i] % 2 == 1) {
+ oddLen++
+ }
+ while (oddLen >= k) {
+ hasK = true
+ if (nums[startIndex++] % 2 == 1) {
+ oddLen--
+ }
+ num++
+ }
+ res += num
+ while (hasK && ++endIndex < nums.size && nums[endIndex] % 2 == 0) {
+ res += num
+ }
+ num = 0
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1249_minimum_remove_to_make_valid_parentheses/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1249_minimum_remove_to_make_valid_parentheses/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..896ce301
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1249_minimum_remove_to_make_valid_parentheses/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1249\. Minimum Remove to Make Valid Parentheses
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string s of `'('` , `')'` and lowercase English characters.
+
+Your task is to remove the minimum number of parentheses ( `'('` or `')'`, in any positions ) so that the resulting _parentheses string_ is valid and return **any** valid string.
+
+Formally, a _parentheses string_ is valid if and only if:
+
+* It is the empty string, contains only lowercase characters, or
+* It can be written as `AB` (`A` concatenated with `B`), where `A` and `B` are valid strings, or
+* It can be written as `(A)`, where `A` is a valid string.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "lee(t(c)o)de)"
+
+**Output:** "lee(t(c)o)de"
+
+**Explanation:** "lee(t(co)de)" , "lee(t(c)ode)" would also be accepted.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "a)b(c)d"
+
+**Output:** "ab(c)d"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "))(("
+
+**Output:** ""
+
+**Explanation:** An empty string is also valid.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s[i]` is either`'('` , `')'`, or lowercase English letter`.`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minRemoveToMakeValid(s: String): String {
+ var closingParantheis = 0
+ for (ch in s.toCharArray()) {
+ if (ch == ')') {
+ closingParantheis++
+ }
+ }
+ val result = StringBuilder()
+ var openingParanthesis = 0
+ for (ch in s.toCharArray()) {
+ if (ch == ')' && openingParanthesis == 0) {
+ closingParantheis--
+ } else {
+ if (ch == ')') {
+ openingParanthesis--
+ }
+ if (ch == '(' && closingParantheis == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if (ch == '(') {
+ openingParanthesis++
+ closingParantheis--
+ }
+ result.append(ch)
+ }
+ }
+ return result.toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1250_check_if_it_is_a_good_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1250_check_if_it_is_a_good_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cdc5e3b3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1250_check_if_it_is_a_good_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1250\. Check If It Is a Good Array
+
+Hard
+
+Given an array `nums` of positive integers. Your task is to select some subset of `nums`, multiply each element by an integer and add all these numbers. The array is said to be **good **if you can obtain a sum of `1` from the array by any possible subset and multiplicand.
+
+Return `True` if the array is **good **otherwise return `False`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [12,5,7,23]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Pick numbers 5 and 7. 5\*3 + 7\*(-2) = 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [29,6,10]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Pick numbers 29, 6 and 10. 29\*1 + 6\*(-3) + 10\*(-1) = 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,6]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 10^5`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 10^9`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private fun gcd(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
+ return if (b == 0) {
+ a
+ } else gcd(b, a % b)
+ }
+
+ fun isGoodArray(nums: IntArray): Boolean {
+ var ans = nums[0]
+ for (element in nums) {
+ ans = gcd(ans, element)
+ if (ans == 1) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1251_average_selling_price/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1251_average_selling_price/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e28112f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1251_average_selling_price/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1251\. Average Selling Price
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Prices`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | product_id | int |
+ | start_date | date |
+ | end_date | date |
+ | price | int |
+ +---------------+---------+
+
+(product_id, start_date, end_date) is the primary key for this table. Each row of this table indicates the price of the product_id in the period from start_date to end_date. For each product_id there will be no two overlapping periods. That means there will be no two intersecting periods for the same product_id.
+
+Table: `UnitsSold`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | product_id | int |
+ | purchase_date | date |
+ | units | int |
+ +---------------+---------+
+
+There is no primary key for this table, it may contain duplicates. Each row of this table indicates the date, units, and product_id of each product sold.
+
+Write an SQL query to find the average selling price for each product. `average_price` should be **rounded to 2 decimal places**.
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** Prices table:
+
+ +------------+------------+------------+--------+
+ | product_id | start_date | end_date | price |
+ +------------+------------+------------+--------+
+ | 1 | 2019-02-17 | 2019-02-28 | 5 |
+ | 1 | 2019-03-01 | 2019-03-22 | 20 |
+ | 2 | 2019-02-01 | 2019-02-20 | 15 |
+ | 2 | 2019-02-21 | 2019-03-31 | 30 |
+ +------------+------------+------------+--------+
+
+UnitsSold table:
+
+ +------------+---------------+-------+
+ | product_id | purchase_date | units |
+ +------------+---------------+-------+
+ | 1 | 2019-02-25 | 100 |
+ | 1 | 2019-03-01 | 15 |
+ | 2 | 2019-02-10 | 200 |
+ | 2 | 2019-03-22 | 30 |
+ +------------+---------------+-------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +------------+---------------+
+ | product_id | average_price |
+ +------------+---------------+
+ | 1 | 6.96 |
+ | 2 | 16.96 |
+ +------------+---------------+
+
+**Explanation:** Average selling price = Total Price of Product / Number of products sold. Average selling price for product 1 = ((100 * 5) + (15 * 20)) / 115 = 6.96 Average selling price for product 2 = ((200 * 15) + (30 * 30)) / 230 = 16.96
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT p.product_id,
+ROUND(SUM(p.price * u.units) / SUM(u.units), 2) AS average_price
+FROM
+Prices AS p
+NATURAL JOIN
+UnitsSold AS u
+WHERE
+u.purchase_date BETWEEN p.start_date AND p.end_date
+GROUP BY p.product_id;
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1252_cells_with_odd_values_in_a_matrix/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1252_cells_with_odd_values_in_a_matrix/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1c30666c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1252_cells_with_odd_values_in_a_matrix/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1252\. Cells with Odd Values in a Matrix
+
+Easy
+
+There is an `m x n` matrix that is initialized to all `0`'s. There is also a 2D array `indices` where each indices[i] = [ri, ci] represents a **0-indexed location** to perform some increment operations on the matrix.
+
+For each location `indices[i]`, do **both** of the following:
+
+1. Increment **all** the cells on row ri.
+2. Increment **all** the cells on column ci.
+
+Given `m`, `n`, and `indices`, return _the **number of odd-valued cells** in the matrix after applying the increment to all locations in_ `indices`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** m = 2, n = 3, indices = \[\[0,1],[1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** Initial matrix = \[\[0,0,0],[0,0,0]].
+
+After applying first increment it becomes [[1,2,1],[0,1,0]].
+
+The final matrix is [[1,3,1],[1,3,1]], which contains 6 odd numbers.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** m = 2, n = 2, indices = \[\[1,1],[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Final matrix = \[\[2,2],[2,2]]. There are no odd numbers in the final matrix.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= m, n <= 50`
+* `1 <= indices.length <= 100`
+* 0 <= ri < m
+* 0 <= ci < n
+
+**Follow up:** Could you solve this in `O(n + m + indices.length)` time with only `O(n + m)` extra space?
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun oddCells(n: Int, m: Int, indices: Array): Int {
+ val matrix = Array(n) { IntArray(m) }
+ for (index in indices) {
+ addOneToRow(matrix, index[0])
+ addOneToColumn(matrix, index[1])
+ }
+ var oddNumberCount = 0
+ for (ints in matrix) {
+ for (j in matrix[0].indices) {
+ if (ints[j] % 2 != 0) {
+ oddNumberCount++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return oddNumberCount
+ }
+
+ private fun addOneToColumn(matrix: Array, columnIndex: Int) {
+ for (i in matrix.indices) {
+ matrix[i][columnIndex] += 1
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun addOneToRow(matrix: Array, rowIndex: Int) {
+ for (j in matrix[0].indices) {
+ matrix[rowIndex][j] += 1
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1253_reconstruct_a_2_row_binary_matrix/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1253_reconstruct_a_2_row_binary_matrix/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e76c0645
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1253_reconstruct_a_2_row_binary_matrix/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1253\. Reconstruct a 2-Row Binary Matrix
+
+Medium
+
+Given the following details of a matrix with `n` columns and `2` rows :
+
+* The matrix is a binary matrix, which means each element in the matrix can be `0` or `1`.
+* The sum of elements of the 0-th(upper) row is given as `upper`.
+* The sum of elements of the 1-st(lower) row is given as `lower`.
+* The sum of elements in the i-th column(0-indexed) is `colsum[i]`, where `colsum` is given as an integer array with length `n`.
+
+Your task is to reconstruct the matrix with `upper`, `lower` and `colsum`.
+
+Return it as a 2-D integer array.
+
+If there are more than one valid solution, any of them will be accepted.
+
+If no valid solution exists, return an empty 2-D array.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** upper = 2, lower = 1, colsum = [1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** [[1,1,0],[0,0,1]]
+
+**Explanation:** [[1,0,1],[0,1,0]], and [[0,1,1],[1,0,0]] are also correct answers.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** upper = 2, lower = 3, colsum = [2,2,1,1]
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** upper = 5, lower = 5, colsum = [2,1,2,0,1,0,1,2,0,1]
+
+**Output:** [[1,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0],[1,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,1]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= colsum.length <= 10^5`
+* `0 <= upper, lower <= colsum.length`
+* `0 <= colsum[i] <= 2`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun reconstructMatrix(upper: Int, lower: Int, colsum: IntArray): List> {
+ val res: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ val n = colsum.size
+ val upperRow = IntArray(n)
+ val lowerRow = IntArray(n)
+ var currentUpperSum = 0
+ var currentLowerSum = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ if (colsum[i] >= 1) {
+ upperRow[i] = 1
+ lowerRow[i] = 1
+ currentUpperSum++
+ currentLowerSum++
+ }
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ if (colsum[i] == 1 && currentUpperSum > upper) {
+ currentUpperSum--
+ upperRow[i] = 0
+ }
+ }
+ for (i in upperRow.indices) {
+ if (colsum[i] == 1 && upperRow[i] == 1) {
+ currentLowerSum--
+ lowerRow[i] = 0
+ }
+ }
+ if (currentUpperSum != upper || currentLowerSum != lower) {
+ return res
+ }
+ res.add(ArrayList())
+ res.add(ArrayList())
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ res[0].add(upperRow[i])
+ res[1].add(lowerRow[i])
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1254_number_of_closed_islands/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1254_number_of_closed_islands/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..be39aafc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1254_number_of_closed_islands/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1254\. Number of Closed Islands
+
+Medium
+
+Given a 2D `grid` consists of `0s` (land) and `1s` (water). An _island_ is a maximal 4-directionally connected group of `0s` and a _closed island_ is an island **totally** (all left, top, right, bottom) surrounded by `1s.`
+
+Return the number of _closed islands_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0],[1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0],[1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0],[1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Islands in gray are closed because they are completely surrounded by water (group of 1s).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+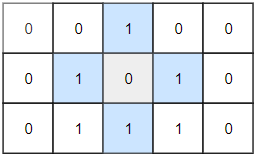
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[0,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,1,0],[0,1,1,1,0]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,1,1,1,1,1,1],
+ [1,0,0,0,0,0,1],
+ [1,0,1,1,1,0,1],
+ [1,0,1,0,1,0,1],
+ [1,0,1,1,1,0,1],
+ [1,0,0,0,0,0,1],
+ [1,1,1,1,1,1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= grid.length, grid[0].length <= 100`
+* `0 <= grid[i][j] <=1`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private var rows = 0
+ private var cols = 0
+ private var isLand = false
+ fun closedIsland(grid: Array): Int {
+ rows = grid.size
+ cols = grid[0].size
+ var result = 0
+ for (r in 0 until rows) {
+ for (c in 0 until cols) {
+ if (grid[r][c] == 0) {
+ isLand = true
+ dfs(grid, r, c)
+ if (isLand) {
+ result++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(grid: Array, r: Int, c: Int) {
+ if (r == 0 || c == 0 || r == rows - 1 || c == cols - 1) {
+ isLand = false
+ }
+ grid[r][c] = 'k'.code
+ if (r > 0 && grid[r - 1][c] == 0) {
+ dfs(grid, r - 1, c)
+ }
+ if (c > 0 && grid[r][c - 1] == 0) {
+ dfs(grid, r, c - 1)
+ }
+ if (r < rows - 1 && grid[r + 1][c] == 0) {
+ dfs(grid, r + 1, c)
+ }
+ if (c < cols - 1 && grid[r][c + 1] == 0) {
+ dfs(grid, r, c + 1)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1255_maximum_score_words_formed_by_letters/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1255_maximum_score_words_formed_by_letters/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c407f990
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1255_maximum_score_words_formed_by_letters/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1255\. Maximum Score Words Formed by Letters
+
+Hard
+
+Given a list of `words`, list of single `letters` (might be repeating) and `score` of every character.
+
+Return the maximum score of **any** valid set of words formed by using the given letters (`words[i]` cannot be used two or more times).
+
+It is not necessary to use all characters in `letters` and each letter can only be used once. Score of letters `'a'`, `'b'`, `'c'`, ... ,`'z'` is given by `score[0]`, `score[1]`, ... , `score[25]` respectively.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** words = ["dog","cat","dad","good"], letters = ["a","a","c","d","d","d","g","o","o"], score = [1,0,9,5,0,0,3,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,2,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
+
+**Output:** 23
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Score a=1, c=9, d=5, g=3, o=2
+
+Given letters, we can form the words "dad" (5+1+5) and "good" (3+2+2+5) with a score of 23.
+
+Words "dad" and "dog" only get a score of 21.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** words = ["xxxz","ax","bx","cx"], letters = ["z","a","b","c","x","x","x"], score = [4,4,4,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,5,0,10]
+
+**Output:** 27
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Score a=4, b=4, c=4, x=5, z=10
+
+Given letters, we can form the words "ax" (4+5), "bx" (4+5) and "cx" (4+5) with a score of 27.
+
+Word "xxxz" only get a score of 25.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** words = ["leetcode"], letters = ["l","e","t","c","o","d"], score = [0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Letter "e" can only be used once.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= words.length <= 14`
+* `1 <= words[i].length <= 15`
+* `1 <= letters.length <= 100`
+* `letters[i].length == 1`
+* `score.length == 26`
+* `0 <= score[i] <= 10`
+* `words[i]`, `letters[i]` contains only lower case English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private lateinit var score: IntArray
+
+ private fun updateArr(arr: IntArray, s: String, add: Int): Int {
+ var sum = 0
+ for (c in s.toCharArray()) {
+ val ind = c.code - 'a'.code
+ arr[ind] += add
+ if (arr[ind] < 0) {
+ sum = -1
+ }
+ if (sum != -1) {
+ sum += score[ind]
+ }
+ }
+ return sum
+ }
+
+ private fun findMaxScore(words: Array, ind: Int, arr: IntArray): Int {
+ if (ind == words.size) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val excl = findMaxScore(words, ind + 1, arr)
+ var incl = 0
+ val cscore = updateArr(arr, words[ind], -1)
+ if (cscore != -1) {
+ incl = cscore + findMaxScore(words, ind + 1, arr)
+ }
+ updateArr(arr, words[ind], 1)
+ return Math.max(incl, excl)
+ }
+
+ fun maxScoreWords(words: Array, letters: CharArray, score: IntArray): Int {
+ val arr = IntArray(26)
+ for (c in letters) {
+ arr[c.code - 'a'.code]++
+ }
+ this.score = score
+ return findMaxScore(words, 0, arr)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1260_shift_2d_grid/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1260_shift_2d_grid/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..049a80a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1260_shift_2d_grid/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1260\. Shift 2D Grid
+
+Easy
+
+Given a 2D `grid` of size `m x n` and an integer `k`. You need to shift the `grid` `k` times.
+
+In one shift operation:
+
+* Element at `grid[i][j]` moves to `grid[i][j + 1]`.
+* Element at `grid[i][n - 1]` moves to `grid[i + 1][0]`.
+* Element at `grid[m - 1][n - 1]` moves to `grid[0][0]`.
+
+Return the _2D grid_ after applying shift operation `k` times.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** `grid` = \[\[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 1
+
+**Output:** [[9,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** `grid` = \[\[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10],[12,0,21,13]], k = 4
+
+**Output:** [[12,0,21,13],[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10]]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** `grid` = \[\[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 9
+
+**Output:** [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m <= 50`
+* `1 <= n <= 50`
+* `-1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 1000`
+* `0 <= k <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun shiftGrid(grid: Array, k: Int): List> {
+ val flat = IntArray(grid.size * grid[0].size)
+ var index = 0
+ for (ints in grid) {
+ for (j in grid[0].indices) {
+ flat[index++] = ints[j]
+ }
+ }
+ val mode = k % flat.size
+ var readingIndex = flat.size - mode
+ if (readingIndex == flat.size) {
+ readingIndex = 0
+ }
+ val result: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ for (i in grid.indices) {
+ val eachRow: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (j in grid[0].indices) {
+ eachRow.add(flat[readingIndex++])
+ if (readingIndex == flat.size) {
+ readingIndex = 0
+ }
+ }
+ result.add(eachRow)
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1261_find_elements_in_a_contaminated_binary_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1261_find_elements_in_a_contaminated_binary_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fdf32218
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1261_find_elements_in_a_contaminated_binary_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1261\. Find Elements in a Contaminated Binary Tree
+
+Medium
+
+Given a binary tree with the following rules:
+
+1. `root.val == 0`
+2. If `treeNode.val == x` and `treeNode.left != null`, then `treeNode.left.val == 2 * x + 1`
+3. If `treeNode.val == x` and `treeNode.right != null`, then `treeNode.right.val == 2 * x + 2`
+
+Now the binary tree is contaminated, which means all `treeNode.val` have been changed to `-1`.
+
+Implement the `FindElements` class:
+
+* `FindElements(TreeNode* root)` Initializes the object with a contaminated binary tree and recovers it.
+* `bool find(int target)` Returns `true` if the `target` value exists in the recovered binary tree.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input** ["FindElements","find","find"] [[[-1,null,-1]],[1],[2]]
+
+**Output:** [null,false,true]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1]);
+ findElements.find(1); // return False
+ findElements.find(2); // return True
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input** ["FindElements","find","find","find"] [[[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]],[1],[3],[5]]
+
+**Output:** [null,true,true,false]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]);
+ findElements.find(1); // return True
+ findElements.find(3); // return True
+ findElements.find(5); // return False
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input** ["FindElements","find","find","find","find"] [[[-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]],[2],[3],[4],[5]]
+
+**Output:** [null,true,false,false,true]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]);
+ findElements.find(2); // return True
+ findElements.find(3); // return False
+ findElements.find(4); // return False
+ findElements.find(5); // return True
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `TreeNode.val == -1`
+* The height of the binary tree is less than or equal to `20`
+* The total number of nodes is between [1, 104]
+* Total calls of `find()` is between [1, 104]
+* 0 <= target <= 106
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class FindElements(root: TreeNode?) {
+ private val map = HashMap()
+
+ init {
+ helper(root, 0)
+ }
+
+ private fun helper(root: TreeNode?, x: Int) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return
+ }
+ root.`val` = x
+ map[x] = 0
+ helper(root.left, 2 * x + 1)
+ helper(root.right, 2 * x + 2)
+ }
+
+ fun find(target: Int): Boolean {
+ return map.containsKey(target)
+ }
+}
+/*
+ * Your FindElements object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * var obj = FindElements(root)
+ * var param_1 = obj.find(target)
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1262_greatest_sum_divisible_by_three/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1262_greatest_sum_divisible_by_three/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e88d71b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1262_greatest_sum_divisible_by_three/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1262\. Greatest Sum Divisible by Three
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array `nums` of integers, we need to find the maximum possible sum of elements of the array such that it is divisible by three.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,6,5,1,8]
+
+**Output:** 18
+
+**Explanation:** Pick numbers 3, 6, 1 and 8 their sum is 18 (maximum sum divisible by 3).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Since 4 is not divisible by 3, do not pick any number.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4,4]
+
+**Output:** 12
+
+**Explanation:** Pick numbers 1, 3, 4 and 4 their sum is 12 (maximum sum divisible by 3).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 4 * 10^4`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 10^4`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxSumDivThree(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var sum = 0
+ var smallestNumWithMod1 = 10001
+ var secondSmallestNumWithMod1 = 10002
+ var smallestNumWithMod2 = 10001
+ var secondSmallestNumWithMod2 = 10002
+ for (i in nums) {
+ sum += i
+ if (i % 3 == 1) {
+ if (i <= smallestNumWithMod1) {
+ val temp = smallestNumWithMod1
+ smallestNumWithMod1 = i
+ secondSmallestNumWithMod1 = temp
+ } else if (i < secondSmallestNumWithMod1) {
+ secondSmallestNumWithMod1 = i
+ }
+ }
+ if (i % 3 == 2) {
+ if (i <= smallestNumWithMod2) {
+ val temp = smallestNumWithMod2
+ smallestNumWithMod2 = i
+ secondSmallestNumWithMod2 = temp
+ } else if (i < secondSmallestNumWithMod2) {
+ secondSmallestNumWithMod2 = i
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (sum % 3 == 0) {
+ return sum
+ } else if (sum % 3 == 2) {
+ val min = Math.min(smallestNumWithMod2, smallestNumWithMod1 + secondSmallestNumWithMod1)
+ return sum - min
+ } else if (sum % 3 == 1) {
+ val min = Math.min(smallestNumWithMod1, smallestNumWithMod2 + secondSmallestNumWithMod2)
+ return sum - min
+ }
+ return sum
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1263_minimum_moves_to_move_a_box_to_their_target_location/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1263_minimum_moves_to_move_a_box_to_their_target_location/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fc1dd75b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1263_minimum_moves_to_move_a_box_to_their_target_location/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,187 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1263\. Minimum Moves to Move a Box to Their Target Location
+
+Hard
+
+A storekeeper is a game in which the player pushes boxes around in a warehouse trying to get them to target locations.
+
+The game is represented by an `m x n` grid of characters `grid` where each element is a wall, floor, or box.
+
+Your task is to move the box `'B'` to the target position `'T'` under the following rules:
+
+* The character `'S'` represents the player. The player can move up, down, left, right in `grid` if it is a floor (empty cell).
+* The character `'.'` represents the floor which means a free cell to walk.
+* The character `'#'` represents the wall which means an obstacle (impossible to walk there).
+* There is only one box `'B'` and one target cell `'T'` in the `grid`.
+* The box can be moved to an adjacent free cell by standing next to the box and then moving in the direction of the box. This is a **push**.
+* The player cannot walk through the box.
+
+Return _the minimum number of **pushes** to move the box to the target_. If there is no way to reach the target, return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:**
+
+ grid = [ ["#","#","#","#","#","#"],
+ ["#","T","#","#","#","#"],
+ ["#",".",".","B",".","#"],
+ ["#",".","#","#",".","#"],
+ ["#",".",".",".","S","#"],
+ ["#","#","#","#","#","#"]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** We return only the number of times the box is pushed.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ grid = [ ["#","#","#","#","#","#"],
+ ["#","T","#","#","#","#"],
+ ["#",".",".","B",".","#"],
+ ["#","#","#","#",".","#"],
+ ["#",".",".",".","S","#"],
+ ["#","#","#","#","#","#"]]
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ grid = [ ["#","#","#","#","#","#"],
+ ["#","T",".",".","#","#"],
+ ["#",".","#","B",".","#"],
+ ["#",".",".",".",".","#"],
+ ["#",".",".",".","S","#"],
+ ["#","#","#","#","#","#"]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** push the box down, left, left, up and up.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 20`
+* `grid` contains only characters `'.'`, `'#'`, `'S'`, `'T'`, or `'B'`.
+* There is only one character `'S'`, `'B'`, and `'T'` in the `grid`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ private var n = 0
+ private var m = 0
+ private lateinit var grid: Array
+ private val dirs = arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 0), intArrayOf(0, 1), intArrayOf(-1, 0), intArrayOf(0, -1))
+
+ fun minPushBox(grid: Array): Int {
+ n = grid.size
+ m = grid[0].size
+ this.grid = grid
+ val box = IntArray(2)
+ val target = IntArray(2)
+ val player = IntArray(2)
+ findLocations(box, target, player)
+ val q: Queue = LinkedList()
+ q.offer(intArrayOf(box[0], box[1], player[0], player[1]))
+ // for 4 directions
+ val visited = Array(n) { Array(m) { BooleanArray(4) } }
+ var steps = 0
+ while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
+ var size = q.size
+ while (size-- > 0) {
+ val cur = q.poll()
+ if (cur != null && cur[0] == target[0] && cur[1] == target[1]) {
+ return steps
+ }
+ for (i in 0..3) {
+ if (cur != null) {
+ val newPlayerLoc = intArrayOf(cur[0] + dirs[i][0], cur[1] + dirs[i][1])
+ val newBoxLoc = intArrayOf(cur[0] - dirs[i][0], cur[1] - dirs[i][1])
+ if (visited[cur[0]][cur[1]][i] ||
+ isOutOfBounds(newPlayerLoc, newBoxLoc) ||
+ !isReachable(newPlayerLoc, cur)
+ ) {
+ continue
+ }
+ visited[cur[0]][cur[1]][i] = true
+ q.offer(intArrayOf(newBoxLoc[0], newBoxLoc[1], cur[0], cur[1]))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ steps++
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ private fun isReachable(targetPlayerLoc: IntArray, cur: IntArray): Boolean {
+ val visited = Array(n) { BooleanArray(m) }
+ visited[cur[0]][cur[1]] = true
+ visited[cur[2]][cur[3]] = true
+ val q: Queue = LinkedList()
+ q.offer(intArrayOf(cur[2], cur[3]))
+ while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val playerLoc = q.poll()
+ if (playerLoc[0] == targetPlayerLoc[0] && playerLoc[1] == targetPlayerLoc[1]) {
+ return true
+ }
+ for (d in dirs) {
+ val x = playerLoc[0] + d[0]
+ val y = playerLoc[1] + d[1]
+ if (isOutOfBounds(x, y) || visited[x][y]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ visited[x][y] = true
+ q.offer(intArrayOf(x, y))
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ private fun isOutOfBounds(player: IntArray, box: IntArray): Boolean {
+ return isOutOfBounds(player[0], player[1]) || isOutOfBounds(box[0], box[1])
+ }
+
+ private fun isOutOfBounds(x: Int, y: Int): Boolean {
+ return x < 0 || y < 0 || x == n || y == m || grid[x][y] == '#'
+ }
+
+ private fun findLocations(box: IntArray, target: IntArray, player: IntArray) {
+ var p = false
+ var t = false
+ var b = false
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ for (j in 0 until m) {
+ if (grid[i][j] == 'S') {
+ player[0] = i
+ player[1] = j
+ p = true
+ } else if (grid[i][j] == 'T') {
+ target[0] = i
+ target[1] = j
+ t = true
+ } else if (grid[i][j] == 'B') {
+ box[0] = i
+ box[1] = j
+ b = true
+ }
+ if (p && b && t) {
+ // found all
+ return
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1266_minimum_time_visiting_all_points/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1266_minimum_time_visiting_all_points/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c5e2793d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1266_minimum_time_visiting_all_points/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1266\. Minimum Time Visiting All Points
+
+Easy
+
+On a 2D plane, there are `n` points with integer coordinates points[i] = [xi, yi]. Return _the **minimum time** in seconds to visit all the points in the order given by_ `points`.
+
+You can move according to these rules:
+
+* In `1` second, you can either:
+ * move vertically by one unit,
+ * move horizontally by one unit, or
+ * move diagonally `sqrt(2)` units (in other words, move one unit vertically then one unit horizontally in `1` second).
+* You have to visit the points in the same order as they appear in the array.
+* You are allowed to pass through points that appear later in the order, but these do not count as visits.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** points = \[\[1,1],[3,4],[-1,0]]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:** One optimal path is **[1,1]** -> [2,2] -> [3,3] -> **[3,4]** \-> [2,3] -> [1,2] -> [0,1] -> **[-1,0]**
+
+Time from [1,1] to [3,4] = 3 seconds
+
+Time from [3,4] to [-1,0] = 4 seconds
+
+Total time = 7 seconds
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** points = \[\[3,2],[-2,2]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `points.length == n`
+* `1 <= n <= 100`
+* `points[i].length == 2`
+* `-1000 <= points[i][0], points[i][1] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minTimeToVisitAllPoints(points: Array): Int {
+ var minTime = 0
+ for (i in 0 until points.size - 1) {
+ minTime += chebyshevDistance(points[i], points[i + 1])
+ }
+ return minTime
+ }
+
+ private fun chebyshevDistance(pointA: IntArray, pointB: IntArray): Int {
+ return Math.max(Math.abs(pointA[0] - pointB[0]), Math.abs(pointA[1] - pointB[1]))
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1267_count_servers_that_communicate/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1267_count_servers_that_communicate/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6433ac2a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1267_count_servers_that_communicate/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1267\. Count Servers that Communicate
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a map of a server center, represented as a `m * n` integer matrix `grid`, where 1 means that on that cell there is a server and 0 means that it is no server. Two servers are said to communicate if they are on the same row or on the same column.
+
+Return the number of servers that communicate with any other server.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,0],[0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** No servers can communicate with others.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,0],[1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** All three servers can communicate with at least one other server.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,1,0,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The two servers in the first row can communicate with each other. The two servers in the third column can communicate with each other. The server at right bottom corner can't communicate with any other server.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m <= 250`
+* `1 <= n <= 250`
+* `grid[i][j] == 0 or 1`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countServers(grid: Array): Int {
+ val m = grid.size
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ val rowCount = IntArray(m)
+ val columnCount = IntArray(n)
+ var total = 0
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
+ rowCount[i]++
+ columnCount[j]++
+ total++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (grid[i][j] == 1 && rowCount[i] == 1 && columnCount[j] == 1) {
+ total--
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return total
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1268_search_suggestions_system/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1268_search_suggestions_system/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b6e6d1a1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1268_search_suggestions_system/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1268\. Search Suggestions System
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an array of strings `products` and a string `searchWord`.
+
+Design a system that suggests at most three product names from `products` after each character of `searchWord` is typed. Suggested products should have common prefix with `searchWord`. If there are more than three products with a common prefix return the three lexicographically minimums products.
+
+Return _a list of lists of the suggested products after each character of_ `searchWord` _is typed_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** products = ["mobile","mouse","moneypot","monitor","mousepad"], searchWord = "mouse"
+
+**Output:**
+
+ [
+ ["mobile","moneypot","monitor"],
+ ["mobile","moneypot","monitor"],
+ ["mouse","mousepad"],
+ ["mouse","mousepad"],
+ ["mouse","mousepad"]
+ ]
+
+**Explanation:** products sorted lexicographically = ["mobile","moneypot","monitor","mouse","mousepad"] After typing m and mo all products match and we show user ["mobile","moneypot","monitor"] After typing mou, mous and mouse the system suggests ["mouse","mousepad"]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** products = ["havana"], searchWord = "havana"
+
+**Output:** [["havana"],["havana"],["havana"],["havana"],["havana"],["havana"]]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** products = ["bags","baggage","banner","box","cloths"], searchWord = "bags"
+
+**Output:** [["baggage","bags","banner"],["baggage","bags","banner"],["baggage","bags"],["bags"]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= products.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= products[i].length <= 3000`
+* 1 <= sum(products[i].length) <= 2 * 104
+* All the strings of `products` are **unique**.
+* `products[i]` consists of lowercase English letters.
+* `1 <= searchWord.length <= 1000`
+* `searchWord` consists of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private var result: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+
+ fun suggestedProducts(products: Array, searchWord: String): List> {
+ // Sort products array first in lexicographically order
+ products.sort()
+ // Iterate through each "type" of searchWord by using substring
+ for (endIndex in 1..searchWord.length) {
+ val subSearchWord = searchWord.substring(0, endIndex)
+ // Find result for each "type" and add to result list
+ val curResult = findResult(products, subSearchWord)
+ result.add(curResult)
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+
+ private fun findResult(sortedProducts: Array, searchWord: String): List {
+ val curResult: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ // Binary search returns the first index possible search result
+ val startIndex = binarySearch(sortedProducts, searchWord)
+ // Iterate the following 3 string in products or exit if reach end first
+ var i = startIndex
+ while (i < startIndex + 3 && i < sortedProducts.size) {
+ val cur = sortedProducts[i]
+ // Only add to curResult if prefix match, otherwise break and return
+ if (isPrefix(searchWord, cur)) {
+ curResult.add(cur)
+ } else {
+ return curResult
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ return curResult
+ }
+
+ // Compare char by char to check if searchWord is a prefix of product
+ private fun isPrefix(searchWord: String, product: String): Boolean {
+ for (i in searchWord.indices) {
+ val sw = searchWord[i]
+ val pr = product[i]
+ return if (sw == pr) {
+ continue
+ } else {
+ false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+
+ // Binary search to find the first index of possible search result
+ // The word at the found index should be the least word that's greater or equal to
+ // the target search word lexicographically.
+ private fun binarySearch(sortedProducts: Array, searchWord: String): Int {
+ var start = 0
+ var end = sortedProducts.size - 1
+ while (start < end) {
+ val mid = (start + end) / 2
+ val midString = sortedProducts[mid]
+ // If mid word is lexicographically less than target word,
+ // continue search on right side
+ if (searchWord.compareTo(midString) > 0) {
+ start = mid + 1
+ continue
+ }
+ // If found the exact match
+ if (midString == searchWord) {
+ return mid
+ }
+ // If mid word is lexicographically greater than target word (possible solution)
+ if (searchWord.compareTo(midString) < 0) {
+ // If mid is at 0,
+ // or word at (mid - 1) is If mid word is lexicographically less than target word less than target word, this means we found the least word that's greater than target
+ return if (mid == 0 || searchWord.compareTo(sortedProducts[mid - 1]) > 0) {
+ mid
+ } else {
+ end = mid - 1
+ continue
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return start
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1269_number_of_ways_to_stay_in_the_same_place_after_some_steps/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1269_number_of_ways_to_stay_in_the_same_place_after_some_steps/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b1809ee4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1269_number_of_ways_to_stay_in_the_same_place_after_some_steps/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1269\. Number of Ways to Stay in the Same Place After Some Steps
+
+Hard
+
+You have a pointer at index `0` in an array of size `arrLen`. At each step, you can move 1 position to the left, 1 position to the right in the array, or stay in the same place (The pointer should not be placed outside the array at any time).
+
+Given two integers `steps` and `arrLen`, return the number of ways such that your pointer still at index `0` after **exactly** `steps` steps. Since the answer may be too large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** steps = 3, arrLen = 2
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** There are 4 differents ways to stay at index 0 after 3 steps.
+
+Right, Left, Stay
+
+Stay, Right, Left
+
+Right, Stay, Left
+
+Stay, Stay, Stay
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** steps = 2, arrLen = 4
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** There are 2 differents ways to stay at index 0 after 2 steps
+
+Right, Left
+
+Stay, Stay
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** steps = 4, arrLen = 2
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= steps <= 500`
+* 1 <= arrLen <= 106
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private var n = 0
+ private lateinit var dp: Array
+
+ private fun dfs(i: Int, st: Int): Int {
+ if (i < 0 || i >= n) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (st == 0) {
+ return if (i == 0) 1 else 0
+ }
+ if (dp[i][st] == -1) {
+ val mod = 1000000007
+ dp[i][st] = ((dfs(i + 1, st - 1) + dfs(i, st - 1)) % mod + dfs(i - 1, st - 1)) % mod
+ }
+ return dp[i][st]
+ }
+
+ fun numWays(steps: Int, arrLen: Int): Int {
+ n = Math.min(steps, arrLen)
+ dp = Array(n) { IntArray(steps + 1) }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ dp[i].fill(-1)
+ }
+ dfs(0, steps)
+ return dp[0][steps]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1275_find_winner_on_a_tic_tac_toe_game/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1275_find_winner_on_a_tic_tac_toe_game/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..11d8dc0a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1275_find_winner_on_a_tic_tac_toe_game/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1275\. Find Winner on a Tic Tac Toe Game
+
+Easy
+
+**Tic-tac-toe** is played by two players `A` and `B` on a `3 x 3` grid. The rules of Tic-Tac-Toe are:
+
+* Players take turns placing characters into empty squares `' '`.
+* The first player `A` always places `'X'` characters, while the second player `B` always places `'O'` characters.
+* `'X'` and `'O'` characters are always placed into empty squares, never on filled ones.
+* The game ends when there are **three** of the same (non-empty) character filling any row, column, or diagonal.
+* The game also ends if all squares are non-empty.
+* No more moves can be played if the game is over.
+
+Given a 2D integer array `moves` where moves[i] = [rowi, coli] indicates that the ith move will be played on grid[rowi][coli]. return _the winner of the game if it exists_ (`A` or `B`). In case the game ends in a draw return `"Draw"`. If there are still movements to play return `"Pending"`.
+
+You can assume that `moves` is valid (i.e., it follows the rules of **Tic-Tac-Toe**), the grid is initially empty, and `A` will play first.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** moves = \[\[0,0],[2,0],[1,1],[2,1],[2,2]]
+
+**Output:** "A"
+
+**Explanation:** A wins, they always play first.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+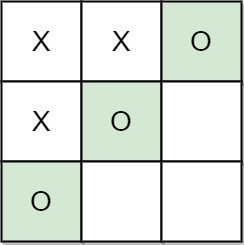
+
+**Input:** moves = \[\[0,0],[1,1],[0,1],[0,2],[1,0],[2,0]]
+
+**Output:** "B"
+
+**Explanation:** B wins.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** moves = \[\[0,0],[1,1],[2,0],[1,0],[1,2],[2,1],[0,1],[0,2],[2,2]]
+
+**Output:** "Draw"
+
+**Explanation:** The game ends in a draw since there are no moves to make.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= moves.length <= 9`
+* `moves[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= rowi, coli <= 2
+* There are no repeated elements on `moves`.
+* `moves` follow the rules of tic tac toe.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun tictactoe(moves: Array): String {
+ val board = Array(3) { arrayOfNulls(3) }
+ for (i in moves.indices) {
+ if (i % 2 == 0) {
+ board[moves[i][0]][moves[i][1]] = "X"
+ } else {
+ board[moves[i][0]][moves[i][1]] = "O"
+ }
+ if (i > 3 && wins(board) != "") {
+ return wins(board)
+ }
+ }
+ return if (moves.size == 9) "Draw" else "Pending"
+ }
+
+ private fun wins(board: Array>): String {
+ for (i in 0..2) {
+ if (board[i][0] == null) {
+ break
+ }
+ val str = board[i][0]
+ if (str == board[i][1] && str == board[i][2]) {
+ return getWinner(str)
+ }
+ }
+ for (j in 0..2) {
+ if (board[0][j] == null) {
+ break
+ }
+ val str = board[0][j]
+ if (str == board[1][j] && str == board[2][j]) {
+ return getWinner(str)
+ }
+ }
+ if (board[1][1] == null) {
+ return ""
+ }
+ val str = board[1][1]
+ return if (str == board[0][0] && str == board[2][2] || str == board[0][2] && str == board[2][0]) {
+ getWinner(str)
+ } else ""
+ }
+
+ private fun getWinner(str: String?): String {
+ return if (str == "X") {
+ "A"
+ } else {
+ "B"
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1276_number_of_burgers_with_no_waste_of_ingredients/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1276_number_of_burgers_with_no_waste_of_ingredients/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..58889b2c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1276_number_of_burgers_with_no_waste_of_ingredients/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1276\. Number of Burgers with No Waste of Ingredients
+
+Medium
+
+Given two integers `tomatoSlices` and `cheeseSlices`. The ingredients of different burgers are as follows:
+
+* **Jumbo Burger:** `4` tomato slices and `1` cheese slice.
+* **Small Burger:** `2` Tomato slices and `1` cheese slice.
+
+Return `[total_jumbo, total_small]` so that the number of remaining `tomatoSlices` equal to `0` and the number of remaining `cheeseSlices` equal to `0`. If it is not possible to make the remaining `tomatoSlices` and `cheeseSlices` equal to `0` return `[]`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** tomatoSlices = 16, cheeseSlices = 7
+
+**Output:** [1,6] **Explantion:** To make one jumbo burger and 6 small burgers we need 4\*1 + 2\*6 = 16 tomato and 1 + 6 = 7 cheese. There will be no remaining ingredients.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** tomatoSlices = 17, cheeseSlices = 4
+
+**Output:** [] **Explantion:** There will be no way to use all ingredients to make small and jumbo burgers.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** tomatoSlices = 4, cheeseSlices = 17
+
+**Output:** [] **Explantion:** Making 1 jumbo burger there will be 16 cheese remaining and making 2 small burgers there will be 15 cheese remaining.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= tomatoSlices, cheeseSlices <= 107
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numOfBurgers(tomatoSlices: Int, cheeseSlices: Int): List {
+ val numbers: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val numberOfCheese = cheeseSlices * 4
+ val remaining = numberOfCheese - tomatoSlices
+ if (remaining >= 0 && remaining % 2 != 1) {
+ val numberOfSmall = remaining / 2
+ val numberOfLarge = cheeseSlices - numberOfSmall
+ if (numberOfLarge < 0) {
+ return numbers
+ }
+ numbers.add(numberOfLarge)
+ numbers.add(numberOfSmall)
+ }
+ return numbers
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1277_count_square_submatrices_with_all_ones/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1277_count_square_submatrices_with_all_ones/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..69e97d14
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1277_count_square_submatrices_with_all_ones/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1277\. Count Square Submatrices with All Ones
+
+Medium
+
+Given a `m * n` matrix of ones and zeros, return how many **square** submatrices have all ones.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** matrix = [ [0,1,1,1], [1,1,1,1], [0,1,1,1] ]
+
+**Output:** 15
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are **10** squares of side 1.
+
+There are **4** squares of side 2.
+
+There is **1** square of side 3.
+
+Total number of squares = 10 + 4 + 1 = **15**.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** matrix = [ [1,0,1], [1,1,0], [1,1,0] ]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are **6** squares of side 1.
+
+There is **1** square of side 2.
+
+Total number of squares = 6 + 1 = **7**.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= arr.length <= 300`
+* `1 <= arr[0].length <= 300`
+* `0 <= arr[i][j] <= 1`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countSquares(matrix: Array): Int {
+ var total = 0
+ for (ints in matrix) {
+ total += ints[0]
+ }
+ for (i in 1 until matrix[0].size) {
+ total += matrix[0][i]
+ }
+ for (i in 1 until matrix.size) {
+ for (j in 1 until matrix[0].size) {
+ if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {
+ matrix[i][j] = (
+ Math.min(
+ matrix[i - 1][j - 1],
+ Math.min(matrix[i - 1][j], matrix[i][j - 1])
+ ) +
+ 1
+ )
+ }
+ total += matrix[i][j]
+ }
+ }
+ return total
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1278_palindrome_partitioning_iii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1278_palindrome_partitioning_iii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e6d04d37
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1278_palindrome_partitioning_iii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1278\. Palindrome Partitioning III
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a string `s` containing lowercase letters and an integer `k`. You need to :
+
+* First, change some characters of `s` to other lowercase English letters.
+* Then divide `s` into `k` non-empty disjoint substrings such that each substring is a palindrome.
+
+Return _the minimal number of characters that you need to change to divide the string_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abc", k = 2
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** You can split the string into "ab" and "c", and change 1 character in "ab" to make it palindrome.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aabbc", k = 3
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** You can split the string into "aa", "bb" and "c", all of them are palindrome.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "leetcode", k = 8
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= k <= s.length <= 100`.
+* `s` only contains lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun palindromePartition(s: String, k: Int): Int {
+ val n = s.length
+ val pal = Array(n + 1) { IntArray(n + 1) }
+ fillPal(s, n, pal)
+ val dp = Array(n + 1) { IntArray(k + 1) }
+ for (row in dp) {
+ row.fill(-1)
+ }
+ return calculateMinCost(s, 0, n, k, pal, dp)
+ }
+
+ private fun calculateMinCost(
+ s: String,
+ index: Int,
+ n: Int,
+ k: Int,
+ pal: Array,
+ dp: Array
+ ): Int {
+ if (index == n) {
+ return n
+ }
+ if (k == 1) {
+ return pal[index][n - 1]
+ }
+ if (dp[index][k] != -1) {
+ return dp[index][k]
+ }
+ var ans = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ for (i in index until n) {
+ ans = Math.min(ans, pal[index][i] + calculateMinCost(s, i + 1, n, k - 1, pal, dp))
+ }
+ dp[index][k] = ans
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun fillPal(s: String, n: Int, pal: Array) {
+ for (gap in 0 until n) {
+ var i = 0
+ var j = gap
+ while (j < n) {
+ if (gap == 0) {
+ pal[i][i] = 0
+ } else if (gap == 1) {
+ if (s[i] == s[i + 1]) {
+ pal[i][i + 1] = 0
+ } else {
+ pal[i][i + 1] = 1
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (s[i] == s[j]) {
+ pal[i][j] = pal[i + 1][j - 1]
+ } else {
+ pal[i][j] = pal[i + 1][j - 1] + 1
+ }
+ }
+ i++
+ j++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1280_students_and_examinations/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1280_students_and_examinations/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e20d0970
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1280_students_and_examinations/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1280\. Students and Examinations
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Students`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | student_id | int |
+ | student_name | varchar |
+ +---------------+---------+
+
+student_id is the primary key for this table. Each row of this table contains the ID and the name of one student in the school.
+
+Table: `Subjects`
+
+ +--------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +--------------+---------+
+ | subject_name | varchar |
+ +--------------+---------+
+
+subject_name is the primary key for this table. Each row of this table contains the name of one subject in the school.
+
+Table: `Examinations`
+
+ +--------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +--------------+---------+
+ | student_id | int |
+ | subject_name | varchar |
+ +--------------+---------+
+
+There is no primary key for this table. It may contain duplicates. Each student from the Students table takes every course from the Subjects table. Each row of this table indicates that a student with ID student_id attended the exam of subject_name.
+
+Write an SQL query to find the number of times each student attended each exam.
+
+Return the result table ordered by `student_id` and `subject_name`.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** Students table:
+
+ +------------+--------------+
+ | student_id | student_name |
+ +------------+--------------+
+ | 1 | Alice |
+ | 2 | Bob |
+ | 13 | John |
+ | 6 | Alex |
+ +------------+--------------+
+
+Subjects table:
+
+ +--------------+
+ | subject_name |
+ +--------------+
+ | Math |
+ | Physics |
+ | Programming |
+ +--------------+
+
+Examinations table:
+
+ +------------+--------------+
+ | student_id | subject_name |
+ +------------+--------------+
+ | 1 | Math |
+ | 1 | Physics |
+ | 1 | Programming |
+ | 2 | Programming |
+ | 1 | Physics |
+ | 1 | Math |
+ | 13 | Math |
+ | 13 | Programming |
+ | 13 | Physics |
+ | 2 | Math |
+ | 1 | Math |
+ +------------+--------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +------------+--------------+--------------+----------------+
+ | student_id | student_name | subject_name | attended_exams |
+ +------------+--------------+--------------+----------------+
+ | 1 | Alice | Math | 3 |
+ | 1 | Alice | Physics | 2 |
+ | 1 | Alice | Programming | 1 |
+ | 2 | Bob | Math | 1 |
+ | 2 | Bob | Physics | 0 |
+ | 2 | Bob | Programming | 1 |
+ | 6 | Alex | Math | 0 |
+ | 6 | Alex | Physics | 0 |
+ | 6 | Alex | Programming | 0 |
+ | 13 | John | Math | 1 |
+ | 13 | John | Physics | 1 |
+ | 13 | John | Programming | 1 |
+ +------------+--------------+--------------+----------------+
+
+**Explanation:** The result table should contain all students and all subjects. Alice attended the Math exam 3 times, the Physics exam 2 times, and the Programming exam 1 time. Bob attended the Math exam 1 time, the Programming exam 1 time, and did not attend the Physics exam. Alex did not attend any exams. John attended the Math exam 1 time, the Physics exam 1 time, and the Programming exam 1 time.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT s.student_id, s.student_name, sub.subject_name,
+sum(case when sub.subject_name = e.subject_name then 1 else 0 end) as attended_exams
+FROM Students s
+cross join subjects sub
+left join examinations e on e.student_id=s.student_id
+group by 1,2,3
+order by 1,2,3
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1281_subtract_the_product_and_sum_of_digits_of_an_integer/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1281_subtract_the_product_and_sum_of_digits_of_an_integer/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2f23259c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1281_subtract_the_product_and_sum_of_digits_of_an_integer/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1281\. Subtract the Product and Sum of Digits of an Integer
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer number `n`, return the difference between the product of its digits and the sum of its digits.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 234
+
+**Output:** 15
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Product of digits = 2 \* 3 \* 4 = 24
+
+Sum of digits = 2 + 3 + 4 = 9
+
+Result = 24 - 9 = 15
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4421
+
+**Output:** 21
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Product of digits = 4 \* 4 \* 2 \* 1 = 32
+
+Sum of digits = 4 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 11
+
+Result = 32 - 11 = 21
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 10^5`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun subtractProductAndSum(n: Int): Int {
+ var n = n
+ var product = 1
+ var sum = 0
+ while (n != 0) {
+ val digit = n % 10
+ product = product * digit
+ sum = sum + digit
+ n /= 10
+ }
+ return product - sum
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1282_group_the_people_given_the_group_size_they_belong_to/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1282_group_the_people_given_the_group_size_they_belong_to/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4e504728
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1282_group_the_people_given_the_group_size_they_belong_to/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1282\. Group the People Given the Group Size They Belong To
+
+Medium
+
+There are `n` people that are split into some unknown number of groups. Each person is labeled with a **unique ID** from `0` to `n - 1`.
+
+You are given an integer array `groupSizes`, where `groupSizes[i]` is the size of the group that person `i` is in. For example, if `groupSizes[1] = 3`, then person `1` must be in a group of size `3`.
+
+Return _a list of groups such that each person `i` is in a group of size `groupSizes[i]`_.
+
+Each person should appear in **exactly one group**, and every person must be in a group. If there are multiple answers, **return any of them**. It is **guaranteed** that there will be **at least one** valid solution for the given input.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** groupSizes = [3,3,3,3,3,1,3]
+
+**Output:** [[5],[0,1,2],[3,4,6]]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The first group is [5]. The size is 1, and groupSizes[5] = 1.
+
+The second group is [0,1,2]. The size is 3, and groupSizes[0] = groupSizes[1] = groupSizes[2] = 3.
+
+The third group is [3,4,6]. The size is 3, and groupSizes[3] = groupSizes[4] = groupSizes[6] = 3.
+
+Other possible solutions are [[2,1,6],[5],[0,4,3]] and [[5],[0,6,2],[4,3,1]].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** groupSizes = [2,1,3,3,3,2]
+
+**Output:** [[1],[0,5],[2,3,4]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `groupSizes.length == n`
+* `1 <= n <= 500`
+* `1 <= groupSizes[i] <= n`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun groupThePeople(groupSizes: IntArray): List> {
+ val map: MutableMap> = HashMap()
+ for (i in groupSizes.indices) {
+ val list = map.getOrDefault(groupSizes[i], ArrayList())
+ list.add(i)
+ map[groupSizes[i]] = list
+ }
+ val result: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ for ((key, list) in map) {
+ var i = 0
+ do {
+ result.add(list.subList(i, i + key))
+ i += key
+ } while (i + key <= list.size)
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1283_find_the_smallest_divisor_given_a_threshold/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1283_find_the_smallest_divisor_given_a_threshold/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f54e7282
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1283_find_the_smallest_divisor_given_a_threshold/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1283\. Find the Smallest Divisor Given a Threshold
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `threshold`, we will choose a positive integer `divisor`, divide all the array by it, and sum the division's result. Find the **smallest** `divisor` such that the result mentioned above is less than or equal to `threshold`.
+
+Each result of the division is rounded to the nearest integer greater than or equal to that element. (For example: `7/3 = 3` and `10/2 = 5`).
+
+The test cases are generated so that there will be an answer.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,5,9], threshold = 6
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** We can get a sum to 17 (1+2+5+9) if the divisor is 1. If the divisor is 4 we can get a sum of 7 (1+1+2+3) and if the divisor is 5 the sum will be 5 (1+1+1+2).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [44,22,33,11,1], threshold = 5
+
+**Output:** 44
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 5 * 104
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 106
+* nums.length <= threshold <= 106
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun smallestDivisor(nums: IntArray, threshold: Int): Int {
+ var l = 1
+ var r = 1000000
+ while (l <= r) {
+ val mid = l + (r - l) / 2
+ if (helper(mid, nums) > threshold) {
+ l = mid + 1
+ } else {
+ r = mid - 1
+ }
+ }
+ return l
+ }
+
+ private fun helper(mid: Int, nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var res = 0
+ for (num in nums) {
+ res += (num + mid - 1) / mid
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1284_minimum_number_of_flips_to_convert_binary_matrix_to_zero_matrix/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1284_minimum_number_of_flips_to_convert_binary_matrix_to_zero_matrix/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..552f5f69
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1284_minimum_number_of_flips_to_convert_binary_matrix_to_zero_matrix/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1284\. Minimum Number of Flips to Convert Binary Matrix to Zero Matrix
+
+Hard
+
+Given a `m x n` binary matrix `mat`. In one step, you can choose one cell and flip it and all the four neighbors of it if they exist (Flip is changing `1` to `0` and `0` to `1`). A pair of cells are called neighbors if they share one edge.
+
+Return the _minimum number of steps_ required to convert `mat` to a zero matrix or `-1` if you cannot.
+
+A **binary matrix** is a matrix with all cells equal to `0` or `1` only.
+
+A **zero matrix** is a matrix with all cells equal to `0`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+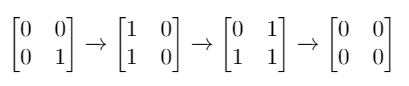
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[0,0],[0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** One possible solution is to flip (1, 0) then (0, 1) and finally (1, 1) as shown.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[0]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Given matrix is a zero matrix. We do not need to change it.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[1,0,0],[1,0,0]]
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** Given matrix cannot be a zero matrix.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == mat.length`
+* `n == mat[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 3`
+* `mat[i][j]` is either `0` or `1`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.ArrayDeque
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ private lateinit var visited: MutableSet
+
+ private fun isValid(x: Int, y: Int, r: Int, c: Int): Boolean {
+ return x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < r && y < c
+ }
+
+ private fun next(n: Int, r: Int, c: Int): List {
+ val ans: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val dx = intArrayOf(0, 0, 0, 1, -1)
+ val dy = intArrayOf(0, 1, -1, 0, 0)
+ for (i in 0 until r) {
+ for (j in 0 until c) {
+ var newMask = n
+ for (k in dx.indices) {
+ val nx = i + dx[k]
+ val ny = j + dy[k]
+ if (isValid(nx, ny, r, c)) {
+ newMask = newMask xor (1 shl nx * 3 + ny)
+ }
+ }
+ if (visited.add(newMask)) {
+ ans.add(newMask)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ fun minFlips(mat: Array): Int {
+ var mask = 0
+ val r = mat.size
+ val c = mat[0].size
+ if (r == 1 && c == 1) {
+ return if (mat[0][0] == 0) 0 else 1
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until r) {
+ for (j in 0 until c) {
+ mask = mask or (mat[i][j] shl i * 3 + j)
+ }
+ }
+ if (mask == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ visited = HashSet()
+ val q: Queue = ArrayDeque()
+ var count = 1
+ q.add(mask)
+ visited.add(mask)
+ while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val qSize = q.size
+ for (i in 0 until qSize) {
+ val currMask = q.poll()
+ val nextStates = next(currMask, r, c)
+ for (nextState in nextStates) {
+ if (nextState == 0) {
+ return count
+ }
+ q.add(nextState)
+ }
+ }
+ count++
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1286_iterator_for_combination/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1286_iterator_for_combination/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ba326f8b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1286_iterator_for_combination/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1286\. Iterator for Combination
+
+Medium
+
+Design the `CombinationIterator` class:
+
+* `CombinationIterator(string characters, int combinationLength)` Initializes the object with a string `characters` of **sorted distinct** lowercase English letters and a number `combinationLength` as arguments.
+* `next()` Returns the next combination of length `combinationLength` in **lexicographical order**.
+* `hasNext()` Returns `true` if and only if there exists a next combination.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input** ["CombinationIterator", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"] [["abc", 2], [], [], [], [], [], []]
+
+**Output:** [null, "ab", true, "ac", true, "bc", false]
+
+**Explanation:** CombinationIterator itr = new CombinationIterator("abc", 2); itr.next(); // return "ab" itr.hasNext(); // return True itr.next(); // return "ac" itr.hasNext(); // return True itr.next(); // return "bc" itr.hasNext(); // return False
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= combinationLength <= characters.length <= 15`
+* All the characters of `characters` are **unique**.
+* At most 104 calls will be made to `next` and `hasNext`.
+* It is guaranteed that all calls of the function `next` are valid.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class CombinationIterator(characters: String, private val combinationLength: Int) {
+ private val list: MutableList
+ private var index = 0
+ private val visited: BooleanArray
+
+ init {
+ list = ArrayList()
+ visited = BooleanArray(characters.length)
+ buildAllCombinations(characters, 0, StringBuilder(), visited)
+ }
+
+ private fun buildAllCombinations(
+ characters: String,
+ start: Int,
+ sb: StringBuilder,
+ visited: BooleanArray
+ ) {
+ if (sb.length == combinationLength) {
+ list.add(sb.toString())
+ } else {
+ var i = start
+ while (i < characters.length) {
+ if (!visited[i]) {
+ sb.append(characters[i])
+ visited[i] = true
+ buildAllCombinations(characters, i++, sb, visited)
+ visited[i - 1] = false
+ sb.setLength(sb.length - 1)
+ } else {
+ i++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ operator fun next(): String {
+ return list[index++]
+ }
+
+ operator fun hasNext(): Boolean {
+ return index < list.size
+ }
+}
+/*
+ * Your CombinationIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * var obj = CombinationIterator(characters, combinationLength)
+ * var param_1 = obj.next()
+ * var param_2 = obj.hasNext()
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1287_element_appearing_more_than_25_in_sorted_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1287_element_appearing_more_than_25_in_sorted_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..21f57058
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1287_element_appearing_more_than_25_in_sorted_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1287\. Element Appearing More Than 25% In Sorted Array
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer array **sorted** in non-decreasing order, there is exactly one integer in the array that occurs more than 25% of the time, return that integer.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,2,6,6,6,6,7,10]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,1]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= arr.length <= 104
+* 0 <= arr[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findSpecialInteger(arr: IntArray): Int {
+ val quarter = arr.size / 4
+ for (i in 0 until arr.size - quarter) {
+ if (arr[i] == arr[i + quarter]) {
+ return arr[i]
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1288_remove_covered_intervals/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1288_remove_covered_intervals/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5a3b2ea4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1288_remove_covered_intervals/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1288\. Remove Covered Intervals
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array `intervals` where intervals[i] = [li, ri] represent the interval [li, ri), remove all intervals that are covered by another interval in the list.
+
+The interval `[a, b)` is covered by the interval `[c, d)` if and only if `c <= a` and `b <= d`.
+
+Return _the number of remaining intervals_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** intervals = \[\[1,4],[3,6],[2,8]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Interval [3,6] is covered by [2,8], therefore it is removed.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** intervals = \[\[1,4],[2,3]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= intervals.length <= 1000`
+* `intervals[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= li < ri <= 105
+* All the given intervals are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun removeCoveredIntervals(intervals: Array): Int {
+ val q: Queue = PriorityQueue { a: IntArray, b: IntArray
+ ->
+ if (a[0] == b[0]) b[1] - a[1] else a[0] - b[0]
+ }
+ for (interval in intervals) {
+ q.offer(interval)
+ }
+ var prev = q.poll()
+ var count = 0
+ while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val curr = q.poll()
+ if (curr[0] >= prev[0] && curr[1] <= prev[1]) {
+ count++
+ } else {
+ prev = curr
+ }
+ }
+ return intervals.size - count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1289_minimum_falling_path_sum_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1289_minimum_falling_path_sum_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d9b4e346
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1289_minimum_falling_path_sum_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1289\. Minimum Falling Path Sum II
+
+Hard
+
+Given an `n x n` integer matrix `grid`, return _the minimum sum of a **falling path with non-zero shifts**_.
+
+A **falling path with non-zero shifts** is a choice of exactly one element from each row of `grid` such that no two elements chosen in adjacent rows are in the same column.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** arr = \[\[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
+
+**Output:** 13
+
+**Explanation:** The possible falling paths are: [1,5,9], [1,5,7], [1,6,7], [1,6,8], [2,4,8], [2,4,9], [2,6,7], [2,6,8], [3,4,8], [3,4,9], [3,5,7], [3,5,9] The falling path with the smallest sum is [1,5,7], so the answer is 13.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[7]]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == grid.length == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= n <= 200`
+* `-99 <= grid[i][j] <= 99`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minFallingPathSum(grid: Array): Int {
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ var prev = IntArray(n)
+ var curr = IntArray(n)
+ var prevMinOne = 0
+ var prevMinTwo = 0
+ for (ints in grid) {
+ var currMinOne = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var currMinTwo = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ val prevMin = if (prev[j] == prevMinOne) prevMinTwo else prevMinOne
+ curr[j] = ints[j] + prevMin
+ if (curr[j] < currMinOne) {
+ currMinTwo = currMinOne
+ currMinOne = curr[j]
+ } else if (curr[j] < currMinTwo) {
+ currMinTwo = curr[j]
+ }
+ }
+ prevMinOne = currMinOne
+ prevMinTwo = currMinTwo
+ // reuse curr array, avoid new int[] in every row
+ val temp = prev
+ prev = curr
+ curr = temp
+ }
+ return prevMinOne
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1290_convert_binary_number_in_a_linked_list_to_integer/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1290_convert_binary_number_in_a_linked_list_to_integer/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..51d29d0b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1290_convert_binary_number_in_a_linked_list_to_integer/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1290\. Convert Binary Number in a Linked List to Integer
+
+Easy
+
+Given `head` which is a reference node to a singly-linked list. The value of each node in the linked list is either `0` or `1`. The linked list holds the binary representation of a number.
+
+Return the _decimal value_ of the number in the linked list.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** head = [1,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** (101) in base 2 = (5) in base 10
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** head = [0]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The Linked List is not empty.
+* Number of nodes will not exceed `30`.
+* Each node's value is either `0` or `1`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.ListNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var li = ListNode(5)
+ * var v = li.`val`
+ * Definition for singly-linked list.
+ * class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var next: ListNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun getDecimalValue(head: ListNode?): Int {
+ var l = 0
+ var curr = head
+ while (curr!!.next != null) {
+ l++
+ curr = curr.next
+ }
+ curr = head
+ var num = 0
+ while (curr != null) {
+ num += curr.`val` * Math.pow(2.0, l--.toDouble()).toInt()
+ curr = curr.next
+ }
+ return num
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1291_sequential_digits/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1291_sequential_digits/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43454b76
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1291_sequential_digits/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1291\. Sequential Digits
+
+Medium
+
+An integer has _sequential digits_ if and only if each digit in the number is one more than the previous digit.
+
+Return a **sorted** list of all the integers in the range `[low, high]` inclusive that have sequential digits.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** low = 100, high = 300
+
+**Output:** [123,234]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** low = 1000, high = 13000
+
+**Output:** [1234,2345,3456,4567,5678,6789,12345]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `10 <= low <= high <= 10^9`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun sequentialDigits(low: Int, high: Int): List {
+ val arr = intArrayOf(
+ 12, 23, 34, 45, 56, 67, 78, 89, 123, 234, 345, 456, 567, 678, 789, 1234, 2345, 3456,
+ 4567, 5678, 6789, 12345, 23456, 34567, 45678, 56789, 123456, 234567, 345678, 456789,
+ 1234567, 2345678, 3456789, 12345678, 23456789, 123456789
+ )
+ val result: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (j in arr) {
+ // 234 148 234 256
+ if (j in low..high) {
+ result.add(j)
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1292_maximum_side_length_of_a_square_with_sum_less_than_or_equal_to_threshold/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1292_maximum_side_length_of_a_square_with_sum_less_than_or_equal_to_threshold/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7801e7e9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1292_maximum_side_length_of_a_square_with_sum_less_than_or_equal_to_threshold/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1292\. Maximum Side Length of a Square with Sum Less than or Equal to Threshold
+
+Medium
+
+Given a `m x n` matrix `mat` and an integer `threshold`, return _the maximum side-length of a square with a sum less than or equal to_ `threshold` _or return_ `0` _if there is no such square_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[1,1,3,2,4,3,2],[1,1,3,2,4,3,2],[1,1,3,2,4,3,2]], threshold = 4
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The maximum side length of square with sum less than 4 is 2 as shown.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2]], threshold = 1
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == mat.length`
+* `n == mat[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 300`
+* 0 <= mat[i][j] <= 104
+* 0 <= threshold <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxSideLength(mat: Array, threshold: Int): Int {
+ val m = mat.size
+ val n = mat[0].size
+ val prefix = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (i == 0 && j == 0) {
+ prefix[i][j] = mat[i][j]
+ } else if (i == 0) {
+ prefix[i][j] = mat[i][j] + prefix[0][j - 1]
+ } else if (j == 0) {
+ prefix[i][j] = mat[i][j] + prefix[i - 1][0]
+ } else {
+ prefix[i][j] = mat[i][j] + prefix[i][j - 1] + prefix[i - 1][j] - prefix[i - 1][j - 1]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ var low = 1
+ var high = Math.min(m, n)
+ var ans = 0
+ while (low <= high) {
+ val mid = (low + high) / 2
+ if (min(mid, prefix) > threshold) {
+ high = mid - 1
+ } else {
+ ans = mid
+ low = mid + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ fun min(length: Int, prefix: Array): Int {
+ var min = 0
+ for (i in length - 1 until prefix.size) {
+ for (j in length - 1 until prefix[0].size) {
+ min = if (i == length - 1 && j == length - 1) {
+ prefix[i][j]
+ } else if (i - length < 0) {
+ Math.min(min, prefix[i][j] - prefix[i][j - length])
+ } else if (j - length < 0) {
+ Math.min(min, prefix[i][j] - prefix[i - length][j])
+ } else {
+ Math.min(
+ min,
+ (
+ prefix[i][j] -
+ prefix[i][j - length] -
+ prefix[i - length][j]
+ ) +
+ prefix[i - length][j - length]
+ )
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return min
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1293_shortest_path_in_a_grid_with_obstacles_elimination/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1293_shortest_path_in_a_grid_with_obstacles_elimination/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..72d11cb1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1293_shortest_path_in_a_grid_with_obstacles_elimination/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1293\. Shortest Path in a Grid with Obstacles Elimination
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an `m x n` integer matrix `grid` where each cell is either `0` (empty) or `1` (obstacle). You can move up, down, left, or right from and to an empty cell in **one step**.
+
+Return _the minimum number of **steps** to walk from the upper left corner_ `(0, 0)` _to the lower right corner_ `(m - 1, n - 1)` _given that you can eliminate **at most**_ `k` _obstacles_. If it is not possible to find such walk return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,0],[0,1,1],[0,0,0]], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The shortest path without eliminating any obstacle is 10.
+
+The shortest path with one obstacle elimination at position (3,2) is 6. Such path is (0,0) -> (0,1) -> (0,2) -> (1,2) -> (2,2) -> **(3,2)** -> (4,2).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[0,1,1],[1,1,1],[1,0,0]], k = 1
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** We need to eliminate at least two obstacles to find such a walk.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 40`
+* `1 <= k <= m * n`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either `0` **or** `1`.
+* `grid[0][0] == grid[m - 1][n - 1] == 0`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun shortestPath(grid: Array, k: Int): Int {
+ if (grid.size == 1 && grid[0].size == 1 && grid[0][0] == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ // 4 potential moves:
+ val moves = arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 0), intArrayOf(-1, 0), intArrayOf(0, 1), intArrayOf(0, -1))
+ val m = grid.size
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ // use obs to record the min total obstacles when traverse to the position
+ val obs = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ obs[i][j] = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ }
+ }
+ obs[0][0] = 0
+ // Queue to record {x cord, y cord, total obstacles when trvavers to this position}
+ val que: Queue = LinkedList()
+ que.add(intArrayOf(0, 0, 0))
+ var level = 0
+ while (que.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val size = que.size
+ level++
+ for (i in 0 until size) {
+ val current = que.poll()
+ for (move in moves) {
+ val next = intArrayOf(current[0] + move[0], current[1] + move[1])
+ if (next[0] == m - 1 && next[1] == n - 1) {
+ return level
+ }
+ if (next[0] < 0 || next[0] > m - 1 || next[1] < 0 || next[1] > n - 1) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if (current[2] + grid[next[0]][next[1]] < obs[next[0]][next[1]] &&
+ current[2] + grid[next[0]][next[1]] <= k
+ ) {
+ obs[next[0]][next[1]] = current[2] + grid[next[0]][next[1]]
+ que.add(intArrayOf(next[0], next[1], obs[next[0]][next[1]]))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1295_find_numbers_with_even_number_of_digits/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1295_find_numbers_with_even_number_of_digits/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e24b8f1f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1295_find_numbers_with_even_number_of_digits/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1295\. Find Numbers with Even Number of Digits
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array `nums` of integers, return how many of them contain an **even number** of digits.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [12,345,2,6,7896]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+12 contains 2 digits (even number of digits).
+
+345 contains 3 digits (odd number of digits).
+
+2 contains 1 digit (odd number of digits).
+
+6 contains 1 digit (odd number of digits).
+
+7896 contains 4 digits (even number of digits).
+
+Therefore only 12 and 7896 contain an even number of digits.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [555,901,482,1771]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** Only 1771 contains an even number of digits.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 500`
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findNumbers(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ // initialising variable to hold number of digits and numbers having even number of digits
+ var digitCount = 0
+ var evendigitCount = 0
+ // traversing through the array
+ for (num in nums) {
+ var number = num
+ while (number != 0) {
+ // counting digits for each number
+ digitCount++
+ number /= 10
+ }
+ // incrementing variable for numbers having even number of digits
+ if (digitCount % 2 == 0) {
+ evendigitCount++
+ }
+ // reassigning the value to reset digits for next number in iteration
+ digitCount = 0
+ }
+ return evendigitCount
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1296_divide_array_in_sets_of_k_consecutive_numbers/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1296_divide_array_in_sets_of_k_consecutive_numbers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8dc54451
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1296_divide_array_in_sets_of_k_consecutive_numbers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1296\. Divide Array in Sets of K Consecutive Numbers
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `nums` and a positive integer `k`, check whether it is possible to divide this array into sets of `k` consecutive numbers.
+
+Return `true` _if it is possible_. Otherwise, return `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5,6], k = 4
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Array can be divided into [1,2,3,4] and [3,4,5,6].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,2,1,2,3,4,3,4,5,9,10,11], k = 3
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Array can be divided into [1,2,3] , [2,3,4] , [3,4,5] and [9,10,11].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4], k = 3
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** Each array should be divided in subarrays of size 3.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= k <= nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+**Note:** This question is the same as 846: [https://leetcode.com/problems/hand-of-straights/](https://leetcode.com/problems/hand-of-straights/)
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun isPossibleDivide(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Boolean {
+ nums.sort()
+ val map = HashMap()
+ for (num in nums) {
+ map[num] = map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1
+ }
+ for (num in nums) {
+ if (map[num] == 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ for (v in num until num + k) {
+ if (!map.containsKey(v) || map[v] == 0) {
+ return false
+ } else {
+ map[v] = map[v]!! - 1
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1297_maximum_number_of_occurrences_of_a_substring/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1297_maximum_number_of_occurrences_of_a_substring/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c42e40b3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1297_maximum_number_of_occurrences_of_a_substring/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1297\. Maximum Number of Occurrences of a Substring
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string `s`, return the maximum number of ocurrences of **any** substring under the following rules:
+
+* The number of unique characters in the substring must be less than or equal to `maxLetters`.
+* The substring size must be between `minSize` and `maxSize` inclusive.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aababcaab", maxLetters = 2, minSize = 3, maxSize = 4
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Substring "aab" has 2 ocurrences in the original string.
+
+It satisfies the conditions, 2 unique letters and size 3 (between minSize and maxSize).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aaaa", maxLetters = 1, minSize = 3, maxSize = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Substring "aaa" occur 2 times in the string. It can overlap.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `1 <= maxLetters <= 26`
+* `1 <= minSize <= maxSize <= min(26, s.length)`
+* `s` consists of only lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("UNUSED_PARAMETER")
+class Solution {
+ fun maxFreq(s: String, max: Int, minSize: Int, maxSize: Int): Int {
+ // the map of occurrences
+ val sub2Count: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ // sliding window indices
+ var lo = 0
+ var hi = minSize - 1
+ var maxCount = 0
+ // unique letters counter
+ val uniq = CharArray(26)
+ var uniqCount = 0
+ // initial window calculation - `hi` is excluded here!
+ for (ch in s.substring(lo, hi).toCharArray()) {
+ uniq[ch.code - 'a'.code] = uniq[ch.code - 'a'.code] + 1.toChar().code
+ if (uniq[ch.code - 'a'.code].code == 1) {
+ uniqCount++
+ }
+ }
+ while (hi < s.length) {
+ // handle increment of hi
+ val hiCh = s[hi]
+ uniq[hiCh.code - 'a'.code] = uniq[hiCh.code - 'a'.code] + 1.toChar().code
+ if (uniq[hiCh.code - 'a'.code].code == 1) {
+ uniqCount++
+ }
+ ++hi
+ // add the substring to the map of occurences
+ val sub = s.substring(lo, hi)
+ if (uniqCount <= max) {
+ var count = 1
+ if (sub2Count.containsKey(sub)) {
+ count += sub2Count[sub]!!
+ }
+ sub2Count[sub] = count
+ maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, count)
+ }
+ // handle increment of lo
+ val loCh = s[lo]
+ uniq[loCh.code - 'a'.code] = uniq[loCh.code - 'a'.code] - 1.toChar().code
+ if (uniq[loCh.code - 'a'.code].code == 0) {
+ uniqCount--
+ }
+ ++lo
+ }
+ return maxCount
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1298_maximum_candies_you_can_get_from_boxes/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1298_maximum_candies_you_can_get_from_boxes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..579138ab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1298_maximum_candies_you_can_get_from_boxes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1298\. Maximum Candies You Can Get from Boxes
+
+Hard
+
+You have `n` boxes labeled from `0` to `n - 1`. You are given four arrays: `status`, `candies`, `keys`, and `containedBoxes` where:
+
+* `status[i]` is `1` if the ith box is open and `0` if the ith box is closed,
+* `candies[i]` is the number of candies in the ith box,
+* `keys[i]` is a list of the labels of the boxes you can open after opening the ith box.
+* `containedBoxes[i]` is a list of the boxes you found inside the ith box.
+
+You are given an integer array `initialBoxes` that contains the labels of the boxes you initially have. You can take all the candies in **any open box** and you can use the keys in it to open new boxes and you also can use the boxes you find in it.
+
+Return _the maximum number of candies you can get following the rules above_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** status = [1,0,1,0], candies = [7,5,4,100], keys = \[\[],[],[1],[]], containedBoxes = \[\[1,2],[3],[],[]], initialBoxes = [0]
+
+**Output:** 16
+
+**Explanation:** You will be initially given box 0. You will find 7 candies in it and boxes 1 and 2.
+
+Box 1 is closed and you do not have a key for it so you will open box 2. You will find 4 candies and a key to box 1 in box 2.
+
+In box 1, you will find 5 candies and box 3 but you will not find a key to box 3 so box 3 will remain closed.
+
+Total number of candies collected = 7 + 4 + 5 = 16 candy.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** status = [1,0,0,0,0,0], candies = [1,1,1,1,1,1], keys = \[\[1,2,3,4,5],[],[],[],[],[]], containedBoxes = \[\[1,2,3,4,5],[],[],[],[],[]], initialBoxes = [0]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** You have initially box 0. Opening it you can find boxes 1,2,3,4 and 5 and their keys.
+
+The total number of candies will be 6.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == status.length == candies.length == keys.length == containedBoxes.length`
+* `1 <= n <= 1000`
+* `status[i]` is either `0` or `1`.
+* `1 <= candies[i] <= 1000`
+* `0 <= keys[i].length <= n`
+* `0 <= keys[i][j] < n`
+* All values of `keys[i]` are **unique**.
+* `0 <= containedBoxes[i].length <= n`
+* `0 <= containedBoxes[i][j] < n`
+* All values of `containedBoxes[i]` are unique.
+* Each box is contained in one box at most.
+* `0 <= initialBoxes.length <= n`
+* `0 <= initialBoxes[i] < n`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxCandies(
+ status: IntArray,
+ candies: IntArray,
+ keys: Array,
+ containedBoxes: Array,
+ initialBoxes: IntArray
+ ): Int {
+ var collectedCandies = 0
+ val boxes: Queue = LinkedList()
+ for (box in initialBoxes) {
+ boxes.offer(box)
+ }
+ var unseen = 0
+ while (boxes.isNotEmpty()) {
+ if (unseen == boxes.size) {
+ break
+ }
+ val curBox = boxes.poll()
+ if (status[curBox] == 0) {
+ unseen++
+ boxes.offer(curBox)
+ } else {
+ unseen = 0
+ // collect candies
+ collectedCandies += candies[curBox]
+ // open keys
+ for (key in keys[curBox]) {
+ status[key] = 1
+ }
+ // collect contained boxes
+ for (box in containedBoxes[curBox]) {
+ boxes.offer(box)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return collectedCandies
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1299_replace_elements_with_greatest_element_on_right_side/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1299_replace_elements_with_greatest_element_on_right_side/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ea371e04
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1299_replace_elements_with_greatest_element_on_right_side/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1299\. Replace Elements with Greatest Element on Right Side
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array `arr`, replace every element in that array with the greatest element among the elements to its right, and replace the last element with `-1`.
+
+After doing so, return the array.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [17,18,5,4,6,1]
+
+**Output:** [18,6,6,6,1,-1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+- index 0 --> the greatest element to the right of index 0 is index 1 (18).
+
+- index 1 --> the greatest element to the right of index 1 is index 4 (6).
+
+- index 2 --> the greatest element to the right of index 2 is index 4 (6).
+
+- index 3 --> the greatest element to the right of index 3 is index 4 (6).
+
+- index 4 --> the greatest element to the right of index 4 is index 5 (1).
+
+- index 5 --> there are no elements to the right of index 5, so we put -1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [400]
+
+**Output:** [-1]
+
+**Explanation:** There are no elements to the right of index 0.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= arr.length <= 104
+* 1 <= arr[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun replaceElements(arr: IntArray): IntArray {
+ var max = -1
+ for (i in arr.indices.reversed()) {
+ val temp = arr[i]
+ arr[i] = max
+ max = Math.max(max, temp)
+ }
+ return arr
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1300_sum_of_mutated_array_closest_to_target/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1300_sum_of_mutated_array_closest_to_target/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ae12eb80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1201_1300/s1300_sum_of_mutated_array_closest_to_target/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1300\. Sum of Mutated Array Closest to Target
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `arr` and a target value `target`, return the integer `value` such that when we change all the integers larger than `value` in the given array to be equal to `value`, the sum of the array gets as close as possible (in absolute difference) to `target`.
+
+In case of a tie, return the minimum such integer.
+
+Notice that the answer is not neccesarilly a number from `arr`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [4,9,3], target = 10
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** When using 3 arr converts to [3, 3, 3] which sums 9 and that's the optimal answer.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [2,3,5], target = 10
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [60864,25176,27249,21296,20204], target = 56803
+
+**Output:** 11361
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= arr.length <= 104
+* 1 <= arr[i], target <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findBestValue(arr: IntArray, target: Int): Int {
+ arr.sort()
+ val n = arr.size
+ var lo = 0
+ var hi = arr[n - 1]
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var ans = -1
+ while (lo <= hi) {
+ val mid = (lo + hi) / 2
+ val m = check(mid, arr, target)
+ val l = check(mid - 1, arr, target)
+ val r = check(mid + 1, arr, target)
+ if (m < min || m == min && ans > mid) {
+ min = m
+ ans = mid
+ } else if (l <= r) {
+ hi = mid - 1
+ } else {
+ lo = mid + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ fun check(v: Int, arr: IntArray, target: Int): Int {
+ var sum = 0
+ for (i in arr.indices) {
+ sum += if (arr[i] >= v) {
+ return Math.abs(sum + (arr.size - i) * v - target)
+ } else {
+ arr[i]
+ }
+ }
+ return Math.abs(sum - target)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1321_restaurant_growth/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1321_restaurant_growth/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..87c91b9c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1321_restaurant_growth/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1321\. Restaurant Growth
+
+Medium
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Customer`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | customer_id | int |
+ | name | varchar |
+ | visited_on | date |
+ | amount | int |
+ +---------------+---------+
+
+(customer_id, visited_on) is the primary key for this table. This table contains data about customer transactions in a restaurant. visited_on is the date on which the customer with ID (customer_id) has visited the restaurant. amount is the total paid by a customer.
+
+You are the restaurant owner and you want to analyze a possible expansion (there will be at least one customer every day).
+
+Write an SQL query to compute the moving average of how much the customer paid in a seven days window (i.e., current day + 6 days before). `average_amount` should be **rounded to two decimal places**.
+
+Return result table ordered by `visited_on` **in ascending order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** Customer table:
+
+ +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+
+ | customer_id | name | visited_on | amount |
+ +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+
+ | 1 | Jhon | 2019-01-01 | 100 |
+ | 2 | Daniel | 2019-01-02 | 110 |
+ | 3 | Jade | 2019-01-03 | 120 |
+ | 4 | Khaled | 2019-01-04 | 130 |
+ | 5 | Winston | 2019-01-05 | 110 |
+ | 6 | Elvis | 2019-01-06 | 140 |
+ | 7 | Anna | 2019-01-07 | 150 |
+ | 8 | Maria | 2019-01-08 | 80 |
+ | 9 | Jaze | 2019-01-09 | 110 |
+ | 1 | Jhon | 2019-01-10 | 130 |
+ | 3 | Jade | 2019-01-10 | 150 |
+ +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +--------------+--------------+----------------+
+ | visited_on | amount | average_amount |
+ +--------------+--------------+----------------+
+ | 2019-01-07 | 860 | 122.86 |
+ | 2019-01-08 | 840 | 120 |
+ | 2019-01-09 | 840 | 120 |
+ | 2019-01-10 | 1000 | 142.86 |
+ +--------------+--------------+----------------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+1st moving average from 2019-01-01 to 2019-01-07 has an average_amount of (100 + 110 + 120 + 130 + 110 + 140 + 150)/7 = 122.86
+
+2nd moving average from 2019-01-02 to 2019-01-08 has an average_amount of (110 + 120 + 130 + 110 + 140 + 150 + 80)/7 = 120
+
+3rd moving average from 2019-01-03 to 2019-01-09 has an average_amount of (120 + 130 + 110 + 140 + 150 + 80 + 110)/7 = 120
+
+4th moving average from 2019-01-04 to 2019-01-10 has an average_amount of (130 + 110 + 140 + 150 + 80 + 110 + 130 + 150)/7 = 142.86
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+with cteX as
+(select visited_on, sum(amount) as amount from customer
+group by visited_on)
+
+
+SELECT visited_on, SUM(amount) OVER(ROWS BETWEEN 6 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW) AS amount,
+round(AVG(amount) OVER(ROWS BETWEEN 6 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW), 2) as average_amount FROM cteX
+order by visited_on
+limit 6, 10000
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1327_list_the_products_ordered_in_a_period/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1327_list_the_products_ordered_in_a_period/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b04991a6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1327_list_the_products_ordered_in_a_period/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1327\. List the Products Ordered in a Period
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Products`
+
+ +------------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +------------------+---------+
+ | product_id | int |
+ | product_name | varchar |
+ | product_category | varchar |
+ +------------------+---------+
+
+product_id is the primary key for this table. This table contains data about the company's products.
+
+Table: `Orders`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | product_id | int |
+ | order_date | date |
+ | unit | int |
+ +---------------+---------+
+
+There is no primary key for this table. It may have duplicate rows. product_id is a foreign key to the Products table. unit is the number of products ordered in order_date.
+
+Write an SQL query to get the names of products that have at least `100` units ordered in **February 2020** and their amount.
+
+Return result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** Products table:
+
+ +-------------+-----------------------+------------------+
+ | product_id | product_name | product_category |
+ +-------------+-----------------------+------------------+
+ | 1 | Leetcode Solutions | Book |
+ | 2 | Jewels of Stringology | Book |
+ | 3 | HP | Laptop |
+ | 4 | Lenovo | Laptop |
+ | 5 | Leetcode Kit | T-shirt |
+ +-------------+-----------------------+------------------+
+
+Orders table:
+
+ +--------------+--------------+----------+
+ | product_id | order_date | unit |
+ +--------------+--------------+----------+
+ | 1 | 2020-02-05 | 60 |
+ | 1 | 2020-02-10 | 70 |
+ | 2 | 2020-01-18 | 30 |
+ | 2 | 2020-02-11 | 80 |
+ | 3 | 2020-02-17 | 2 |
+ | 3 | 2020-02-24 | 3 |
+ | 4 | 2020-03-01 | 20 |
+ | 4 | 2020-03-04 | 30 |
+ | 4 | 2020-03-04 | 60 |
+ | 5 | 2020-02-25 | 50 |
+ | 5 | 2020-02-27 | 50 |
+ | 5 | 2020-03-01 | 50 |
+ +--------------+--------------+----------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +--------------------+---------+
+ | product_name | unit |
+ +--------------------+---------+
+ | Leetcode Solutions | 130 |
+ | Leetcode Kit | 100 |
+ +--------------------+---------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Products with product_id = 1 is ordered in February a total of (60 + 70) = 130.
+
+Products with product_id = 2 is ordered in February a total of 80. Products with product_id = 3 is ordered in February a total of (2 + 3) = 5.
+
+Products with product_id = 4 was not ordered in February 2020. Products with product_id = 5 is ordered in February a total of (50 + 50) = 100.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT * FROM (
+ SELECT
+ a.product_name,
+ SUM(b.unit) as unit
+ FROM Products a
+ LEFT JOIN Orders b
+ ON a.product_id = b.product_id
+ WHERE b.order_date BETWEEN '2020-02-01' AND '2020-02-29'
+ GROUP BY a.product_name
+) AS d
+GROUP BY d.product_name
+HAVING d.unit >= 100
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1341_movie_rating/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1341_movie_rating/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..734a0159
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1301_1400/s1341_movie_rating/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1341\. Movie Rating
+
+Medium
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Movies`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | movie_id | int |
+ | title | varchar |
+ +---------------+---------+
+
+movie_id is the primary key for this table. title is the name of the movie.
+
+Table: `Users`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | user_id | int |
+ | name | varchar |
+ +---------------+---------+
+
+user_id is the primary key for this table.
+
+Table: `MovieRating`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | movie_id | int |
+ | user_id | int |
+ | rating | int |
+ | created_at | date |
+ +---------------+---------+
+
+(movie_id, user_id) is the primary key for this table. This table contains the rating of a movie by a user in their review. created_at is the user's review date.
+
+Write an SQL query to:
+
+* Find the name of the user who has rated the greatest number of movies. In case of a tie, return the lexicographically smaller user name.
+* Find the movie name with the **highest average** rating in `February 2020`. In case of a tie, return the lexicographically smaller movie name.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** Movies table:
+
+ +-------------+--------------+
+ | movie_id | title |
+ +-------------+--------------+
+ | 1 | Avengers |
+ | 2 | Frozen 2 |
+ | 3 | Joker |
+ +-------------+--------------+
+
+Users table:
+
+ +-------------+--------------+
+ | user_id | name |
+ +-------------+--------------+
+ | 1 | Daniel |
+ | 2 | Monica |
+ | 3 | Maria |
+ | 4 | James |
+ +-------------+--------------+
+
+MovieRating table:
+
+ +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+
+ | movie_id | user_id | rating | created_at |
+ +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+
+ | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2020-01-12 |
+ | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2020-02-11 |
+ | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2020-02-12 |
+ | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2020-01-01 |
+ | 2 | 1 | 5 | 2020-02-17 |
+ | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2020-02-01 |
+ | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2020-03-01 |
+ | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2020-02-22 |
+ | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2020-02-25 |
+ +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +--------------+
+ | results |
+ +--------------+
+ | Daniel |
+ | Frozen 2 |
+ +--------------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Daniel and Monica have rated 3 movies ("Avengers", "Frozen 2" and "Joker") but Daniel is smaller lexicographically.
+
+Frozen 2 and Joker have a rating average of 3.5 in February but Frozen 2 is smaller lexicographically.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+with cte as
+(SELECT name, COUNT(RATING) as cnt,
+DENSE_RANK() over(order by COUNT(RATING) desc, name asc) as rnk FROM MovieRating r
+INNER JOIN Users u ON r.user_id = u.user_id
+GROUP BY u.user_id
+limit 1),
+
+cte2 as
+(SELECT title, avg(rating) as avgr from MovieRating r
+INNER JOIN Movies m ON r.movie_id = m.movie_id
+where month(created_at) = 2
+group by r.movie_id
+order by avg(rating) desc, title asc
+limit 1)
+
+select name as results from cte
+union all
+select title from cte2
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1451_rearrange_words_in_a_sentence/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1451_rearrange_words_in_a_sentence/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bab6d4bc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1451_rearrange_words_in_a_sentence/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1451\. Rearrange Words in a Sentence
+
+Medium
+
+Given a sentence `text` (A _sentence_ is a string of space-separated words) in the following format:
+
+* First letter is in upper case.
+* Each word in `text` are separated by a single space.
+
+Your task is to rearrange the words in text such that all words are rearranged in an increasing order of their lengths. If two words have the same length, arrange them in their original order.
+
+Return the new text following the format shown above.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** text = "Leetcode is cool"
+
+**Output:** "Is cool leetcode"
+
+**Explanation:** There are 3 words, "Leetcode" of length 8, "is" of length 2 and "cool" of length 4. Output is ordered by length and the new first word starts with capital letter.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** text = "Keep calm and code on"
+
+**Output:** "On and keep calm code"
+
+**Explanation:** Output is ordered as follows:
+
+"On" 2 letters.
+
+"and" 3 letters.
+
+"keep" 4 letters in case of tie order by position in original text.
+
+"calm" 4 letters.
+
+"code" 4 letters.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** text = "To be or not to be"
+
+**Output:** "To be or to be not"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `text` begins with a capital letter and then contains lowercase letters and single space between words.
+* `1 <= text.length <= 10^5`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.TreeMap
+
+class Solution {
+ fun arrangeWords(text: String): String {
+ val map = TreeMap>()
+ val words = text.split(" ").dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()
+ for (word in words) {
+ val len = word.length
+ map.putIfAbsent(len, ArrayList())
+ map[len]!!.add(word.lowercase())
+ }
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ var first = true
+ for ((_, strings) in map) {
+ for (str in strings) {
+ val localStr = if (first) {
+ first = false
+ str[0].uppercaseChar().toString() + str.substring(1)
+ } else {
+ str
+ }
+ sb.append(localStr).append(" ")
+ }
+ }
+ return sb.substring(0, sb.length - 1)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1452_people_whose_list_of_favorite_companies_is_not_a_subset_of_another_list/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1452_people_whose_list_of_favorite_companies_is_not_a_subset_of_another_list/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5c94b67c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1452_people_whose_list_of_favorite_companies_is_not_a_subset_of_another_list/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1452\. People Whose List of Favorite Companies Is Not a Subset of Another List
+
+Medium
+
+Given the array `favoriteCompanies` where `favoriteCompanies[i]` is the list of favorites companies for the `ith` person (**indexed from 0**).
+
+_Return the indices of people whose list of favorite companies is not a **subset** of any other list of favorites companies_. You must return the indices in increasing order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** favoriteCompanies = \[\["leetcode","google","facebook"],["google","microsoft"],["google","facebook"],["google"],["amazon"]]
+
+**Output:** [0,1,4]
+
+**Explanation:** Person with index=2 has favoriteCompanies[2]=["google","facebook"] which is a subset of favoriteCompanies[0]=["leetcode","google","facebook"] corresponding to the person with index 0. Person with index=3 has favoriteCompanies[3]=["google"] which is a subset of favoriteCompanies[0]=["leetcode","google","facebook"] and favoriteCompanies[1]=["google","microsoft"]. Other lists of favorite companies are not a subset of another list, therefore, the answer is [0,1,4].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** favoriteCompanies = \[\["leetcode","google","facebook"],["leetcode","amazon"],["facebook","google"]]
+
+**Output:** [0,1]
+
+**Explanation:** In this case favoriteCompanies[2]=["facebook","google"] is a subset of favoriteCompanies[0]=["leetcode","google","facebook"], therefore, the answer is [0,1].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** favoriteCompanies = \[\["leetcode"],["google"],["facebook"],["amazon"]]
+
+**Output:** [0,1,2,3]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= favoriteCompanies.length <= 100`
+* `1 <= favoriteCompanies[i].length <= 500`
+* `1 <= favoriteCompanies[i][j].length <= 20`
+* All strings in `favoriteCompanies[i]` are **distinct**.
+* All lists of favorite companies are **distinct**, that is, If we sort alphabetically each list then `favoriteCompanies[i] != favoriteCompanies[j].`
+* All strings consist of lowercase English letters only.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun peopleIndexes(favoriteCompanies: List?>): List {
+ val n = favoriteCompanies.size
+ val res: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val `in`: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ for (list in favoriteCompanies) {
+ `in`.add(HashSet(list))
+ }
+ outer@ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ for (j in res) {
+ if (isSubset(`in`[i], `in`[j])) {
+ continue@outer
+ }
+ }
+ for (j in i + 1 until n) {
+ if (isSubset(`in`[i], `in`[j])) {
+ continue@outer
+ }
+ }
+ res.add(i)
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+
+ private fun isSubset(subset: Set, set: Set): Boolean {
+ return if (subset.size >= set.size) {
+ false
+ } else set.containsAll(subset)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1453_maximum_number_of_darts_inside_of_a_circular_dartboard/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1453_maximum_number_of_darts_inside_of_a_circular_dartboard/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7ae120ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1453_maximum_number_of_darts_inside_of_a_circular_dartboard/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1453\. Maximum Number of Darts Inside of a Circular Dartboard
+
+Hard
+
+Alice is throwing `n` darts on a very large wall. You are given an array `darts` where darts[i] = [xi, yi] is the position of the ith dart that Alice threw on the wall.
+
+Bob knows the positions of the `n` darts on the wall. He wants to place a dartboard of radius `r` on the wall so that the maximum number of darts that Alice throws lies on the dartboard.
+
+Given the integer `r`, return _the maximum number of darts that can lie on the dartboard_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** darts = \[\[-2,0],[2,0],[0,2],[0,-2]], r = 2
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** Circle dartboard with center in (0,0) and radius = 2 contain all points.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** darts = \[\[-3,0],[3,0],[2,6],[5,4],[0,9],[7,8]], r = 5
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** Circle dartboard with center in (0,4) and radius = 5 contain all points except the point (7,8).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= darts.length <= 100`
+* `darts[i].length == 2`
+* -104 <= xi, yi <= 104
+* `1 <= r <= 5000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private class Angle(var a: Double, var enter: Boolean) : Comparable {
+ override fun compareTo(other: Angle): Int {
+ if (a > other.a) {
+ return 1
+ } else if (a < other.a) {
+ return -1
+ } else if (enter == other.enter) {
+ return 0
+ } else if (enter) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ return 1
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun getPointsInside(i: Int, r: Double, n: Int, points: Array, dis: Array): Int {
+ val angles: MutableList = ArrayList(2 * n)
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (i != j && dis[i][j] <= 2 * r) {
+ val b = Math.acos(dis[i][j] / (2 * r))
+ val a = Math.atan2(
+ points[j][1] - points[i][1] * 1.0,
+ points[j][0] * 1.0 - points[i][0]
+ )
+ val alpha = a - b
+ val beta = a + b
+ angles.add(Angle(alpha, true))
+ angles.add(Angle(beta, false))
+ }
+ }
+ angles.sort()
+ var count = 1
+ var res = 1
+ for (a in angles) {
+ if (a.enter) {
+ count++
+ } else {
+ count--
+ }
+ if (count > res) {
+ res = count
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+
+ fun numPoints(points: Array, r: Int): Int {
+ val n = points.size
+ val dis = Array(n) { DoubleArray(n) }
+ for (i in 0 until n - 1) {
+ for (j in i + 1 until n) {
+ dis[j][i] = Math.sqrt(
+ Math.pow(points[i][0] * 1.0 - points[j][0], 2.0) +
+ Math.pow(points[i][1] * 1.0 - points[j][1], 2.0)
+ )
+ dis[i][j] = dis[j][i]
+ }
+ }
+ var ans = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ ans = Math.max(ans, getPointsInside(i, r.toDouble(), n, points, dis))
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1455_check_if_a_word_occurs_as_a_prefix_of_any_word_in_a_sentence/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1455_check_if_a_word_occurs_as_a_prefix_of_any_word_in_a_sentence/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..041ff2f9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1455_check_if_a_word_occurs_as_a_prefix_of_any_word_in_a_sentence/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1455\. Check If a Word Occurs As a Prefix of Any Word in a Sentence
+
+Easy
+
+Given a `sentence` that consists of some words separated by a **single space**, and a `searchWord`, check if `searchWord` is a prefix of any word in `sentence`.
+
+Return _the index of the word in_ `sentence` _(**1-indexed**) where_ `searchWord` _is a prefix of this word_. If `searchWord` is a prefix of more than one word, return the index of the first word **(minimum index)**. If there is no such word return `-1`.
+
+A **prefix** of a string `s` is any leading contiguous substring of `s`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** sentence = "i love eating burger", searchWord = "burg"
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** "burg" is prefix of "burger" which is the 4th word in the sentence.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** sentence = "this problem is an easy problem", searchWord = "pro"
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** "pro" is prefix of "problem" which is the 2nd and the 6th word in the sentence, but we return 2 as it's the minimal index.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** sentence = "i am tired", searchWord = "you"
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** "you" is not a prefix of any word in the sentence.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= sentence.length <= 100`
+* `1 <= searchWord.length <= 10`
+* `sentence` consists of lowercase English letters and spaces.
+* `searchWord` consists of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun isPrefixOfWord(sentence: String, searchWord: String): Int {
+ val words = sentence.split(" ").dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()
+ for (i in words.indices) {
+ if (words[i].startsWith(searchWord)) {
+ return i + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1456_maximum_number_of_vowels_in_a_substring_of_given_length/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1456_maximum_number_of_vowels_in_a_substring_of_given_length/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0feae80f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1456_maximum_number_of_vowels_in_a_substring_of_given_length/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1456\. Maximum Number of Vowels in a Substring of Given Length
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string `s` and an integer `k`, return _the maximum number of vowel letters in any substring of_ `s` _with length_ `k`.
+
+**Vowel letters** in English are `'a'`, `'e'`, `'i'`, `'o'`, and `'u'`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abciiidef", k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The substring "iii" contains 3 vowel letters.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aeiou", k = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Any substring of length 2 contains 2 vowels.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "leetcode", k = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** "lee", "eet" and "ode" contain 2 vowels.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s` consists of lowercase English letters.
+* `1 <= k <= s.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private fun isVowel(c: Char): Boolean {
+ return c == 'a' || c == 'e' || c == 'i' || c == 'o' || c == 'u'
+ }
+
+ fun maxVowels(s: String, k: Int): Int {
+ var maxVowelCount = 0
+ var vowelCount = 0
+ var i = 0
+ var j = 0
+ while (j < s.length) {
+ val c = s[j]
+ if (isVowel(c)) {
+ vowelCount++
+ }
+ if (j - i + 1 == k) {
+ maxVowelCount = Math.max(maxVowelCount, vowelCount)
+ if (isVowel(s[i])) {
+ vowelCount--
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ j++
+ }
+ return maxVowelCount
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1457_pseudo_palindromic_paths_in_a_binary_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1457_pseudo_palindromic_paths_in_a_binary_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e2f192a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1457_pseudo_palindromic_paths_in_a_binary_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1457\. Pseudo-Palindromic Paths in a Binary Tree
+
+Medium
+
+Given a binary tree where node values are digits from 1 to 9. A path in the binary tree is said to be **pseudo-palindromic** if at least one permutation of the node values in the path is a palindrome.
+
+_Return the number of **pseudo-palindromic** paths going from the root node to leaf nodes._
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [2,3,1,3,1,null,1]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the red path [2,3,3], the green path [2,1,1], and the path [2,3,1]. Among these paths only red path and green path are pseudo-palindromic paths since the red path [2,3,3] can be rearranged in [3,2,3] (palindrome) and the green path [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** root = [2,1,1,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,1]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the green path [2,1,1], the path [2,1,3,1], and the path [2,1]. Among these paths only the green path is pseudo-palindromic since [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** root = [9]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 105].
+* `1 <= Node.val <= 9`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ private var ans = 0
+ private lateinit var arr: IntArray
+
+ fun pseudoPalindromicPaths(root: TreeNode?): Int {
+ ans = 0
+ arr = IntArray(10)
+ path(root)
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun isPalidrome(): Int {
+ var c = 0
+ var s = 0
+ for (i in 0..9) {
+ s += arr[i]
+ if (arr[i] % 2 != 0) {
+ c++
+ }
+ }
+ if (s % 2 == 0) {
+ return if (c == 0) 1 else 0
+ }
+ return if (c <= 1) 1 else 0
+ }
+
+ private fun path(root: TreeNode?) {
+ if (root == null) {
+ return
+ }
+ if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
+ arr[root.`val`]++
+ ans += isPalidrome()
+ arr[root.`val`]--
+ return
+ }
+ arr[root.`val`]++
+ path(root.left)
+ path(root.right)
+ arr[root.`val`]--
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1458_max_dot_product_of_two_subsequences/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1458_max_dot_product_of_two_subsequences/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a5629f80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1458_max_dot_product_of_two_subsequences/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1458\. Max Dot Product of Two Subsequences
+
+Hard
+
+Given two arrays `nums1` and `nums2`.
+
+Return the maximum dot product between **non-empty** subsequences of nums1 and nums2 with the same length.
+
+A subsequence of a array is a new array which is formed from the original array by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (ie, `[2,3,5]` is a subsequence of `[1,2,3,4,5]` while `[1,5,3]` is not).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [2,1,-2,5], nums2 = [3,0,-6]
+
+**Output:** 18
+
+**Explanation:** Take subsequence [2,-2] from nums1 and subsequence [3,-6] from nums2. Their dot product is (2\*3 + (-2)\*(-6)) = 18.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [3,-2], nums2 = [2,-6,7]
+
+**Output:** 21
+
+**Explanation:** Take subsequence [3] from nums1 and subsequence [7] from nums2. Their dot product is (3\*7) = 21.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [-1,-1], nums2 = [1,1]
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** Take subsequence [-1] from nums1 and subsequence [1] from nums2. Their dot product is -1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 500`
+* `-1000 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxDotProduct(nums1: IntArray, nums2: IntArray): Int {
+ val marks = Array(nums1.size) { IntArray(nums2.size) }
+ for (i in nums1.indices) {
+ for (j in nums2.indices) {
+ var max = nums1[i] * nums2[j]
+ if (i > 0 && j > 0) {
+ max = Math.max(max, max + marks[i - 1][j - 1])
+ }
+ if (i > 0) {
+ max = Math.max(max, marks[i - 1][j])
+ }
+ if (j > 0) {
+ max = Math.max(max, marks[i][j - 1])
+ }
+ marks[i][j] = max
+ }
+ }
+ return marks[nums1.size - 1][nums2.size - 1]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1460_make_two_arrays_equal_by_reversing_subarrays/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1460_make_two_arrays_equal_by_reversing_subarrays/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f5cd5bf5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1460_make_two_arrays_equal_by_reversing_subarrays/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1460\. Make Two Arrays Equal by Reversing Sub-arrays
+
+Easy
+
+You are given two integer arrays of equal length `target` and `arr`. In one step, you can select any **non-empty sub-array** of `arr` and reverse it. You are allowed to make any number of steps.
+
+Return `true` _if you can make_ `arr` _equal to_ `target`_or_ `false` _otherwise_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** target = [1,2,3,4], arr = [2,4,1,3]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** You can follow the next steps to convert arr to target:
+
+1- Reverse sub-array [2,4,1], arr becomes [1,4,2,3]
+
+2- Reverse sub-array [4,2], arr becomes [1,2,4,3]
+
+3- Reverse sub-array [4,3], arr becomes [1,2,3,4]
+
+There are multiple ways to convert arr to target, this is not the only way to do so.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** target = [7], arr = [7]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** arr is equal to target without any reverses.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** target = [3,7,9], arr = [3,7,11]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** arr does not have value 9 and it can never be converted to target.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `target.length == arr.length`
+* `1 <= target.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= target[i] <= 1000`
+* `1 <= arr[i] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun canBeEqual(target: IntArray, arr: IntArray): Boolean {
+ val n = target.size
+ target.sort()
+ arr.sort()
+ var count = 0
+ for (i in target.indices) {
+ if (target[i] == arr[i]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ return count == n
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1461_check_if_a_string_contains_all_binary_codes_of_size_k/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1461_check_if_a_string_contains_all_binary_codes_of_size_k/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6ec269e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1461_check_if_a_string_contains_all_binary_codes_of_size_k/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1461\. Check If a String Contains All Binary Codes of Size K
+
+Medium
+
+Given a binary string `s` and an integer `k`, return `true` _if every binary code of length_ `k` _is a substring of_ `s`. Otherwise, return `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "00110110", k = 2
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** The binary codes of length 2 are "00", "01", "10" and "11". They can be all found as substrings at indices 0, 1, 3 and 2 respectively.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "0110", k = 1
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** The binary codes of length 1 are "0" and "1", it is clear that both exist as a substring.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "0110", k = 2
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** The binary code "00" is of length 2 and does not exist in the array.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 5 * 105
+* `s[i]` is either `'0'` or `'1'`.
+* `1 <= k <= 20`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun hasAllCodes(s: String, k: Int): Boolean {
+ val total = Math.pow(2.0, k.toDouble()).toInt()
+ var start = 0
+ var end = start + k
+ val st: MutableSet = HashSet()
+ while (end <= s.length) {
+ val sbStr = s.substring(start, end)
+ st.add(sbStr)
+ if (st.size == total) {
+ return true
+ }
+ start++
+ end++
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1462_course_schedule_iv/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1462_course_schedule_iv/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e3daab30
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1462_course_schedule_iv/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1462\. Course Schedule IV
+
+Medium
+
+There are a total of `numCourses` courses you have to take, labeled from `0` to `numCourses - 1`. You are given an array `prerequisites` where prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that you **must** take course ai first if you want to take course bi.
+
+* For example, the pair `[0, 1]` indicates that you have to take course `0` before you can take course `1`.
+
+Prerequisites can also be **indirect**. If course `a` is a prerequisite of course `b`, and course `b` is a prerequisite of course `c`, then course `a` is a prerequisite of course `c`.
+
+You are also given an array `queries` where queries[j] = [uj, vj]. For the jth query, you should answer whether course uj is a prerequisite of course vj or not.
+
+Return _a boolean array_ `answer`_, where_ `answer[j]` _is the answer to the_ jth _query._
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** numCourses = 2, prerequisites = \[\[1,0]], queries = \[\[0,1],[1,0]]
+
+**Output:** [false,true]
+
+**Explanation:** The pair [1, 0] indicates that you have to take course 1 before you can take course 0. Course 0 is not a prerequisite of course 1, but the opposite is true.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [], queries = \[\[1,0],[0,1]]
+
+**Output:** [false,false]
+
+**Explanation:** There are no prerequisites, and each course is independent.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** numCourses = 3, prerequisites = \[\[1,2],[1,0],[2,0]], queries = \[\[1,0],[1,2]]
+
+**Output:** [true,true]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= numCourses <= 100`
+* `0 <= prerequisites.length <= (numCourses * (numCourses - 1) / 2)`
+* `prerequisites[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= ai, bi <= n - 1
+* ai != bi
+* All the pairs [ai, bi] are **unique**.
+* The prerequisites graph has no cycles.
+* 1 <= queries.length <= 104
+* 0 <= ui, vi <= n - 1
+* ui != vi
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun checkIfPrerequisite(
+ numCourses: Int,
+ prerequisites: Array,
+ queries: Array
+ ): List {
+ val m: MutableMap> = HashMap()
+ val ind = IntArray(numCourses)
+ for (p in prerequisites) {
+ m.computeIfAbsent(p[1]) { _: Int? -> ArrayList() }.add(p[0])
+ ind[p[0]]++
+ }
+ val r = Array(numCourses) { BooleanArray(numCourses) }
+ val q: Queue = LinkedList()
+ for (i in 0 until numCourses) {
+ if (ind[i] == 0) {
+ q.add(i)
+ }
+ }
+ while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val j = q.poll()
+ for (k in m.getOrDefault(j, ArrayList())) {
+ r[k][j] = true
+ for (l in r.indices) {
+ if (r[j][l]) {
+ r[k][l] = true
+ }
+ }
+ ind[k]--
+ if (ind[k] == 0) {
+ q.offer(k)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ val a: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (qr in queries) {
+ a.add(r[qr[0]][qr[1]])
+ }
+ return a
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1463_cherry_pickup_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1463_cherry_pickup_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7c820985
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1463_cherry_pickup_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1463\. Cherry Pickup II
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a `rows x cols` matrix `grid` representing a field of cherries where `grid[i][j]` represents the number of cherries that you can collect from the `(i, j)` cell.
+
+You have two robots that can collect cherries for you:
+
+* **Robot #1** is located at the **top-left corner** `(0, 0)`, and
+* **Robot #2** is located at the **top-right corner** `(0, cols - 1)`.
+
+Return _the maximum number of cherries collection using both robots by following the rules below_:
+
+* From a cell `(i, j)`, robots can move to cell `(i + 1, j - 1)`, `(i + 1, j)`, or `(i + 1, j + 1)`.
+* When any robot passes through a cell, It picks up all cherries, and the cell becomes an empty cell.
+* When both robots stay in the same cell, only one takes the cherries.
+* Both robots cannot move outside of the grid at any moment.
+* Both robots should reach the bottom row in `grid`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[3,1,1],[2,5,1],[1,5,5],[2,1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 24
+
+**Explanation:** Path of robot #1 and #2 are described in color green and blue respectively.
+
+Cherries taken by Robot #1, (3 + 2 + 5 + 2) = 12.
+
+Cherries taken by Robot #2, (1 + 5 + 5 + 1) = 12.
+
+Total of cherries: 12 + 12 = 24.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,0,0,0,0,0,1],[2,0,0,0,0,3,0],[2,0,9,0,0,0,0],[0,3,0,5,4,0,0],[1,0,2,3,0,0,6]]
+
+**Output:** 28
+
+**Explanation:** Path of robot #1 and #2 are described in color green and blue respectively.
+
+Cherries taken by Robot #1, (1 + 9 + 5 + 2) = 17.
+
+Cherries taken by Robot #2, (1 + 3 + 4 + 3) = 11.
+
+Total of cherries: 17 + 11 = 28.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `rows == grid.length`
+* `cols == grid[i].length`
+* `2 <= rows, cols <= 70`
+* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun cherryPickup(grid: Array): Int {
+ val m = grid.size
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ val dp = Array(n) { Array(n) { IntArray(m) } }
+ dp[0][n - 1][0] = grid[0][0] + grid[0][n - 1]
+ for (k in 1 until m) {
+ for (i in 0..Math.min(n - 1, k)) {
+ for (j in n - 1 downTo Math.max(0, n - 1 - k)) {
+ dp[i][j][k] = maxOfLast(dp, i, j, k) + grid[k][i] + if (i == j) 0 else grid[k][j]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ var result = 0
+ for (i in 0..Math.min(n - 1, m)) {
+ for (j in n - 1 downTo Math.max(0, n - 1 - m)) {
+ result = Math.max(result, dp[i][j][m - 1])
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+
+ private fun maxOfLast(dp: Array>, i: Int, j: Int, k: Int): Int {
+ var result = 0
+ for (x in -1..1) {
+ for (y in -1..1) {
+ val r = i + x
+ val c = j + y
+ if (r >= 0 && r < dp[0].size && c >= 0 && c < dp[0].size) {
+ result = Math.max(result, dp[r][c][k - 1])
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1464_maximum_product_of_two_elements_in_an_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1464_maximum_product_of_two_elements_in_an_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5c7ed919
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1464_maximum_product_of_two_elements_in_an_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1464\. Maximum Product of Two Elements in an Array
+
+Easy
+
+Given the array of integers `nums`, you will choose two different indices `i` and `j` of that array. _Return the maximum value of_ `(nums[i]-1)*(nums[j]-1)`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,4,5,2]
+
+**Output:** 12
+
+**Explanation:** If you choose the indices i=1 and j=2 (indexed from 0), you will get the maximum value, that is, (nums[1]-1)\*(nums[2]-1) = (4-1)\*(5-1) = 3\*4 = 12.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,5,4,5]
+
+**Output:** 16
+
+**Explanation:** Choosing the indices i=1 and j=3 (indexed from 0), you will get the maximum value of (5-1)\*(5-1) = 16.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,7]
+
+**Output:** 12
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= nums.length <= 500`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 10^3`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxProduct(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var first = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ var second = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ for (num in nums) {
+ if (num >= first) {
+ second = first
+ first = num
+ } else if (num >= second) {
+ second = num
+ }
+ }
+ return (first - 1) * (second - 1)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1465_maximum_area_of_a_piece_of_cake_after_horizontal_and_vertical_cuts/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1465_maximum_area_of_a_piece_of_cake_after_horizontal_and_vertical_cuts/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f0d81c1e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1465_maximum_area_of_a_piece_of_cake_after_horizontal_and_vertical_cuts/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1465\. Maximum Area of a Piece of Cake After Horizontal and Vertical Cuts
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a rectangular cake of size `h x w` and two arrays of integers `horizontalCuts` and `verticalCuts` where:
+
+* `horizontalCuts[i]` is the distance from the top of the rectangular cake to the ith horizontal cut and similarly, and
+* `verticalCuts[j]` is the distance from the left of the rectangular cake to the jth vertical cut.
+
+Return _the maximum area of a piece of cake after you cut at each horizontal and vertical position provided in the arrays_ `horizontalCuts` _and_ `verticalCuts`. Since the answer can be a large number, return this **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [1,2,4], verticalCuts = [1,3]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The figure above represents the given rectangular cake. Red lines are the horizontal and vertical cuts. After you cut the cake, the green piece of cake has the maximum area.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [3,1], verticalCuts = [1]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** The figure above represents the given rectangular cake. Red lines are the horizontal and vertical cuts. After you cut the cake, the green and yellow pieces of cake have the maximum area.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [3], verticalCuts = [3]
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= h, w <= 109
+* 1 <= horizontalCuts.length <= min(h - 1, 105)
+* 1 <= verticalCuts.length <= min(w - 1, 105)
+* `1 <= horizontalCuts[i] < h`
+* `1 <= verticalCuts[i] < w`
+* All the elements in `horizontalCuts` are distinct.
+* All the elements in `verticalCuts` are distinct.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxArea(h: Int, w: Int, horizontalCuts: IntArray, verticalCuts: IntArray): Int {
+ horizontalCuts.sort()
+ verticalCuts.sort()
+ var maxVertical = Math.max(0L, verticalCuts[0].toLong())
+ for (i in 1 until verticalCuts.size) {
+ val diff = verticalCuts[i] - verticalCuts[i - 1]
+ maxVertical = Math.max(maxVertical, diff.toLong())
+ }
+ maxVertical = Math.max(maxVertical, w.toLong() - verticalCuts[verticalCuts.size - 1])
+ var maxHorizontal = Math.max(0L, horizontalCuts[0].toLong())
+ for (i in 1 until horizontalCuts.size) {
+ val diff = horizontalCuts[i] - horizontalCuts[i - 1]
+ maxHorizontal = Math.max(maxHorizontal, diff.toLong())
+ }
+ maxHorizontal = Math.max(maxHorizontal, h.toLong() - horizontalCuts[horizontalCuts.size - 1])
+ return (maxVertical % 1000000007 * maxHorizontal % 1000000007).toInt() % 1000000007
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1466_reorder_routes_to_make_all_paths_lead_to_the_city_zero/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1466_reorder_routes_to_make_all_paths_lead_to_the_city_zero/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a081854c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1466_reorder_routes_to_make_all_paths_lead_to_the_city_zero/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1466\. Reorder Routes to Make All Paths Lead to the City Zero
+
+Medium
+
+There are `n` cities numbered from `0` to `n - 1` and `n - 1` roads such that there is only one way to travel between two different cities (this network form a tree). Last year, The ministry of transport decided to orient the roads in one direction because they are too narrow.
+
+Roads are represented by `connections` where connections[i] = [ai, bi] represents a road from city ai to city bi.
+
+This year, there will be a big event in the capital (city `0`), and many people want to travel to this city.
+
+Your task consists of reorienting some roads such that each city can visit the city `0`. Return the **minimum** number of edges changed.
+
+It's **guaranteed** that each city can reach city `0` after reorder.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 6, connections = \[\[0,1],[1,3],[2,3],[4,0],[4,5]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Change the direction of edges show in red such that each node can reach the node 0 (capital).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 5, connections = \[\[1,0],[1,2],[3,2],[3,4]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Change the direction of edges show in red such that each node can reach the node 0 (capital).
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, connections = \[\[1,0],[2,0]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= n <= 5 * 104
+* `connections.length == n - 1`
+* `connections[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= ai, bi <= n - 1
+* ai != bi
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minReorder(n: Int, connections: Array): Int {
+ val q: Queue = LinkedList()
+ val vis = BooleanArray(n)
+ val adj: MutableList> = ArrayList()
+ var count = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ adj.add(ArrayList())
+ }
+ for (tup in connections) {
+ adj[tup[0]].add(tup[1])
+ adj[tup[1]].add(-tup[0])
+ }
+ q.offer(0)
+ vis[0] = true
+ while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val node = q.poll()
+ for (it in adj[node]) {
+ if (!vis[Math.abs(it)]) {
+ vis[Math.abs(it)] = true
+ if (it > 0) {
+ count++
+ }
+ q.offer(Math.abs(it))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1467_probability_of_a_two_boxes_having_the_same_number_of_distinct_balls/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1467_probability_of_a_two_boxes_having_the_same_number_of_distinct_balls/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6211806a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1467_probability_of_a_two_boxes_having_the_same_number_of_distinct_balls/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1467\. Probability of a Two Boxes Having The Same Number of Distinct Balls
+
+Hard
+
+Given `2n` balls of `k` distinct colors. You will be given an integer array `balls` of size `k` where `balls[i]` is the number of balls of color `i`.
+
+All the balls will be **shuffled uniformly at random**, then we will distribute the first `n` balls to the first box and the remaining `n` balls to the other box (Please read the explanation of the second example carefully).
+
+Please note that the two boxes are considered different. For example, if we have two balls of colors `a` and `b`, and two boxes `[]` and `()`, then the distribution `[a] (b)` is considered different than the distribution `[b] (a)` (Please read the explanation of the first example carefully).
+
+Return _the probability_ that the two boxes have the same number of distinct balls. Answers within 10-5 of the actual value will be accepted as correct.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** balls = [1,1]
+
+**Output:** 1.00000
+
+**Explanation:** Only 2 ways to divide the balls equally:
+
+- A ball of color 1 to box 1 and a ball of color 2 to box 2
+
+- A ball of color 2 to box 1 and a ball of color 1 to box 2
+
+In both ways, the number of distinct colors in each box is equal. The probability is 2/2 = 1
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** balls = [2,1,1]
+
+**Output:** 0.66667
+
+**Explanation:** We have the set of balls [1, 1, 2, 3]
+
+This set of balls will be shuffled randomly and we may have one of the 12 distinct shuffles with equal probability (i.e. 1/12):
+
+[1,1 / 2,3], [1,1 / 3,2], [1,2 / 1,3], [1,2 / 3,1], [1,3 / 1,2], [1,3 / 2,1], [2,1 / 1,3], [2,1 / 3,1], [2,3 / 1,1], [3,1 / 1,2], [3,1 / 2,1], [3,2 / 1,1]
+
+After that, we add the first two balls to the first box and the second two balls to the second box. We can see that 8 of these 12 possible random distributions have the same number of distinct colors of balls in each box.
+
+Probability is 8/12 = 0.66667
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** balls = [1,2,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 0.60000
+
+**Explanation:** The set of balls is [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4]. It is hard to display all the 180 possible random shuffles of this set but it is easy to check that 108 of them will have the same number of distinct colors in each box. Probability = 108 / 180 = 0.6
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= balls.length <= 8`
+* `1 <= balls[i] <= 6`
+* `sum(balls)` is even.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun getProbability(balls: IntArray): Double {
+ val m = balls.size
+ var s = 0
+ for (b in balls) {
+ s += b
+ }
+ val c = Array(s + 1) { DoubleArray(s / 2 + 1) }
+ c[0][0] = 1.0
+ for (i in 1 until s + 1) {
+ c[i][0] = 1.0
+ for (j in 1 until s / 2 + 1) {
+ c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j] + c[i - 1][j - 1]
+ }
+ }
+ var dp = Array(2 * m + 1) { DoubleArray(s / 2 + 1) }
+ dp[m][0] = 1.0
+ var sum = 0
+ for (b in balls) {
+ sum += b
+ val ndp = Array(2 * m + 1) { DoubleArray(s / 2 + 1) }
+ for (i in 0..b) {
+ for (j in 0 until 2 * m + 1) {
+ for (k in 0 until s / 2 + 1) {
+ if (dp[j][k] == 0.0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ val nk = k + i
+ val nr = sum - nk
+ if (nk <= s / 2 && nr <= s / 2) {
+ val i1 = if (i == b) j + 1 else j
+ val nj = if (i == 0) j - 1 else i1
+ ndp[nj][nk] += dp[j][k] * c[b][i]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ dp = ndp
+ }
+ return dp[m][s / 2] / c[s][s / 2]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1470_shuffle_the_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1470_shuffle_the_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5e12a74b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1470_shuffle_the_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1470\. Shuffle the Array
+
+Easy
+
+Given the array `nums` consisting of `2n` elements in the form [x1,x2,...,xn,y1,y2,...,yn].
+
+_Return the array in the form_ [x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn].
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,5,1,3,4,7], n = 3
+
+**Output:** [2,3,5,4,1,7]
+
+**Explanation:** Since x1\=2, x2\=5, x3\=1, y1\=3, y2\=4, y3\=7 then the answer is [2,3,5,4,1,7].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4,4,3,2,1], n = 4
+
+**Output:** [1,4,2,3,3,2,4,1]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,2,2], n = 2
+
+**Output:** [1,2,1,2]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 500`
+* `nums.length == 2n`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 10^3`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun shuffle(nums: IntArray, n: Int): IntArray {
+ val result = IntArray(nums.size)
+ var i = 0
+ var j = 0
+ while (i < n && j < 2 * n) {
+ result[j] = nums[i]
+ result[++j] = nums[i + n]
+ i++
+ j++
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1471_the_k_strongest_values_in_an_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1471_the_k_strongest_values_in_an_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a602085
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1471_the_k_strongest_values_in_an_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1471\. The k Strongest Values in an Array
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `arr` and an integer `k`.
+
+A value `arr[i]` is said to be stronger than a value `arr[j]` if `|arr[i] - m| > |arr[j] - m|` where `m` is the **median** of the array.
+If `|arr[i] - m| == |arr[j] - m|`, then `arr[i]` is said to be stronger than `arr[j]` if `arr[i] > arr[j]`.
+
+Return _a list of the strongest `k`_ values in the array. return the answer **in any arbitrary order**.
+
+**Median** is the middle value in an ordered integer list. More formally, if the length of the list is n, the median is the element in position `((n - 1) / 2)` in the sorted list **(0-indexed)**.
+
+* For `arr = [6, -3, 7, 2, 11]`, `n = 5` and the median is obtained by sorting the array `arr = [-3, 2, 6, 7, 11]` and the median is `arr[m]` where `m = ((5 - 1) / 2) = 2`. The median is `6`.
+* For `arr = [-7, 22, 17, 3]`, `n = 4` and the median is obtained by sorting the array `arr = [-7, 3, 17, 22]` and the median is `arr[m]` where `m = ((4 - 1) / 2) = 1`. The median is `3`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
+
+**Output:** [5,1]
+
+**Explanation:** Median is 3, the elements of the array sorted by the strongest are [5,1,4,2,3]. The strongest 2 elements are [5, 1]. [1, 5] is also **accepted** answer. Please note that although \|5 - 3\| == \|1 - 3\| but 5 is stronger than 1 because 5 > 1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,1,3,5,5], k = 2
+
+**Output:** [5,5]
+
+**Explanation:** Median is 3, the elements of the array sorted by the strongest are [5,5,1,1,3]. The strongest 2 elements are [5, 5].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [6,7,11,7,6,8], k = 5
+
+**Output:** [11,8,6,6,7]
+
+**Explanation:** Median is 7, the elements of the array sorted by the strongest are [11,8,6,6,7,7]. Any permutation of [11,8,6,6,7] is **accepted**.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= arr.length <= 105
+* -105 <= arr[i] <= 105
+* `1 <= k <= arr.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun getStrongest(arr: IntArray, k: Int): IntArray {
+ arr.sort()
+ val array = IntArray(k)
+ val median = arr[(arr.size - 1) / 2]
+ var start = 0
+ var end = arr.size - 1
+ for (i in 0 until k) {
+ if (Math.abs(arr[end] - median) >= Math.abs(arr[start] - median)) {
+ array[i] = arr[end]
+ end -= 1
+ } else {
+ array[i] = arr[start]
+ start += 1
+ }
+ }
+ return array
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1472_design_browser_history/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1472_design_browser_history/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..68db2633
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1472_design_browser_history/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1472\. Design Browser History
+
+Medium
+
+You have a **browser** of one tab where you start on the `homepage` and you can visit another `url`, get back in the history number of `steps` or move forward in the history number of `steps`.
+
+Implement the `BrowserHistory` class:
+
+* `BrowserHistory(string homepage)` Initializes the object with the `homepage` of the browser.
+* `void visit(string url)` Visits `url` from the current page. It clears up all the forward history.
+* `string back(int steps)` Move `steps` back in history. If you can only return `x` steps in the history and `steps > x`, you will return only `x` steps. Return the current `url` after moving back in history **at most** `steps`.
+* `string forward(int steps)` Move `steps` forward in history. If you can only forward `x` steps in the history and `steps > x`, you will forward only `x` steps. Return the current `url` after forwarding in history **at most** `steps`.
+
+**Example:**
+
+**Input:** ["BrowserHistory","visit","visit","visit","back","back","forward","visit","forward","back","back"] [["leetcode.com"],["google.com"],["facebook.com"],["youtube.com"],[1],[1],[1],["linkedin.com"],[2],[2],[7]]
+
+**Output:** [null,null,null,null,"facebook.com","google.com","facebook.com",null,"linkedin.com","google.com","leetcode.com"]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+BrowserHistory browserHistory = new BrowserHistory("leetcode.com");
+
+browserHistory.visit("google.com"); // You are in "leetcode.com". Visit "google.com"
+
+browserHistory.visit("facebook.com"); // You are in "google.com". Visit "facebook.com"
+
+browserHistory.visit("youtube.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "youtube.com"
+
+browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "youtube.com", move back to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
+
+browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "facebook.com", move back to "google.com" return "google.com"
+
+browserHistory.forward(1); // You are in "google.com", move forward to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
+
+browserHistory.visit("linkedin.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "linkedin.com"
+
+browserHistory.forward(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", you cannot move forward any steps.
+
+browserHistory.back(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", move back two steps to "facebook.com" then to "google.com". return "google.com"
+
+browserHistory.back(7); // You are in "google.com", you can move back only one step to "leetcode.com". return "leetcode.com"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= homepage.length <= 20`
+* `1 <= url.length <= 20`
+* `1 <= steps <= 100`
+* `homepage` and `url` consist of '.' or lower case English letters.
+* At most `5000` calls will be made to `visit`, `back`, and `forward`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class BrowserHistory(homepage: String) {
+ internal class Node(var url: String) {
+ var prev: Node? = null
+ var next: Node? = null
+ }
+
+ private var curr: Node?
+
+ init {
+ curr = Node(homepage)
+ }
+
+ fun visit(url: String) {
+ val newNode = Node(url)
+ curr!!.next = newNode
+ newNode.prev = curr
+ curr = curr!!.next
+ }
+
+ fun back(steps: Int): String {
+ var steps = steps
+ while (curr!!.prev != null && steps-- > 0) {
+ curr = curr!!.prev
+ }
+ return curr!!.url
+ }
+
+ fun forward(steps: Int): String {
+ var steps = steps
+ while (curr!!.next != null && steps-- > 0) {
+ curr = curr!!.next
+ }
+ return curr!!.url
+ }
+}
+/*
+ * Your BrowserHistory object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * var obj = BrowserHistory(homepage)
+ * obj.visit(url)
+ * var param_2 = obj.back(steps)
+ * var param_3 = obj.forward(steps)
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1473_paint_house_iii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1473_paint_house_iii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c2030e14
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1473_paint_house_iii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1473\. Paint House III
+
+Hard
+
+There is a row of `m` houses in a small city, each house must be painted with one of the `n` colors (labeled from `1` to `n`), some houses that have been painted last summer should not be painted again.
+
+A neighborhood is a maximal group of continuous houses that are painted with the same color.
+
+* For example: `houses = [1,2,2,3,3,2,1,1]` contains `5` neighborhoods `[{1}, {2,2}, {3,3}, {2}, {1,1}]`.
+
+Given an array `houses`, an `m x n` matrix `cost` and an integer `target` where:
+
+* `houses[i]`: is the color of the house `i`, and `0` if the house is not painted yet.
+* `cost[i][j]`: is the cost of paint the house `i` with the color `j + 1`.
+
+Return _the minimum cost of painting all the remaining houses in such a way that there are exactly_ `target` _neighborhoods_. If it is not possible, return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** houses = [0,0,0,0,0], cost = \[\[1,10],[10,1],[10,1],[1,10],[5,1]], m = 5, n = 2, target = 3
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Explanation:** Paint houses of this way [1,2,2,1,1]
+
+This array contains target = 3 neighborhoods, [{1}, {2,2}, {1,1}].
+
+Cost of paint all houses (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 5) = 9.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** houses = [0,2,1,2,0], cost = \[\[1,10],[10,1],[10,1],[1,10],[5,1]], m = 5, n = 2, target = 3
+
+**Output:** 11
+
+**Explanation:** Some houses are already painted, Paint the houses of this way [2,2,1,2,2]
+
+This array contains target = 3 neighborhoods, [{2,2}, {1}, {2,2}].
+
+Cost of paint the first and last house (10 + 1) = 11.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** houses = [3,1,2,3], cost = \[\[1,1,1],[1,1,1],[1,1,1],[1,1,1]], m = 4, n = 3, target = 3
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** Houses are already painted with a total of 4 neighborhoods [{3},{1},{2},{3}] different of target = 3.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == houses.length == cost.length`
+* `n == cost[i].length`
+* `1 <= m <= 100`
+* `1 <= n <= 20`
+* `1 <= target <= m`
+* `0 <= houses[i] <= n`
+* 1 <= cost[i][j] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private lateinit var prev: Array
+ private lateinit var curr: Array
+ private lateinit var mins: Array
+
+ fun minCost(houses: IntArray, cost: Array, m: Int, n: Int, target: Int): Int {
+ prev = Array(n) { IntArray(target) }
+ curr = Array(n) { IntArray(target) }
+ mins = Array(2) { IntArray(target) }
+ for (i in 0 until m) calculate(i, houses, cost, n, target)
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ for (i in 0 until n) min = Math.min(min, curr[i][target - 1])
+ return if (min == Int.MAX_VALUE) -1 else min
+ }
+
+ private fun calculate(house: Int, houses: IntArray, cost: Array, n: Int, target: Int) {
+ swap()
+ calculateMins(n, target)
+ if (houses[house] > 0) costInPaintedHouse(house, houses, cost, target) else costNotPaintedHouse(
+ house,
+ cost,
+ target
+ )
+ }
+
+ private fun costInPaintedHouse(house: Int, houses: IntArray, cost: Array, target: Int) {
+ val color = houses[house] - 1
+ for (i in cost[house].indices) {
+ val group = Math.min(target - 1, house)
+ val newG = house == group
+ if (i == color) {
+ curr[i][0] = prev[i][0]
+ for (j in 1..group) {
+ curr[i][j] = if (mins[0][j - 1] == prev[i][j - 1]) mins[1][j - 1] else mins[0][j - 1]
+ curr[i][j] = if (newG && j == group) curr[i][j] else Math.min(curr[i][j], prev[i][j])
+ }
+ } else for (j in 0..group) curr[i][j] = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun costNotPaintedHouse(house: Int, cost: Array, target: Int) {
+ for (i in cost[house].indices) {
+ val group = Math.min(target - 1, house)
+ val newG = house == group
+ curr[i][0] = if (prev[i][0] == Int.MAX_VALUE) prev[i][0] else prev[i][0] + cost[house][i]
+ for (j in 1..group) {
+ curr[i][j] = if (mins[0][j - 1] == prev[i][j - 1]) mins[1][j - 1] else mins[0][j - 1]
+ curr[i][j] = if (newG && j == group) curr[i][j] else Math.min(curr[i][j], prev[i][j])
+ curr[i][j] = if (curr[i][j] == Int.MAX_VALUE) Int.MAX_VALUE else curr[i][j] + cost[house][i]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun swap() {
+ val temp = prev
+ prev = curr
+ curr = temp
+ }
+
+ private fun calculateMins(n: Int, target: Int) {
+ for (i in 0 until target - 1) {
+ mins[0][i] = prev[0][i]
+ mins[1][i] = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ for (j in 1 until n) {
+ if (prev[j][i] <= mins[0][i]) {
+ mins[1][i] = mins[0][i]
+ mins[0][i] = prev[j][i]
+ } else if (prev[j][i] <= mins[1][i]) mins[1][i] = prev[j][i]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1475_final_prices_with_a_special_discount_in_a_shop/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1475_final_prices_with_a_special_discount_in_a_shop/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b7ef16e7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1475_final_prices_with_a_special_discount_in_a_shop/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1475\. Final Prices With a Special Discount in a Shop
+
+Easy
+
+Given the array `prices` where `prices[i]` is the price of the `ith` item in a shop. There is a special discount for items in the shop, if you buy the `ith` item, then you will receive a discount equivalent to `prices[j]` where `j` is the **minimum** index such that `j > i` and `prices[j] <= prices[i]`, otherwise, you will not receive any discount at all.
+
+_Return an array where the `ith` element is the final price you will pay for the `ith` item of the shop considering the special discount._
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** prices = [8,4,6,2,3]
+
+**Output:** [4,2,4,2,3]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+For item 0 with price[0]=8 you will receive a discount equivalent to prices[1]=4, therefore, the final price you will pay is 8 - 4 = 4.
+
+For item 1 with price[1]=4 you will receive a discount equivalent to prices[3]=2, therefore, the final price you will pay is 4 - 2 = 2.
+
+For item 2 with price[2]=6 you will receive a discount equivalent to prices[3]=2, therefore, the final price you will pay is 6 - 2 = 4.
+
+For items 3 and 4 you will not receive any discount at all.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,4,5]
+
+**Explanation:** In this case, for all items, you will not receive any discount at all.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** prices = [10,1,1,6]
+
+**Output:** [9,0,1,6]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= prices.length <= 500`
+* `1 <= prices[i] <= 10^3`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun finalPrices(prices: IntArray): IntArray {
+ val result = IntArray(prices.size)
+ for (i in prices.indices) {
+ var foundDiscount = false
+ for (j in i + 1 until prices.size) {
+ if (prices[j] <= prices[i]) {
+ result[i] = prices[i] - prices[j]
+ foundDiscount = true
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ if (!foundDiscount) {
+ result[i] = prices[i]
+ }
+ }
+ result[prices.size - 1] = prices[prices.size - 1]
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1476_subrectangle_queries/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1476_subrectangle_queries/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..940e4599
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1476_subrectangle_queries/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1476\. Subrectangle Queries
+
+Medium
+
+Implement the class `SubrectangleQueries` which receives a `rows x cols` rectangle as a matrix of integers in the constructor and supports two methods:
+
+1. `updateSubrectangle(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2, int newValue)`
+
+* Updates all values with `newValue` in the subrectangle whose upper left coordinate is `(row1,col1)` and bottom right coordinate is `(row2,col2)`.
+
+2. `getValue(int row, int col)`
+
+* Returns the current value of the coordinate `(row,col)` from the rectangle.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input** ["SubrectangleQueries","getValue","updateSubrectangle","getValue","getValue","updateSubrectangle","getValue","getValue"] [[[[1,2,1],[4,3,4],[3,2,1],[1,1,1]]],[0,2],[0,0,3,2,5],[0,2],[3,1],[3,0,3,2,10],[3,1],[0,2]]
+
+**Output:** [null,1,null,5,5,null,10,5]
+
+**Explanation:** SubrectangleQueries subrectangleQueries = new SubrectangleQueries([[1,2,1],[4,3,4],[3,2,1],[1,1,1]]); // The initial rectangle (4x3) looks like: // 1 2 1 // 4 3 4 // 3 2 1 // 1 1 1 subrectangleQueries.getValue(0, 2); // return 1 subrectangleQueries.updateSubrectangle(0, 0, 3, 2, 5); // After this update the rectangle looks like: // 5 5 5 // 5 5 5 // 5 5 5 // 5 5 5 subrectangleQueries.getValue(0, 2); // return 5 subrectangleQueries.getValue(3, 1); // return 5 subrectangleQueries.updateSubrectangle(3, 0, 3, 2, 10); // After this update the rectangle looks like: // 5 5 5 // 5 5 5 // 5 5 5 // 10 10 10 subrectangleQueries.getValue(3, 1); // return 10 subrectangleQueries.getValue(0, 2); // return 5
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input** ["SubrectangleQueries","getValue","updateSubrectangle","getValue","getValue","updateSubrectangle","getValue"] [[[[1,1,1],[2,2,2],[3,3,3]]],[0,0],[0,0,2,2,100],[0,0],[2,2],[1,1,2,2,20],[2,2]]
+
+**Output:** [null,1,null,100,100,null,20]
+
+**Explanation:** SubrectangleQueries subrectangleQueries = new SubrectangleQueries([[1,1,1],[2,2,2],[3,3,3]]); subrectangleQueries.getValue(0, 0); // return 1 subrectangleQueries.updateSubrectangle(0, 0, 2, 2, 100); subrectangleQueries.getValue(0, 0); // return 100 subrectangleQueries.getValue(2, 2); // return 100 subrectangleQueries.updateSubrectangle(1, 1, 2, 2, 20); subrectangleQueries.getValue(2, 2); // return 20
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* There will be at most `500` operations considering both methods: `updateSubrectangle` and `getValue`.
+* `1 <= rows, cols <= 100`
+* `rows == rectangle.length`
+* `cols == rectangle[i].length`
+* `0 <= row1 <= row2 < rows`
+* `0 <= col1 <= col2 < cols`
+* `1 <= newValue, rectangle[i][j] <= 10^9`
+* `0 <= row < rows`
+* `0 <= col < cols`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class SubrectangleQueries(var grid: Array) {
+ fun updateSubrectangle(row1: Int, col1: Int, row2: Int, col2: Int, newValue: Int) {
+ dfs(grid, row1, col1, row2, col2, newValue)
+ }
+
+ fun getValue(row: Int, col: Int): Int {
+ return grid[row][col]
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(rectangle: Array, row1: Int, col1: Int, row2: Int, col2: Int, value: Int) {
+ for (i in row1..row2) {
+ for (j in col1..col2) {
+ rectangle[i][j] = value
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1477_find_two_non_overlapping_sub_arrays_each_with_target_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1477_find_two_non_overlapping_sub_arrays_each_with_target_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a20e7115
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1477_find_two_non_overlapping_sub_arrays_each_with_target_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1477\. Find Two Non-overlapping Sub-arrays Each With Target Sum
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an array of integers `arr` and an integer `target`.
+
+You have to find **two non-overlapping sub-arrays** of `arr` each with a sum equal `target`. There can be multiple answers so you have to find an answer where the sum of the lengths of the two sub-arrays is **minimum**.
+
+Return _the minimum sum of the lengths_ of the two required sub-arrays, or return `-1` if you cannot find such two sub-arrays.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [3,2,2,4,3], target = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Only two sub-arrays have sum = 3 ([3] and [3]). The sum of their lengths is 2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [7,3,4,7], target = 7
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Although we have three non-overlapping sub-arrays of sum = 7 ([7], [3,4] and [7]), but we will choose the first and third sub-arrays as the sum of their lengths is 2.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [4,3,2,6,2,3,4], target = 6
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** We have only one sub-array of sum = 6.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= arr.length <= 105
+* `1 <= arr[i] <= 1000`
+* 1 <= target <= 108
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minSumOfLengths(arr: IntArray, target: Int): Int {
+ var l = 0
+ var r = 0
+ var sum = 0
+ val idx = IntArray(arr.size)
+ idx.fill(arr.size + 1)
+ var ans = 2 * arr.size + 1
+ while (r < arr.size || sum >= target) {
+ if (sum < target) {
+ sum += arr[r]
+ r++
+ } else if (sum > target) {
+ sum -= arr[l]
+ l++
+ } else {
+ val length = r - l
+ idx[r - 1] = length
+ if (l > 0 && idx[l - 1] < arr.size + 1) {
+ ans = Math.min(ans, length + idx[l - 1])
+ }
+ sum -= arr[l]
+ l++
+ }
+ if (r > 1) {
+ idx[r - 1] = Math.min(idx[r - 1], idx[r - 2])
+ }
+ }
+ return if (ans <= 2 * arr.size) ans else -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1478_allocate_mailboxes/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1478_allocate_mailboxes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..72415e70
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1478_allocate_mailboxes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1478\. Allocate Mailboxes
+
+Hard
+
+Given the array `houses` where `houses[i]` is the location of the ith house along a street and an integer `k`, allocate `k` mailboxes in the street.
+
+Return _the **minimum** total distance between each house and its nearest mailbox_.
+
+The test cases are generated so that the answer fits in a 32-bit integer.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** houses = [1,4,8,10,20], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** Allocate mailboxes in position 3, 9 and 20. Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is \|3-1\| + \|4-3\| + \|9-8\| + \|10-9\| + \|20-20\| = 5
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** houses = [2,3,5,12,18], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Explanation:** Allocate mailboxes in position 3 and 14. Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is \|2-3\| + \|3-3\| + \|5-3\| + \|12-14\| + \|18-14\| = 9.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= k <= houses.length <= 100`
+* 1 <= houses[i] <= 104
+* All the integers of `houses` are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun minDistance(houses: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ houses.sort()
+ val n = houses.size
+ val dp = Array(n) { IntArray(k + 1) }
+ for (ar in dp) {
+ ar.fill(-1)
+ }
+ return recur(houses, 0, k, dp)
+ }
+
+ private fun recur(houses: IntArray, idx: Int, k: Int, dp: Array): Int {
+ if (dp[idx][k] != -1) {
+ return dp[idx][k]
+ }
+ if (k == 1) {
+ val dist = calDist(houses, idx, houses.size - 1)
+ dp[idx][k] = dist
+ return dp[idx][k]
+ }
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var i = idx
+ while (i + k - 1 < houses.size) {
+ var dist = calDist(houses, idx, i)
+ dist += recur(houses, i + 1, k - 1, dp)
+ min = Math.min(min, dist)
+ i++
+ }
+ dp[idx][k] = min
+ return min
+ }
+
+ private fun calDist(ar: IntArray, start: Int, end: Int): Int {
+ var start = start
+ var end = end
+ var result = 0
+ while (start < end) {
+ result += ar[end--] - ar[start++]
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1480_running_sum_of_1d_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1480_running_sum_of_1d_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..db484af6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1480_running_sum_of_1d_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1480\. Running Sum of 1d Array
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array `nums`. We define a running sum of an array as `runningSum[i] = sum(nums[0]…nums[i])`.
+
+Return the running sum of `nums`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** [1,3,6,10]
+
+**Explanation:** Running sum is obtained as follows: [1, 1+2, 1+2+3, 1+2+3+4].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,4,5]
+
+**Explanation:** Running sum is obtained as follows: [1, 1+1, 1+1+1, 1+1+1+1, 1+1+1+1+1].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,1,2,10,1]
+
+**Output:** [3,4,6,16,17]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 1000`
+* `-10^6 <= nums[i] <= 10^6`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun runningSum(nums: IntArray): IntArray {
+ var sum = 0
+ val result = IntArray(nums.size)
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ sum += nums[i]
+ result[i] = sum
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1481_least_number_of_unique_integers_after_k_removals/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1481_least_number_of_unique_integers_after_k_removals/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8e4a0f65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1481_least_number_of_unique_integers_after_k_removals/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1481\. Least Number of Unique Integers after K Removals
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `arr` and an integer `k`. Find the _least number of unique integers_ after removing **exactly** `k` elements**.**
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [5,5,4], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** Remove the single 4, only 5 is left.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [4,3,1,1,3,3,2], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Remove 4, 2 and either one of the two 1s or three 3s. 1 and 3 will be left.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= arr.length <= 10^5`
+* `1 <= arr[i] <= 10^9`
+* `0 <= k <= arr.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun findLeastNumOfUniqueInts(arr: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ var k = k
+ val count: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ for (a in arr) {
+ count[a] = 1 + count.getOrDefault(a, 0)
+ }
+ var remaining = count.size
+ var occur = 1
+ val occurrenceCount = IntArray(arr.size + 1)
+ for (v in count.values) {
+ ++occurrenceCount[v]
+ }
+ while (k > 0) {
+ if (k - occur * occurrenceCount[occur] >= 0) {
+ k -= occur * occurrenceCount[occur]
+ remaining -= occurrenceCount[occur++]
+ } else {
+ return remaining - k / occur
+ }
+ }
+ return remaining
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1482_minimum_number_of_days_to_make_m_bouquets/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1482_minimum_number_of_days_to_make_m_bouquets/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b221fb4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1482_minimum_number_of_days_to_make_m_bouquets/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1482\. Minimum Number of Days to Make m Bouquets
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `bloomDay`, an integer `m` and an integer `k`.
+
+You want to make `m` bouquets. To make a bouquet, you need to use `k` **adjacent flowers** from the garden.
+
+The garden consists of `n` flowers, the ith flower will bloom in the `bloomDay[i]` and then can be used in **exactly one** bouquet.
+
+Return _the minimum number of days you need to wait to be able to make_ `m` _bouquets from the garden_. If it is impossible to make m bouquets return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** bloomDay = [1,10,3,10,2], m = 3, k = 1
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Let us see what happened in the first three days. x means flower bloomed and \_ means flower did not bloom in the garden.
+
+We need 3 bouquets each should contain 1 flower.
+
+After day 1: [x, \_, \_, \_, \_] // we can only make one bouquet.
+
+After day 2: [x, \_, \_, \_, x] // we can only make two bouquets.
+
+After day 3: [x, \_, x, \_, x] // we can make 3 bouquets. The answer is 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** bloomDay = [1,10,3,10,2], m = 3, k = 2
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** We need 3 bouquets each has 2 flowers, that means we need 6 flowers. We only have 5 flowers so it is impossible to get the needed bouquets and we return -1.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** bloomDay = [7,7,7,7,12,7,7], m = 2, k = 3
+
+**Output:** 12
+
+**Explanation:** We need 2 bouquets each should have 3 flowers.
+
+Here is the garden after the 7 and 12 days:
+
+After day 7: [x, x, x, x, \_, x, x]
+
+We can make one bouquet of the first three flowers that bloomed. We cannot make another bouquet from the last three flowers that bloomed because they are not adjacent.
+
+After day 12: [x, x, x, x, x, x, x]
+
+It is obvious that we can make two bouquets in different ways.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `bloomDay.length == n`
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* 1 <= bloomDay[i] <= 109
+* 1 <= m <= 106
+* `1 <= k <= n`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minDays(bloomDay: IntArray, m: Int, k: Int): Int {
+ if (bloomDay.size < m.toLong() * k) return -1
+ var minDay = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var maxDay = 0
+ for (day in bloomDay) {
+ if (day > maxDay) {
+ maxDay = day
+ }
+ if (day < minDay) {
+ minDay = day
+ }
+ }
+ var left = minDay
+ var right = maxDay
+ while (left < right) {
+ val mid = left + (right - left) / 2
+ if (canMake(bloomDay, m, k, mid)) {
+ // search in the left
+ right = mid
+ } else {
+ left = mid + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return right
+ }
+
+ private fun canMake(bloomDay: IntArray, m: Int, k: Int, day: Int): Boolean {
+ var count = 0
+ var bouquets = 0
+ for (i in bloomDay.indices) {
+ if (bloomDay[i] > day) {
+ count = 0
+ } else {
+ count++
+ if (count == k) {
+ bouquets++
+ count = 0
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return bouquets >= m
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1483_kth_ancestor_of_a_tree_node/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1483_kth_ancestor_of_a_tree_node/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9d35809b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1483_kth_ancestor_of_a_tree_node/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1483\. Kth Ancestor of a Tree Node
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a tree with `n` nodes numbered from `0` to `n - 1` in the form of a parent array `parent` where `parent[i]` is the parent of ith node. The root of the tree is node `0`. Find the kth ancestor of a given node.
+
+The kth ancestor of a tree node is the kth node in the path from that node to the root node.
+
+Implement the `TreeAncestor` class:
+
+* `TreeAncestor(int n, int[] parent)` Initializes the object with the number of nodes in the tree and the parent array.
+* `int getKthAncestor(int node, int k)` return the kth ancestor of the given node `node`. If there is no such ancestor, return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input** ["TreeAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor"] [[7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]], [3, 1], [5, 2], [6, 3]]
+
+**Output:** [null, 1, 0, -1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+TreeAncestor treeAncestor = new TreeAncestor(7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
+
+treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(3, 1); // returns 1 which is the parent of 3
+
+treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(5, 2); // returns 0 which is the grandparent of 5
+
+treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(6, 3); // returns -1 because there is no such ancestor
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= k <= n <= 5 * 104
+* `parent.length == n`
+* `parent[0] == -1`
+* `0 <= parent[i] < n` for all `0 < i < n`
+* `0 <= node < n`
+* There will be at most 5 * 104 queries.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class TreeAncestor(n: Int, parent: IntArray) {
+ private val steps: MutableList
+ private val stepMap: MutableMap
+
+ init {
+ steps = ArrayList()
+ stepMap = HashMap()
+ steps.add(1)
+ stepMap[1] = parent
+ val stepBase = 10
+ var step = stepBase
+ while (step * 2 < n) {
+ val stepArr = IntArray(n)
+ val lastStepArr = stepMap[steps[steps.size - 1]]
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ var cur = i
+ var repeat = 0
+ while (repeat < stepBase && cur != -1) {
+ cur = lastStepArr!![cur]
+ repeat++
+ }
+ stepArr[i] = cur
+ }
+ steps.add(step)
+ stepMap[step] = stepArr
+ step *= stepBase
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun getKthAncestor(node: Int, k: Int): Int {
+ var node = node
+ var k = k
+ var index = steps.size - 1
+ while (k > 0 && node != -1 && index >= 0) {
+ val step = steps[index]
+ val stepArr = stepMap[step]
+ while (k >= step && node != -1) {
+ node = stepArr!![node]
+ k -= step
+ }
+ index--
+ }
+ return node
+ }
+}
+/*
+ * Your TreeAncestor object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * var obj = TreeAncestor(n, parent)
+ * var param_1 = obj.getKthAncestor(node,k)
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1484_group_sold_products_by_the_date/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1484_group_sold_products_by_the_date/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a9afd8b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1484_group_sold_products_by_the_date/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1484\. Group Sold Products By The Date
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table `Activities`:
+
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | sell_date | date |
+ | product | varchar |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ There is no primary key for this table, it may contain duplicates.
+ Each row of this table contains the product name and the date it was sold in a market.
+
+Write an SQL query to find for each date the number of different products sold and their names.
+
+The sold products names for each date should be sorted lexicographically.
+
+Return the result table ordered by `sell_date`.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Activities table:
+ +------------+------------+
+ | sell_date | product |
+ +------------+------------+
+ | 2020-05-30 | Headphone |
+ | 2020-06-01 | Pencil |
+ | 2020-06-02 | Mask |
+ | 2020-05-30 | Basketball |
+ | 2020-06-01 | Bible |
+ | 2020-06-02 | Mask |
+ | 2020-05-30 | T-Shirt |
+ +------------+------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +------------+----------+------------------------------+
+ | sell_date | num_sold | products |
+ +------------+----------+------------------------------+
+ | 2020-05-30 | 3 | Basketball,Headphone,T-shirt |
+ | 2020-06-01 | 2 | Bible,Pencil |
+ | 2020-06-02 | 1 | Mask |
+ +------------+----------+------------------------------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+For 2020-05-30, Sold items were (Headphone, Basketball, T-shirt), we sort them lexicographically and separate them by a comma.
+
+For 2020-06-01, Sold items were (Pencil, Bible), we sort them lexicographically and separate them by a comma.
+
+For 2020-06-02, the Sold item is (Mask), we just return it.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+SELECT sell_date, COUNT(DISTINCT(product)) as num_sold, GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT(product) ORDER BY product) as products
+FROM Activities
+GROUP BY sell_date
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1486_xor_operation_in_an_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1486_xor_operation_in_an_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b44639de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1486_xor_operation_in_an_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1486\. XOR Operation in an Array
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an integer `n` and an integer `start`.
+
+Define an array `nums` where `nums[i] = start + 2 * i` (**0-indexed**) and `n == nums.length`.
+
+Return _the bitwise XOR of all elements of_ `nums`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5, start = 0
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:** Array nums is equal to [0, 2, 4, 6, 8] where (0 ^ 2 ^ 4 ^ 6 ^ 8) = 8. Where "^" corresponds to bitwise XOR operator.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, start = 3
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:** Array nums is equal to [3, 5, 7, 9] where (3 ^ 5 ^ 7 ^ 9) = 8.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 1000`
+* `0 <= start <= 1000`
+* `n == nums.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun xorOperation(n: Int, start: Int): Int {
+ val nums = IntArray(n)
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ nums[i] = start + 2 * i
+ }
+ var result = 0
+ for (num in nums) {
+ result = result xor num
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1487_making_file_names_unique/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1487_making_file_names_unique/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e9288245
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1487_making_file_names_unique/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1487\. Making File Names Unique
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of strings `names` of size `n`. You will create `n` folders in your file system **such that**, at the ith minute, you will create a folder with the name `names[i]`.
+
+Since two files **cannot** have the same name, if you enter a folder name that was previously used, the system will have a suffix addition to its name in the form of `(k)`, where, `k` is the **smallest positive integer** such that the obtained name remains unique.
+
+Return _an array of strings of length_ `n` where `ans[i]` is the actual name the system will assign to the ith folder when you create it.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** names = ["pes","fifa","gta","pes(2019)"]
+
+**Output:** ["pes","fifa","gta","pes(2019)"]
+
+**Explanation:** Let's see how the file system creates folder names:
+
+"pes" --> not assigned before, remains "pes"
+
+"fifa" --> not assigned before, remains "fifa"
+
+"gta" --> not assigned before, remains "gta"
+
+"pes(2019)" --> not assigned before, remains "pes(2019)"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** names = ["gta","gta(1)","gta","avalon"]
+
+**Output:** ["gta","gta(1)","gta(2)","avalon"]
+
+**Explanation:** Let's see how the file system creates folder names:
+
+"gta" --> not assigned before, remains "gta"
+
+"gta(1)" --> not assigned before, remains "gta(1)"
+
+"gta" --> the name is reserved, system adds (k), since "gta(1)" is also reserved, systems put k = 2. it becomes "gta(2)"
+
+"avalon" --> not assigned before, remains "avalon"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** names = ["onepiece","onepiece(1)","onepiece(2)","onepiece(3)","onepiece"]
+
+**Output:** ["onepiece","onepiece(1)","onepiece(2)","onepiece(3)","onepiece(4)"]
+
+**Explanation:** When the last folder is created, the smallest positive valid k is 4, and it becomes "onepiece(4)".
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= names.length <= 5 * 104
+* `1 <= names[i].length <= 20`
+* `names[i]` consists of lowercase English letters, digits, and/or round brackets.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun getFolderNames(names: Array): Array {
+ val map = HashMap()
+ for (i in names.indices) {
+ var prefix = map.getOrDefault(names[i], 0)
+ if (prefix != 0) {
+ val raw = names[i]
+ while (map.getOrDefault(names[i], 0) != 0) {
+ names[i] = "$raw($prefix)"
+ prefix++
+ }
+ map[raw] = prefix
+ }
+ map[names[i]] = 1
+ }
+ return names
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1488_avoid_flood_in_the_city/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1488_avoid_flood_in_the_city/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..80dacdee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1488_avoid_flood_in_the_city/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1488\. Avoid Flood in The City
+
+Medium
+
+Your country has an infinite number of lakes. Initially, all the lakes are empty, but when it rains over the `nth` lake, the `nth` lake becomes full of water. If it rains over a lake which is **full of water**, there will be a **flood**. Your goal is to avoid the flood in any lake.
+
+Given an integer array `rains` where:
+
+* `rains[i] > 0` means there will be rains over the `rains[i]` lake.
+* `rains[i] == 0` means there are no rains this day and you can choose **one lake** this day and **dry it**.
+
+Return _an array `ans`_ where:
+
+* `ans.length == rains.length`
+* `ans[i] == -1` if `rains[i] > 0`.
+* `ans[i]` is the lake you choose to dry in the `ith` day if `rains[i] == 0`.
+
+If there are multiple valid answers return **any** of them. If it is impossible to avoid flood return **an empty array**.
+
+Notice that if you chose to dry a full lake, it becomes empty, but if you chose to dry an empty lake, nothing changes. (see example 4)
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** rains = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** [-1,-1,-1,-1]
+
+**Explanation:** After the first day full lakes are [1]
+
+After the second day full lakes are [1,2]
+
+After the third day full lakes are [1,2,3]
+
+After the fourth day full lakes are [1,2,3,4]
+
+There's no day to dry any lake and there is no flood in any lake.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** rains = [1,2,0,0,2,1]
+
+**Output:** [-1,-1,2,1,-1,-1]
+
+**Explanation:** After the first day full lakes are [1]
+
+After the second day full lakes are [1,2]
+
+After the third day, we dry lake 2. Full lakes are [1]
+
+After the fourth day, we dry lake 1. There is no full lakes.
+
+After the fifth day, full lakes are [2].
+
+After the sixth day, full lakes are [1,2].
+
+It is easy that this scenario is flood-free. [-1,-1,1,2,-1,-1] is another acceptable scenario.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** rains = [1,2,0,1,2]
+
+**Output:** []
+
+**Explanation:** After the second day, full lakes are [1,2]. We have to dry one lake in the third day.
+
+After that, it will rain over lakes [1,2]. It's easy to prove that no matter which lake you choose to dry in the 3rd day, the other one will flood.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= rains.length <= 105
+* 0 <= rains[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.TreeSet
+
+class Solution {
+ fun avoidFlood(rains: IntArray): IntArray {
+ val hm = HashMap()
+ val tree = TreeSet()
+ val ans = IntArray(rains.size)
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < rains.size) {
+ val rain = rains[i]
+ if (rain != 0) {
+ if (hm.containsKey(rain)) {
+ val mapVal = hm[rain]!!
+ if (tree.ceiling(mapVal) != null) {
+ ans[tree.ceiling(mapVal)] = rain
+ hm[rain] = i
+ tree.remove(tree.ceiling(mapVal))
+ } else {
+ return IntArray(0)
+ }
+ } else {
+ hm[rain] = i
+ }
+ ans[i] = -1
+ } else {
+ tree.add(i)
+ }
+ i += 1
+ }
+ for (tr in tree) {
+ ans[tr] = 1
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1489_find_critical_and_pseudo_critical_edges_in_minimum_spanning_tree/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1489_find_critical_and_pseudo_critical_edges_in_minimum_spanning_tree/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..168dcf46
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1489_find_critical_and_pseudo_critical_edges_in_minimum_spanning_tree/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1489\. Find Critical and Pseudo-Critical Edges in Minimum Spanning Tree
+
+Hard
+
+Given a weighted undirected connected graph with `n` vertices numbered from `0` to `n - 1`, and an array `edges` where edges[i] = [ai, bi, weighti] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between nodes ai and bi. A minimum spanning tree (MST) is a subset of the graph's edges that connects all vertices without cycles and with the minimum possible total edge weight.
+
+Find _all the critical and pseudo-critical edges in the given graph's minimum spanning tree (MST)_. An MST edge whose deletion from the graph would cause the MST weight to increase is called a _critical edge_. On the other hand, a pseudo-critical edge is that which can appear in some MSTs but not all.
+
+Note that you can return the indices of the edges in any order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 5, edges = \[\[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,2],[0,3,2],[0,4,3],[3,4,3],[1,4,6]]
+
+**Output:** [[0,1],[2,3,4,5]]
+
+**Explanation:** The figure above describes the graph.
+
+The following figure shows all the possible MSTs:
+
+
+
+Notice that the two edges 0 and 1 appear in all MSTs, therefore they are critical edges, so we return them in the first list of the output.
+
+The edges 2, 3, 4, and 5 are only part of some MSTs, therefore they are considered pseudo-critical edges. We add them to the second list of the output.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 4, edges = \[\[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[0,3,1]]
+
+**Output:** [[],[0,1,2,3]]
+
+**Explanation:** We can observe that since all 4 edges have equal weight, choosing any 3 edges from the given 4 will yield an MST. Therefore all 4 edges are pseudo-critical.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n <= 100`
+* `1 <= edges.length <= min(200, n * (n - 1) / 2)`
+* `edges[i].length == 3`
+* 0 <= ai < bi < n
+* 1 <= weighti <= 1000
+* All pairs (ai, bi) are **distinct**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+import java.util.LinkedList
+
+class Solution {
+ fun findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(n: Int, edges: Array): List> {
+ // {w, ind}
+ val g = Array(n) { Array(n) { IntArray(2) } }
+ for (i in edges.indices) {
+ val e = edges[i]
+ val f = e[0]
+ val t = e[1]
+ val w = e[2]
+ g[f][t][0] = w
+ g[t][f][0] = w
+ g[f][t][1] = i
+ g[t][f][1] = i
+ }
+ val mst: Array?> = arrayOfNulls(n)
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ mst[i] = LinkedList()
+ }
+ val mstSet = BooleanArray(edges.size)
+ Arrays.sort(edges) { a: IntArray, b: IntArray ->
+ Integer.compare(
+ a[2], b[2]
+ )
+ }
+ buildMST(n, edges, mstSet, mst, g)
+ val ans: MutableList> = ArrayList(2)
+ val pce: MutableSet = HashSet()
+ val ce: MutableList = LinkedList()
+ // pseudo critical edges
+ for (edge in edges) {
+ val f = edge[0]
+ val t = edge[1]
+ val w = edge[2]
+ val ind = g[f][t][1]
+ if (!mstSet[ind]) {
+ val cur: MutableSet = HashSet()
+ val p = path(f, t, w, -1, mst, g, cur)
+ if (p && cur.isNotEmpty()) {
+ pce.addAll(cur)
+ pce.add(ind)
+ }
+ if (!p) {
+ println("Should not reach here")
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // critical edges
+ for (edge in edges) {
+ val f = edge[0]
+ val t = edge[1]
+ val ind = g[f][t][1]
+ if (mstSet[ind] && !pce.contains(ind)) {
+ ce.add(ind)
+ }
+ }
+ ans.add(ce)
+ ans.add(LinkedList(pce))
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun path(
+ f: Int,
+ t: Int,
+ w: Int,
+ p: Int,
+ mst: Array?>,
+ g: Array>,
+ ind: MutableSet
+ ): Boolean {
+ if (f == t) {
+ return true
+ }
+ for (nbr in mst[f]!!) {
+ if (p != nbr && path(nbr, t, w, f, mst, g, ind)) {
+ if (g[f][nbr][0] == w) {
+ ind.add(g[f][nbr][1])
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ private fun buildMST(
+ n: Int,
+ edges: Array,
+ mste: BooleanArray,
+ mstg: Array?>,
+ g: Array>
+ ) {
+ val ds = DisjointSet(n)
+ for (ints in edges) {
+ if (ds.union(ints[0], ints[1])) {
+ mstg[ints[0]]?.add(ints[1])
+ mstg[ints[1]]?.add(ints[0])
+ mste[g[ints[0]][ints[1]][1]] = true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private class DisjointSet(n: Int) {
+ var parent: IntArray
+
+ init {
+ parent = IntArray(n)
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ parent[i] = i
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun find(i: Int): Int {
+ if (i == parent[i]) {
+ return i
+ }
+ parent[i] = find(parent[i])
+ return parent[i]
+ }
+
+ fun union(u: Int, v: Int): Boolean {
+ val pu = find(u)
+ val pv = find(v)
+ if (pu == pv) {
+ return false
+ }
+ parent[pu] = pv
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1491_average_salary_excluding_the_minimum_and_maximum_salary/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1491_average_salary_excluding_the_minimum_and_maximum_salary/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4419cd55
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1491_average_salary_excluding_the_minimum_and_maximum_salary/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1491\. Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and Maximum Salary
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an array of **unique** integers `salary` where `salary[i]` is the salary of the ith employee.
+
+Return _the average salary of employees excluding the minimum and maximum salary_. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** salary = [4000,3000,1000,2000]
+
+**Output:** 2500.00000
+
+**Explanation:** Minimum salary and maximum salary are 1000 and 4000 respectively.
+
+Average salary excluding minimum and maximum salary is (2000+3000) / 2 = 2500
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** salary = [1000,2000,3000]
+
+**Output:** 2000.00000
+
+**Explanation:** Minimum salary and maximum salary are 1000 and 3000 respectively.
+
+Average salary excluding minimum and maximum salary is (2000) / 1 = 2000
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `3 <= salary.length <= 100`
+* 1000 <= salary[i] <= 106
+* All the integers of `salary` are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun average(salary: IntArray): Double {
+ val n = salary.size
+ var min = salary[0]
+ var max = salary[0]
+ var sum = salary[0]
+ for (i in 1 until n) {
+ if (salary[i] < min) {
+ min = salary[i]
+ } else if (salary[i] > max) {
+ max = salary[i]
+ }
+ sum += salary[i]
+ }
+ return (sum - min - max).toDouble() / (n - 2)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1492_the_kth_factor_of_n/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1492_the_kth_factor_of_n/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..926c0dd6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1492_the_kth_factor_of_n/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1492\. The kth Factor of n
+
+Medium
+
+You are given two positive integers `n` and `k`. A factor of an integer `n` is defined as an integer `i` where `n % i == 0`.
+
+Consider a list of all factors of `n` sorted in **ascending order**, return _the_ kth _factor_ in this list or return `-1` if `n` has less than `k` factors.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 12, k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Factors list is [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12], the 3rd factor is 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 7, k = 2
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:** Factors list is [1, 7], the 2nd factor is 7.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, k = 4
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** Factors list is [1, 2, 4], there is only 3 factors. We should return -1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= k <= n <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun kthFactor(n: Int, k: Int): Int {
+ val list: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (i in 1..n) {
+ if (n % i == 0) {
+ list.add(i)
+ }
+ }
+ return if (list.size >= k) list[k - 1] else -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1493_longest_subarray_of_1s_after_deleting_one_element/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1493_longest_subarray_of_1s_after_deleting_one_element/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..17be44d6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1493_longest_subarray_of_1s_after_deleting_one_element/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1493\. Longest Subarray of 1's After Deleting One Element
+
+Medium
+
+Given a binary array `nums`, you should delete one element from it.
+
+Return _the size of the longest non-empty subarray containing only_ `1`_'s in the resulting array_. Return `0` if there is no such subarray.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** After deleting the number in position 2, [1,1,1] contains 3 numbers with value of 1's.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** After deleting the number in position 4, [0,1,1,1,1,1,0,1] longest subarray with value of 1's is [1,1,1,1,1].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** You must delete one element.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* `nums[i]` is either `0` or `1`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun longestSubarray(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var s = 0
+ var e = 0
+ var max = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ var extraZero = false
+ var allOne = true
+ while (e < nums.size) {
+ if (nums[e] == 1) {
+ e++
+ } else if (!extraZero) {
+ allOne = false
+ extraZero = true
+ e++
+ } else {
+ allOne = false
+ max = Math.max(max, e - s - 1)
+ while (nums[s] != 0) {
+ s++
+ }
+ s++
+ extraZero = false
+ }
+ }
+ if (nums[e - 1] == 1) {
+ max = Math.max(max, e - s - 1)
+ }
+ if (allOne) {
+ return nums.size - 1
+ }
+ return if (max == Int.MIN_VALUE) 0 else max
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1494_parallel_courses_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1494_parallel_courses_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..058a06f2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1494_parallel_courses_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1494\. Parallel Courses II
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer `n`, which indicates that there are `n` courses labeled from `1` to `n`. You are also given an array `relations` where relations[i] = [prevCoursei, nextCoursei], representing a prerequisite relationship between course prevCoursei and course nextCoursei: course prevCoursei has to be taken before course nextCoursei. Also, you are given the integer `k`.
+
+In one semester, you can take **at most** `k` courses as long as you have taken all the prerequisites in the **previous** semester for the courses you are taking.
+
+Return _the **minimum** number of semesters needed to take all courses_. The testcases will be generated such that it is possible to take every course.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** n = 4, dependencies = \[\[2,1],[3,1],[1,4]], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The figure above represents the given graph. In the first semester, you can take courses 2 and 3. In the second semester, you can take course 1. In the third semester, you can take course 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** n = 5, dependencies = \[\[2,1],[3,1],[4,1],[1,5]], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The figure above represents the given graph. In the first semester, you can take courses 2 and 3 only since you cannot take more than two per semester. In the second semester, you can take course 4. In the third semester, you can take course 1. In the fourth semester, you can take course 5.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 11, dependencies = [], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 15`
+* `1 <= k <= n`
+* `0 <= relations.length <= n * (n-1) / 2`
+* `relations[i].length == 2`
+* 1 <= prevCoursei, nextCoursei <= n
+* prevCoursei != nextCoursei
+* All the pairs [prevCoursei, nextCoursei] are **unique**.
+* The given graph is a directed acyclic graph.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minNumberOfSemesters(n: Int, relations: Array, k: Int): Int {
+ val pres = IntArray(n)
+ for (r in relations) {
+ val prev = r[0] - 1
+ val next = r[1] - 1
+ pres[next] = pres[next] or (1 shl prev)
+ }
+ val dp = IntArray(1 shl n)
+ dp.fill(n)
+ dp[0] = 0
+ for (mask in dp.indices) {
+ var canTake = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ // already taken
+ if (mask and (1 shl i) != 0) {
+ continue
+ }
+ // satisfy all pres
+ if (mask and pres[i] == pres[i]) {
+ canTake = canTake or (1 shl i)
+ }
+ }
+ // loop each sub-masks
+ var take = canTake
+ while (take > 0) {
+ if (Integer.bitCount(take) > k) {
+ take = take - 1 and canTake
+ continue
+ }
+ dp[take or mask] = Math.min(dp[take or mask], dp[mask] + 1)
+ take = take - 1 and canTake
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[(1 shl n) - 1]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1496_path_crossing/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1496_path_crossing/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..889c684d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1496_path_crossing/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1496\. Path Crossing
+
+Easy
+
+Given a string `path`, where `path[i] = 'N'`, `'S'`, `'E'` or `'W'`, each representing moving one unit north, south, east, or west, respectively. You start at the origin `(0, 0)` on a 2D plane and walk on the path specified by `path`.
+
+Return `true` _if the path crosses itself at any point, that is, if at any time you are on a location you have previously visited_. Return `false` otherwise.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+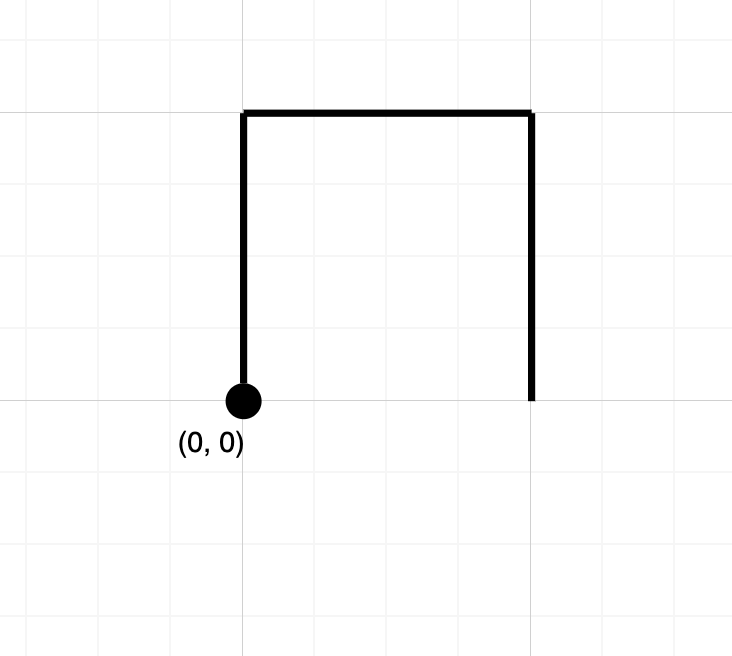
+
+**Input:** path = "NES"
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** Notice that the path doesn't cross any point more than once.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+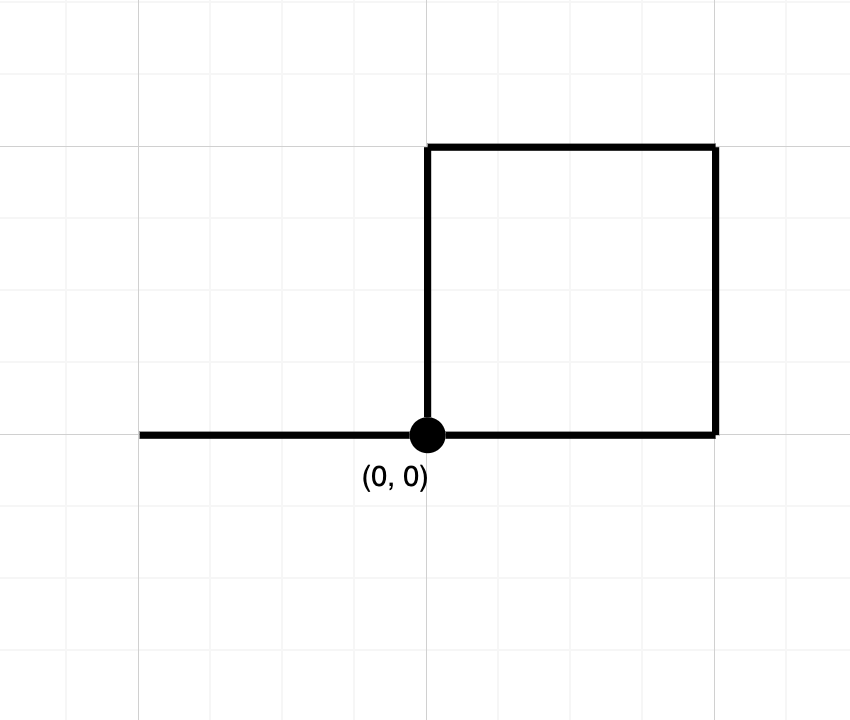
+
+**Input:** path = "NESWW"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Notice that the path visits the origin twice.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= path.length <= 104
+* `path[i]` is either `'N'`, `'S'`, `'E'`, or `'W'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Stack
+
+class Solution {
+ fun isPathCrossing(path: String): Boolean {
+ val visited = Stack()
+ visited.add(Coord(0, 0))
+ for (c in path.toCharArray()) {
+ val last = visited.peek()
+ if (c == 'N') {
+ val nextStep = Coord(last.x, last.y + 1)
+ if (visited.contains(nextStep)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ visited.add(nextStep)
+ } else if (c == 'S') {
+ val nextStep = Coord(last.x, last.y - 1)
+ if (visited.contains(nextStep)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ visited.add(nextStep)
+ } else if (c == 'E') {
+ val nextStep = Coord(last.x - 1, last.y)
+ if (visited.contains(nextStep)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ visited.add(nextStep)
+ } else if (c == 'W') {
+ val nextStep = Coord(last.x + 1, last.y)
+ if (visited.contains(nextStep)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ visited.add(nextStep)
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ internal data class Coord(var x: Int, var y: Int)
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1497_check_if_array_pairs_are_divisible_by_k/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1497_check_if_array_pairs_are_divisible_by_k/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..614e0eca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1497_check_if_array_pairs_are_divisible_by_k/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1497\. Check If Array Pairs Are Divisible by k
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `arr` of even length `n` and an integer `k`.
+
+We want to divide the array into exactly `n / 2` pairs such that the sum of each pair is divisible by `k`.
+
+Return `true` _If you can find a way to do that or_ `false` _otherwise_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3,4,5,10,6,7,8,9], k = 5
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Pairs are (1,9),(2,8),(3,7),(4,6) and (5,10).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6], k = 7
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Pairs are (1,6),(2,5) and(3,4).
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6], k = 10
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** You can try all possible pairs to see that there is no way to divide arr into 3 pairs each with sum divisible by 10.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `arr.length == n`
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* `n` is even.
+* -109 <= arr[i] <= 109
+* 1 <= k <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun canArrange(arr: IntArray, k: Int): Boolean {
+ val freq = IntArray(k)
+ for (num in arr) {
+ freq[Math.abs(num % k + k) % k]++
+ }
+ if (freq[0] % 2 != 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ for (i in 1..k / 2) {
+ if (i == k - i && freq[i] % 2 != 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ if (freq[i] != freq[k - i]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1498_number_of_subsequences_that_satisfy_the_given_sum_condition/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1498_number_of_subsequences_that_satisfy_the_given_sum_condition/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ddf73d5a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1498_number_of_subsequences_that_satisfy_the_given_sum_condition/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1498\. Number of Subsequences That Satisfy the Given Sum Condition
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `target`.
+
+Return _the number of **non-empty** subsequences of_ `nums` _such that the sum of the minimum and maximum element on it is less or equal to_ `target`. Since the answer may be too large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,5,6,7], target = 9
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** There are 4 subsequences that satisfy the condition.
+
+[3] -> Min value + max value <= target (3 + 3 <= 9)
+
+[3,5] -> (3 + 5 <= 9)
+
+[3,5,6] -> (3 + 6 <= 9)
+
+[3,6] -> (3 + 6 <= 9)
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,3,6,8], target = 10
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** There are 6 subsequences that satisfy the condition. (nums can have repeated numbers). [3] , [3] , [3,3], [3,6] , [3,6] , [3,3,6]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,3,3,4,6,7], target = 12
+
+**Output:** 61
+
+**Explanation:** There are 63 non-empty subsequences, two of them do not satisfy the condition ([6,7], [7]). Number of valid subsequences (63 - 2 = 61).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 106
+* 1 <= target <= 106
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numSubseq(nums: IntArray, target: Int): Int {
+ // sorted array will be used to perform binary search
+ nums.sort()
+ val mod = 1000000007
+ // powOf2[i] means (2^i) % mod
+ val powOf2 = IntArray(nums.size)
+ powOf2[0] = 1
+ for (i in 1 until nums.size) {
+ powOf2[i] = powOf2[i - 1] * 2 % mod
+ }
+ var res = 0
+ var left = 0
+ var right = nums.size - 1
+ while (left <= right) {
+ if (nums[left] + nums[right] > target) {
+ // nums[right] which is macimum is too big so decrease it
+ right--
+ } else {
+ // every number between right and left be either picked or not picked
+ // so that is why pow(2, right - left) essentially
+ res = (res + powOf2[right - left]) % mod
+ // increment left to find next set of min and max
+ left++
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1499_max_value_of_equation/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1499_max_value_of_equation/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d03df5fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1401_1500/s1499_max_value_of_equation/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1499\. Max Value of Equation
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an array `points` containing the coordinates of points on a 2D plane, sorted by the x-values, where points[i] = [xi, yi] such that xi < xj for all `1 <= i < j <= points.length`. You are also given an integer `k`.
+
+Return _the maximum value of the equation_ yi + yj + |xi - xj| where |xi - xj| <= k and `1 <= i < j <= points.length`.
+
+It is guaranteed that there exists at least one pair of points that satisfy the constraint |xi - xj| <= k.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** points = \[\[1,3],[2,0],[5,10],[6,-10]], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The first two points satisfy the condition \|xi - xj\| <= 1 and if we calculate the equation we get 3 + 0 + \|1 - 2\| = 4. Third and fourth points also satisfy the condition and give a value of 10 + -10 + \|5 - 6\| = 1.
+
+No other pairs satisfy the condition, so we return the max of 4 and 1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** points = \[\[0,0],[3,0],[9,2]], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Only the first two points have an absolute difference of 3 or less in the x-values, and give the value of 0 + 0 + \|0 - 3\| = 3.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= points.length <= 105
+* `points[i].length == 2`
+* -108 <= xi, yi <= 108
+* 0 <= k <= 2 * 108
+* xi < xj for all `1 <= i < j <= points.length`
+* xi form a strictly increasing sequence.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findMaxValueOfEquation(points: Array, k: Int): Int {
+ var res = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ var max = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ var r = 0
+ var rMax = 0
+ for (l in 0 until points.size - 1) {
+ if (rMax == l) {
+ max = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ r = l + 1
+ rMax = r
+ }
+ while (r < points.size && points[r][0] - points[l][0] <= k) {
+ val v = points[r][0] + points[r][1]
+ if (max < v) {
+ max = v
+ rMax = r
+ }
+ r++
+ }
+ if (points[rMax][0] - points[l][0] <= k) {
+ res = Math.max(
+ res,
+ points[rMax][0] - points[l][0] + points[rMax][1] + points[l][1]
+ )
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1502_can_make_arithmetic_progression_from_sequence/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1502_can_make_arithmetic_progression_from_sequence/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f7e35330
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1502_can_make_arithmetic_progression_from_sequence/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1502\. Can Make Arithmetic Progression From Sequence
+
+Easy
+
+A sequence of numbers is called an **arithmetic progression** if the difference between any two consecutive elements is the same.
+
+Given an array of numbers `arr`, return `true` _if the array can be rearranged to form an **arithmetic progression**. Otherwise, return_ `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [3,5,1]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** We can reorder the elements as [1,3,5] or [5,3,1] with differences 2 and -2 respectively, between each consecutive elements.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,4]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** There is no way to reorder the elements to obtain an arithmetic progression.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= arr.length <= 1000`
+* -106 <= arr[i] <= 106
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun canMakeArithmeticProgression(arr: IntArray): Boolean {
+ arr.sort()
+ for (i in 0 until arr.size - 2) {
+ if (arr[i + 1] - arr[i] != arr[i + 2] - arr[i + 1]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1503_last_moment_before_all_ants_fall_out_of_a_plank/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1503_last_moment_before_all_ants_fall_out_of_a_plank/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e08f6459
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1503_last_moment_before_all_ants_fall_out_of_a_plank/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1503\. Last Moment Before All Ants Fall Out of a Plank
+
+Medium
+
+We have a wooden plank of the length `n` **units**. Some ants are walking on the plank, each ant moves with a speed of **1 unit per second**. Some of the ants move to the **left**, the other move to the **right**.
+
+When two ants moving in two **different** directions meet at some point, they change their directions and continue moving again. Assume changing directions does not take any additional time.
+
+When an ant reaches **one end** of the plank at a time `t`, it falls out of the plank immediately.
+
+Given an integer `n` and two integer arrays `left` and `right`, the positions of the ants moving to the left and the right, return _the moment when the last ant(s) fall out of the plank_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+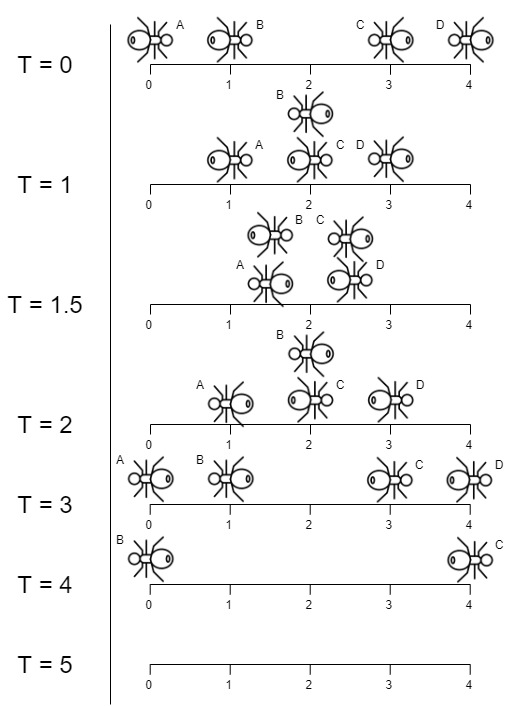
+
+**Input:** n = 4, left = [4,3], right = [0,1]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** In the image above:
+
+-The ant at index 0 is named A and going to the right.
+
+-The ant at index 1 is named B and going to the right.
+
+-The ant at index 3 is named C and going to the left.
+
+-The ant at index 4 is named D and going to the left.
+
+The last moment when an ant was on the plank is t = 4 seconds. After that, it falls immediately out of the plank. (i.e., We can say that at t = 4.0000000001, there are no ants on the plank).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 7, left = [], right = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:** All ants are going to the right, the ant at index 0 needs 7 seconds to fall.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 7, left = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7], right = []
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:** All ants are going to the left, the ant at index 7 needs 7 seconds to fall.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 104
+* `0 <= left.length <= n + 1`
+* `0 <= left[i] <= n`
+* `0 <= right.length <= n + 1`
+* `0 <= right[i] <= n`
+* `1 <= left.length + right.length <= n + 1`
+* All values of `left` and `right` are unique, and each value can appear **only in one** of the two arrays.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun getLastMoment(n: Int, left: IntArray, right: IntArray): Int {
+ var highestLeft = 0
+ var smallestRight = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ for (i in 0..n + 1) {
+ if (i < left.size && left[i] > highestLeft) {
+ highestLeft = left[i]
+ }
+ if (i < right.size && right[i] < smallestRight) {
+ smallestRight = right[i]
+ }
+ }
+ if (left.isNotEmpty() && right.isEmpty()) {
+ return highestLeft
+ }
+ return if (right.isNotEmpty() && left.isEmpty()) {
+ Math.abs(smallestRight - n)
+ } else Math.max(highestLeft, Math.abs(smallestRight - n))
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1504_count_submatrices_with_all_ones/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1504_count_submatrices_with_all_ones/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e6145d35
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1504_count_submatrices_with_all_ones/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1504\. Count Submatrices With All Ones
+
+Medium
+
+Given an `m x n` binary matrix `mat`, _return the number of **submatrices** that have all ones_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[1,0,1],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
+
+**Output:** 13
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are 6 rectangles of side 1x1.
+
+There are 2 rectangles of side 1x2.
+
+There are 3 rectangles of side 2x1.
+
+There is 1 rectangle of side 2x2.
+
+There is 1 rectangle of side 3x1.
+
+Total number of rectangles = 6 + 2 + 3 + 1 + 1 = 13.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,1],[1,1,1,0]]
+
+**Output:** 24
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are 8 rectangles of side 1x1.
+
+There are 5 rectangles of side 1x2.
+
+There are 2 rectangles of side 1x3.
+
+There are 4 rectangles of side 2x1.
+
+There are 2 rectangles of side 2x2.
+
+There are 2 rectangles of side 3x1.
+
+There is 1 rectangle of side 3x2.
+
+Total number of rectangles = 8 + 5 + 2 + 4 + 2 + 2 + 1 = 24.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= m, n <= 150`
+* `mat[i][j]` is either `0` or `1`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numSubmat(mat: Array): Int {
+ val dp = Array(mat.size) { IntArray(mat[0].size) }
+ for (i in mat.indices) {
+ var c = 0
+ for (j in mat[0].indices.reversed()) {
+ if (mat[i][j] == 1) {
+ c++
+ } else {
+ c = 0
+ }
+ dp[i][j] = c
+ }
+ }
+ var ans = 0
+ for (i in mat.indices) {
+ for (j in mat[0].indices) {
+ var x = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ for (k in i until mat.size) {
+ x = Math.min(x, dp[k][j])
+ ans += x
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1505_minimum_possible_integer_after_at_most_k_adjacent_swaps_on_digits/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1505_minimum_possible_integer_after_at_most_k_adjacent_swaps_on_digits/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..57d2d16e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1505_minimum_possible_integer_after_at_most_k_adjacent_swaps_on_digits/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1505\. Minimum Possible Integer After at Most K Adjacent Swaps On Digits
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a string `num` representing **the digits** of a very large integer and an integer `k`. You are allowed to swap any two adjacent digits of the integer **at most** `k` times.
+
+Return _the minimum integer you can obtain also as a string_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** num = "4321", k = 4
+
+**Output:** "1342"
+
+**Explanation:** The steps to obtain the minimum integer from 4321 with 4 adjacent swaps are shown.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** num = "100", k = 1
+
+**Output:** "010"
+
+**Explanation:** It's ok for the output to have leading zeros, but the input is guaranteed not to have any leading zeros.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** num = "36789", k = 1000
+
+**Output:** "36789"
+
+**Explanation:** We can keep the number without any swaps.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= num.length <= 3 * 104
+* `num` consists of only **digits** and does not contain **leading zeros**.
+* 1 <= k <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING")
+class Solution {
+ fun minInteger(num: String, k: Int): String {
+ var k = k
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ val digitPos = IntArray(10)
+ val reduceMove = IntArray(10)
+ var matchAmount = 0
+ val chars = num.toCharArray()
+ digitPos.fill(chars.size)
+ for (i in chars.indices) {
+ val cur = chars[i].code - '0'.code
+ if (digitPos[cur] == chars.size) {
+ digitPos[cur] = i
+ matchAmount++
+ if (matchAmount == 10) {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ var curIndex = 0
+ while (k > 0 && curIndex < chars.size) {
+ for (digit in 0..9) {
+ if (digitPos[digit] < chars.size && digitPos[digit] - reduceMove[digit] <= k) {
+ sb.append(chars[digitPos[digit]])
+ k -= digitPos[digit] - reduceMove[digit]
+ curIndex++
+ reduceMove[digit]++
+ for (j in 0..9) {
+ if (j != digit && digitPos[j] > digitPos[digit]) {
+ reduceMove[j]++
+ }
+ }
+ var find = false
+ for (next in digitPos[digit] + 1 until chars.size) {
+ val cur = chars[next].code - '0'.code
+ if (cur == digit) {
+ find = true
+ digitPos[digit] = next
+ break
+ }
+ if (next < digitPos[cur]) {
+ reduceMove[digit]++
+ }
+ }
+ if (!find) {
+ digitPos[digit] = chars.size
+ }
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ val start = digitPos.min()
+ for (i in start until chars.size) {
+ if (digitPos[chars[i].code - '0'.code] <= i) {
+ sb.append(chars[i])
+ }
+ }
+ return sb.toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1507_reformat_date/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1507_reformat_date/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..636e2092
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1507_reformat_date/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1507\. Reformat Date
+
+Easy
+
+Given a `date` string in the form `Day Month Year`, where:
+
+* `Day` is in the set `{"1st", "2nd", "3rd", "4th", ..., "30th", "31st"}`.
+* `Month` is in the set `{"Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun", "Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec"}`.
+* `Year` is in the range `[1900, 2100]`.
+
+Convert the date string to the format `YYYY-MM-DD`, where:
+
+* `YYYY` denotes the 4 digit year.
+* `MM` denotes the 2 digit month.
+* `DD` denotes the 2 digit day.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** date = "20th Oct 2052"
+
+**Output:** "2052-10-20"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** date = "6th Jun 1933"
+
+**Output:** "1933-06-06"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** date = "26th May 1960"
+
+**Output:** "1960-05-26"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The given dates are guaranteed to be valid, so no error handling is necessary.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun reformatDate(date: String): String {
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ val map: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ map["Jan"] = "01"
+ map["Feb"] = "02"
+ map["Mar"] = "03"
+ map["Apr"] = "04"
+ map["May"] = "05"
+ map["Jun"] = "06"
+ map["Jul"] = "07"
+ map["Aug"] = "08"
+ map["Sep"] = "09"
+ map["Oct"] = "10"
+ map["Nov"] = "11"
+ map["Dec"] = "12"
+ sb.append(date.substring(date.length - 4))
+ sb.append('-')
+ sb.append(map[date.substring(date.length - 8, date.length - 5)])
+ sb.append('-')
+ if (Character.isDigit(date[1])) {
+ sb.append(date, 0, 2)
+ } else {
+ sb.append('0')
+ sb.append(date[0])
+ }
+ return sb.toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1508_range_sum_of_sorted_subarray_sums/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1508_range_sum_of_sorted_subarray_sums/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4754def9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1508_range_sum_of_sorted_subarray_sums/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1508\. Range Sum of Sorted Subarray Sums
+
+Medium
+
+You are given the array `nums` consisting of `n` positive integers. You computed the sum of all non-empty continuous subarrays from the array and then sorted them in non-decreasing order, creating a new array of `n * (n + 1) / 2` numbers.
+
+_Return the sum of the numbers from index_ `left` _to index_ `right` (**indexed from 1**)_, inclusive, in the new array._ Since the answer can be a huge number return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4], n = 4, left = 1, right = 5
+
+**Output:** 13
+
+**Explanation:** All subarray sums are 1, 3, 6, 10, 2, 5, 9, 3, 7, 4. After sorting them in non-decreasing order we have the new array [1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10]. The sum of the numbers from index le = 1 to ri = 5 is 1 + 2 + 3 + 3 + 4 = 13.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4], n = 4, left = 3, right = 4
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** The given array is the same as example 1. We have the new array [1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10]. The sum of the numbers from index le = 3 to ri = 4 is 3 + 3 = 6.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4], n = 4, left = 1, right = 10
+
+**Output:** 50
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == nums.length`
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 100`
+* `1 <= left <= right <= n * (n + 1) / 2`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun rangeSum(nums: IntArray, n: Int, left: Int, right: Int): Int {
+ val len = n * (n + 1) / 2
+ val arr = IntArray(len)
+ var idx = 0
+ var prev = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ for (j in i until n) {
+ arr[idx] = prev + nums[j]
+ prev = arr[idx]
+ idx++
+ }
+ prev = 0
+ }
+ arr.sort()
+ var result = 0
+ val mod = 1000000007
+ for (i in left - 1 until right) {
+ result = (result + arr[i]) % mod
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1509_minimum_difference_between_largest_and_smallest_value_in_three_moves/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1509_minimum_difference_between_largest_and_smallest_value_in_three_moves/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c890c0fb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1509_minimum_difference_between_largest_and_smallest_value_in_three_moves/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1509\. Minimum Difference Between Largest and Smallest Value in Three Moves
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`. In one move, you can choose one element of `nums` and change it by **any value**.
+
+Return _the minimum difference between the largest and smallest value of `nums` after performing **at most three moves**_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [5,3,2,4]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Change the array [5,3,2,4] to [**2**,**2**,2,**2**]. The difference between the maximum and minimum is 2-2 = 0.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,5,0,10,14]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** Change the array [1,5,0,10,14] to [1,**1**,0,**1**,**1**]. The difference between the maximum and minimum is 1-0 = 1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minDifference(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ nums.sort()
+ val n = nums.size
+ var res = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ if (n < 4) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ res = Math.min(res, nums[n - 4] - nums[0])
+ res = Math.min(res, nums[n - 3] - nums[1])
+ res = Math.min(res, nums[n - 2] - nums[2])
+ res = Math.min(res, nums[n - 1] - nums[3])
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1510_stone_game_iv/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1510_stone_game_iv/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..080f24eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1510_stone_game_iv/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1510\. Stone Game IV
+
+Hard
+
+Alice and Bob take turns playing a game, with Alice starting first.
+
+Initially, there are `n` stones in a pile. On each player's turn, that player makes a _move_ consisting of removing **any** non-zero **square number** of stones in the pile.
+
+Also, if a player cannot make a move, he/she loses the game.
+
+Given a positive integer `n`, return `true` if and only if Alice wins the game otherwise return `false`, assuming both players play optimally.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** Alice can remove 1 stone winning the game because Bob doesn't have any moves.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** Alice can only remove 1 stone, after that Bob removes the last one winning the game (2 -> 1 -> 0).
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** n is already a perfect square, Alice can win with one move, removing 4 stones (4 -> 0).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun winnerSquareGame(n: Int): Boolean {
+ val dp = BooleanArray(n + 1)
+ for (i in 1 until n + 1) {
+ var k = 1
+ while (k * k <= i) {
+ if (!dp[i - k * k]) {
+ dp[i] = true
+ break
+ }
+ k++
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[n]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1512_number_of_good_pairs/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1512_number_of_good_pairs/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..10bec6bc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1512_number_of_good_pairs/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1512\. Number of Good Pairs
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array of integers `nums`, return _the number of **good pairs**_.
+
+A pair `(i, j)` is called _good_ if `nums[i] == nums[j]` and `i` < `j`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,1,1,3]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** There are 4 good pairs (0,3), (0,4), (3,4), (2,5) 0-indexed.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** Each pair in the array are _good_.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 100`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numIdenticalPairs(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var count = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ for (j in i + 1 until nums.size) {
+ if (nums[i] == nums[j]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1513_number_of_substrings_with_only_1s/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1513_number_of_substrings_with_only_1s/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..13a11a02
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1513_number_of_substrings_with_only_1s/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1513\. Number of Substrings With Only 1s
+
+Medium
+
+Given a binary string `s`, return _the number of substrings with all characters_ `1`_'s_. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "0110111"
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Explanation:** There are 9 substring in total with only 1's characters. "1" -> 5 times. "11" -> 3 times. "111" -> 1 time.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "101"
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Substring "1" is shown 2 times in s.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "111111"
+
+**Output:** 21
+
+**Explanation:** Each substring contains only 1's characters.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s[i]` is either `'0'` or `'1'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numSub(s: String): Int {
+ var count: Long = 0
+ var res: Long = 0
+ for (ch in s.toCharArray()) {
+ if (ch == '0') {
+ res += count * (count + 1) / 2
+ count = 0
+ } else {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ res += count * (count + 1) / 2
+ return (res % 1000000007).toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1514_path_with_maximum_probability/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1514_path_with_maximum_probability/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a35b9feb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1514_path_with_maximum_probability/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1514\. Path with Maximum Probability
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an undirected weighted graph of `n` nodes (0-indexed), represented by an edge list where `edges[i] = [a, b]` is an undirected edge connecting the nodes `a` and `b` with a probability of success of traversing that edge `succProb[i]`.
+
+Given two nodes `start` and `end`, find the path with the maximum probability of success to go from `start` to `end` and return its success probability.
+
+If there is no path from `start` to `end`, **return 0**. Your answer will be accepted if it differs from the correct answer by at most **1e-5**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**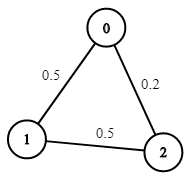**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, edges = \[\[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2
+
+**Output:** 0.25000
+
+**Explanation:** There are two paths from start to end, one having a probability of success = 0.2 and the other has 0.5 \* 0.5 = 0.25.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**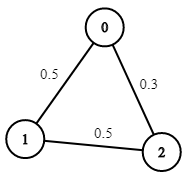**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, edges = \[\[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2
+
+**Output:** 0.30000
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** n = 3, edges = \[\[0,1]], succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2
+
+**Output:** 0.00000
+
+**Explanation:** There is no path between 0 and 2.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n <= 10^4`
+* `0 <= start, end < n`
+* `start != end`
+* `0 <= a, b < n`
+* `a != b`
+* `0 <= succProb.length == edges.length <= 2*10^4`
+* `0 <= succProb[i] <= 1`
+* There is at most one edge between every two nodes.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.ArrayDeque
+import java.util.Queue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxProbability(n: Int, edges: Array, succProb: DoubleArray, start: Int, end: Int): Double {
+ val nodeToNodesList: Array?> = arrayOfNulls(n)
+ val nodeToProbabilitiesList: Array?> = arrayOfNulls(n)
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ nodeToNodesList[i] = mutableListOf()
+ nodeToProbabilitiesList[i] = ArrayList()
+ }
+ for (i in edges.indices) {
+ val u = edges[i][0]
+ val v = edges[i][1]
+ val w = succProb[i]
+ nodeToNodesList[u]?.add(v)
+ nodeToProbabilitiesList[u]?.add(w)
+ nodeToNodesList[v]?.add(u)
+ nodeToProbabilitiesList[v]?.add(w)
+ }
+ val probabilities = DoubleArray(n)
+ probabilities[start] = 1.0
+ val visited = BooleanArray(n)
+ val queue: Queue = ArrayDeque()
+ queue.add(start)
+ visited[start] = true
+ while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val u = queue.poll()
+ visited[u] = false
+ for (i in nodeToNodesList[u]?.indices!!) {
+ val v = nodeToNodesList[u]?.get(i)
+ val w = nodeToProbabilitiesList[u]?.get(i)
+ if (probabilities[u] * w!! > probabilities[v!!]) {
+ probabilities[v] = probabilities[u] * w
+ if (!visited[v]) {
+ visited[v] = true
+ queue.add(v)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return probabilities[end]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1515_best_position_for_a_service_centre/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1515_best_position_for_a_service_centre/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0aea390b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1515_best_position_for_a_service_centre/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1515\. Best Position for a Service Centre
+
+Hard
+
+A delivery company wants to build a new service center in a new city. The company knows the positions of all the customers in this city on a 2D-Map and wants to build the new center in a position such that **the sum of the euclidean distances to all customers is minimum**.
+
+Given an array `positions` where positions[i] = [xi, yi] is the position of the `ith` customer on the map, return _the minimum sum of the euclidean distances_ to all customers.
+
+In other words, you need to choose the position of the service center [xcentre, ycentre] such that the following formula is minimized:
+
+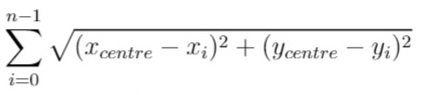
+
+Answers within 10-5 of the actual value will be accepted.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** positions = \[\[0,1],[1,0],[1,2],[2,1]]
+
+**Output:** 4.00000
+
+**Explanation:** As shown, you can see that choosing [xcentre, ycentre] = [1, 1] will make the distance to each customer = 1, the sum of all distances is 4 which is the minimum possible we can achieve.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** positions = \[\[1,1],[3,3]]
+
+**Output:** 2.82843
+
+**Explanation:** The minimum possible sum of distances = sqrt(2) + sqrt(2) = 2.82843
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= positions.length <= 50`
+* `positions[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= xi, yi <= 100
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun getMinDistSum(positions: Array): Double {
+ var minX = Int.MAX_VALUE.toDouble()
+ var minY = Int.MAX_VALUE.toDouble()
+ var maxX = Int.MIN_VALUE.toDouble()
+ var maxY = Int.MIN_VALUE.toDouble()
+ for (pos in positions) {
+ maxX = Math.max(maxX, pos[0].toDouble())
+ maxY = Math.max(maxY, pos[1].toDouble())
+ minX = Math.min(minX, pos[0].toDouble())
+ minY = Math.min(minY, pos[1].toDouble())
+ }
+ var xMid = minX + (maxX - minX) / 2
+ var yMid = minY + (maxY - minY) / 2
+ var jump = Math.max(maxX - minX, maxY - minY)
+ var ans = getTotalDistance(xMid, yMid, positions)
+ while (jump > 0.00001) {
+ val list = getFourCorners(xMid, yMid, jump)
+ var found = false
+ for (point in list) {
+ val pointAns = getTotalDistance(point[0], point[1], positions)
+ if (ans > pointAns) {
+ xMid = point[0]
+ yMid = point[1]
+ ans = pointAns
+ found = true
+ }
+ }
+ if (!found) {
+ jump = jump / 2
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun getFourCorners(xMid: Double, yMid: Double, jump: Double): List {
+ val list: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ list.add(doubleArrayOf(xMid - jump, yMid + jump))
+ list.add(doubleArrayOf(xMid + jump, yMid + jump))
+ list.add(doubleArrayOf(xMid - jump, yMid - jump))
+ list.add(doubleArrayOf(xMid + jump, yMid - jump))
+ return list
+ }
+
+ private fun getTotalDistance(x: Double, y: Double, positions: Array): Double {
+ var totalDistanceSum = 0.0
+ for (point in positions) {
+ val xDistance = x - point[0]
+ val yDistance = y - point[1]
+ totalDistanceSum += Math.sqrt(xDistance * xDistance + yDistance * yDistance)
+ }
+ return totalDistanceSum
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1518_water_bottles/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1518_water_bottles/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a2a56b71
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1518_water_bottles/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1518\. Water Bottles
+
+Easy
+
+There are `numBottles` water bottles that are initially full of water. You can exchange `numExchange` empty water bottles from the market with one full water bottle.
+
+The operation of drinking a full water bottle turns it into an empty bottle.
+
+Given the two integers `numBottles` and `numExchange`, return _the **maximum** number of water bottles you can drink_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** numBottles = 9, numExchange = 3
+
+**Output:** 13
+
+**Explanation:** You can exchange 3 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle. Number of water bottles you can drink: 9 + 3 + 1 = 13.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** numBottles = 15, numExchange = 4
+
+**Output:** 19
+
+**Explanation:** You can exchange 4 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle. Number of water bottles you can drink: 15 + 3 + 1 = 19.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= numBottles <= 100`
+* `2 <= numExchange <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numWaterBottles(numBottles: Int, numExchange: Int): Int {
+ var drunk = numBottles
+ var emptyBottles = numBottles
+ while (emptyBottles >= numExchange) {
+ val exchangedBottles = emptyBottles / numExchange
+ drunk += exchangedBottles
+ val unUsedEmptyBottles = emptyBottles % numExchange
+ emptyBottles = exchangedBottles + unUsedEmptyBottles
+ }
+ return drunk
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1519_number_of_nodes_in_the_sub_tree_with_the_same_label/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1519_number_of_nodes_in_the_sub_tree_with_the_same_label/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7a2804f7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1519_number_of_nodes_in_the_sub_tree_with_the_same_label/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1519\. Number of Nodes in the Sub-Tree With the Same Label
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a tree (i.e. a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of `n` nodes numbered from `0` to `n - 1` and exactly `n - 1` `edges`. The **root** of the tree is the node `0`, and each node of the tree has **a label** which is a lower-case character given in the string `labels` (i.e. The node with the number `i` has the label `labels[i]`).
+
+The `edges` array is given on the form edges[i] = [ai, bi], which means there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
+
+Return _an array of size `n`_ where `ans[i]` is the number of nodes in the subtree of the ith node which have the same label as node `i`.
+
+A subtree of a tree `T` is the tree consisting of a node in `T` and all of its descendant nodes.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 7, edges = \[\[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], labels = "abaedcd"
+
+**Output:** [2,1,1,1,1,1,1]
+
+**Explanation:** Node 0 has label 'a' and its sub-tree has node 2 with label 'a' as well, thus the answer is 2. Notice that any node is part of its sub-tree.
+
+Node 1 has a label 'b'. The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1,4 and 5, as nodes 4 and 5 have different labels than node 1, the answer is just 1 (the node itself).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 4, edges = \[\[0,1],[1,2],[0,3]], labels = "bbbb"
+
+**Output:** [4,2,1,1]
+
+**Explanation:** The sub-tree of node 2 contains only node 2, so the answer is 1.
+
+The sub-tree of node 3 contains only node 3, so the answer is 1.
+
+The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1 and 2, both have label 'b', thus the answer is 2.
+
+The sub-tree of node 0 contains nodes 0, 1, 2 and 3, all with label 'b', thus the answer is 4.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 5, edges = \[\[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[0,4]], labels = "aabab"
+
+**Output:** [3,2,1,1,1]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* `edges.length == n - 1`
+* `edges[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= ai, bi < n
+* ai != bi
+* `labels.length == n`
+* `labels` is consisting of only of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countSubTrees(n: Int, edges: Array, labelsString: String): IntArray {
+ val labelsCount = IntArray(n)
+ if (n <= 0) {
+ return labelsCount
+ }
+ val labels = IntArray(n)
+ var nodeNumber = 0
+ for (label in labelsString.toCharArray()) {
+ labels[nodeNumber++] = label.code - 'a'.code
+ }
+ val graph = ArrayList>()
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ graph.add(ArrayList())
+ }
+ for (edge in edges) {
+ val parent = edge[0]
+ val child = edge[1]
+ graph[parent].add(child)
+ graph[child].add(parent)
+ }
+ getLabelsFrequency(0, graph, labels, labelsCount, 0)
+ return labelsCount
+ }
+
+ private fun getLabelsFrequency(
+ root: Int,
+ graph: ArrayList>,
+ labels: IntArray,
+ labelsCount: IntArray,
+ parent: Int
+ ): IntArray {
+ val labelsFrequency = IntArray(26)
+ val rootLabel = labels[root]
+ labelsFrequency[rootLabel]++
+ for (child in graph[root]) {
+ if (child == parent) {
+ continue
+ }
+ val childLabelsFrequency = getLabelsFrequency(child, graph, labels, labelsCount, root)
+ for (i in childLabelsFrequency.indices) {
+ labelsFrequency[i] += childLabelsFrequency[i]
+ }
+ }
+ labelsCount[root] = labelsFrequency[rootLabel]
+ return labelsFrequency
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1520_maximum_number_of_non_overlapping_substrings/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1520_maximum_number_of_non_overlapping_substrings/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..01362070
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1520_maximum_number_of_non_overlapping_substrings/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1520\. Maximum Number of Non-Overlapping Substrings
+
+Hard
+
+Given a string `s` of lowercase letters, you need to find the maximum number of **non-empty** substrings of `s` that meet the following conditions:
+
+1. The substrings do not overlap, that is for any two substrings `s[i..j]` and `s[k..l]`, either `j < k` or `i > l` is true.
+2. A substring that contains a certain character `c` must also contain all occurrences of `c`.
+
+Find _the maximum number of substrings that meet the above conditions_. If there are multiple solutions with the same number of substrings, _return the one with minimum total length. _It can be shown that there exists a unique solution of minimum total length.
+
+Notice that you can return the substrings in **any** order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "adefaddaccc"
+
+**Output:** ["e","f","ccc"]
+
+**Explanation:** The following are all the possible substrings that meet the conditions:
+[
+
+"adefaddaccc"
+
+"adefadda",
+
+"ef",
+
+"e",
+
+"f",
+
+"ccc",
+
+]
+
+If we choose the first string, we cannot choose anything else and we'd get only 1. If we choose "adefadda", we are left with "ccc" which is the only one that doesn't overlap, thus obtaining 2 substrings. Notice also, that it's not optimal to choose "ef" since it can be split into two. Therefore, the optimal way is to choose ["e","f","ccc"] which gives us 3 substrings. No other solution of the same number of substrings exist.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abbaccd"
+
+**Output:** ["d","bb","cc"]
+
+**Explanation:** Notice that while the set of substrings ["d","abba","cc"] also has length 3, it's considered incorrect since it has larger total length.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 10^5`
+* `s` contains only lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.ArrayDeque
+import java.util.Deque
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxNumOfSubstrings(s: String): List {
+ val lefts = IntArray(26)
+ val rights = IntArray(26)
+ lefts.fill(-1)
+ for (i in s.indices) {
+ val idx = s[i].code - 'a'.code
+ if (lefts[idx] == -1) {
+ lefts[idx] = i
+ }
+ rights[idx] = i
+ }
+ val result: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val stack: Deque = ArrayDeque()
+ var top: IntArray? = null
+ for (i in s.indices) {
+ val idx = s[i].code - 'a'.code
+ if (i == lefts[idx]) {
+ if (top == null || rights[idx] < top[1]) {
+ top = intArrayOf(i, rights[idx])
+ stack.offerFirst(top)
+ } else if (rights[idx] > top[1]) {
+ top[1] = rights[idx]
+ }
+ } else if (top != null && lefts[idx] < top[0]) {
+ var newEnd = rights[idx]
+ while (top != null && top[0] > lefts[idx]) {
+ newEnd = Math.max(newEnd, top[1])
+ stack.pollFirst()
+ top = stack.peekFirst()
+ }
+ if (top != null) {
+ top[1] = Math.max(newEnd, top[1])
+ }
+ }
+ if (top != null && i >= top[1]) {
+ result.add(s.substring(top[0], top[1] + 1))
+ stack.clear()
+ top = null
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1521_find_a_value_of_a_mysterious_function_closest_to_target/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1521_find_a_value_of_a_mysterious_function_closest_to_target/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..89c28341
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1521_find_a_value_of_a_mysterious_function_closest_to_target/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1521\. Find a Value of a Mysterious Function Closest to Target
+
+Hard
+
+
+
+Winston was given the above mysterious function `func`. He has an integer array `arr` and an integer `target` and he wants to find the values `l` and `r` that make the value `|func(arr, l, r) - target|` minimum possible.
+
+Return _the minimum possible value_ of `|func(arr, l, r) - target|`.
+
+Notice that `func` should be called with the values `l` and `r` where `0 <= l, r < arr.length`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [9,12,3,7,15], target = 5
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Calling func with all the pairs of [l,r] = \[\[0,0],[1,1],[2,2],[3,3],[4,4],[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[0,2],[1,3],[2,4],[0,3],[1,4],[0,4]], Winston got the following results [9,12,3,7,15,8,0,3,7,0,0,3,0,0,0]. The value closest to 5 is 7 and 3, thus the minimum difference is 2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1000000,1000000,1000000], target = 1
+
+**Output:** 999999
+
+**Explanation:** Winston called the func with all possible values of [l,r] and he always got 1000000, thus the min difference is 999999.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,4,8,16], target = 0
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= arr.length <= 105
+* 1 <= arr[i] <= 106
+* 0 <= target <= 107
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun closestToTarget(arr: IntArray, target: Int): Int {
+ val prefix = IntArray(22)
+ prefix[0] = -1
+ var res = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ var size = 1
+ for (a in arr) {
+ var ns = 1
+ for (i in 1 until size) {
+ if (prefix[ns - 1] != prefix[i] and a) {
+ prefix[ns++] = prefix[i] and a
+ res = Math.min(res, Math.abs((prefix[i] and a) - target))
+ }
+ }
+ if (prefix[ns - 1] != a) {
+ prefix[ns++] = a
+ res = Math.min(res, Math.abs(a - target))
+ }
+ size = ns
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1523_count_odd_numbers_in_an_interval_range/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1523_count_odd_numbers_in_an_interval_range/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..48addae3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1523_count_odd_numbers_in_an_interval_range/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1523\. Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range
+
+Easy
+
+Given two non-negative integers `low` and `high`. Return the _count of odd numbers between_ `low` _and_ `high`_ (inclusive)_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** low = 3, high = 7
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The odd numbers between 3 and 7 are [3,5,7].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** low = 8, high = 10
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The odd numbers between 8 and 10 are [9].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= low <= high <= 10^9`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countOdds(low: Int, high: Int): Int {
+ return if (low % 2 != 0 || high % 2 != 0) {
+ (high - low) / 2 + 1
+ } else (high - low) / 2
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1524_number_of_sub_arrays_with_odd_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1524_number_of_sub_arrays_with_odd_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fd116b8f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1524_number_of_sub_arrays_with_odd_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1524\. Number of Sub-arrays With Odd Sum
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `arr`, return _the number of subarrays with an **odd** sum_.
+
+Since the answer can be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,3,5]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** All subarrays are [[1],[1,3],[1,3,5],[3],[3,5],[5]]
+
+All sub-arrays sum are [1,4,9,3,8,5].
+
+Odd sums are [1,9,3,5] so the answer is 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [2,4,6]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** All subarrays are [[2],[2,4],[2,4,6],[4],[4,6],[6]]
+
+All sub-arrays sum are [2,6,12,4,10,6].
+
+All sub-arrays have even sum and the answer is 0.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
+
+**Output:** 16
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= arr.length <= 105
+* `1 <= arr[i] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numOfSubarrays(arr: IntArray): Int {
+ var number = if (arr[0] % 2 == 0) 0 else 1
+ var res = number.toLong()
+ for (i in 1 until arr.size) {
+ if (arr[i] % 2 != 0) {
+ number = i - number + 1
+ }
+ res += number.toLong()
+ }
+ val mod: Long = 1000000007
+ return (res % mod).toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1525_number_of_good_ways_to_split_a_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1525_number_of_good_ways_to_split_a_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..57bd5009
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1525_number_of_good_ways_to_split_a_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1525\. Number of Good Ways to Split a String
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a string `s`.
+
+A split is called **good** if you can split `s` into two non-empty strings sleft and sright where their concatenation is equal to `s` (i.e., sleft + sright = s) and the number of distinct letters in sleft and sright is the same.
+
+Return _the number of **good splits** you can make in `s`_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aacaba"
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** There are 5 ways to split `"aacaba"` and 2 of them are good.
+
+("a", "acaba") Left string and right string contains 1 and 3 different letters respectively.
+
+("aa", "caba") Left string and right string contains 1 and 3 different letters respectively.
+
+("aac", "aba") Left string and right string contains 2 and 2 different letters respectively (good split).
+
+("aaca", "ba") Left string and right string contains 2 and 2 different letters respectively (good split).
+
+("aacab", "a") Left string and right string contains 3 and 1 different letters respectively.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abcd"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** Split the string as follows ("ab", "cd").
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s` consists of only lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numSplits(s: String): Int {
+ val hs = HashSet()
+ val dp1 = IntArray(s.length - 1)
+ val dp2 = IntArray(s.length - 1)
+ for (i in 0 until s.length - 1) {
+ val ch = s[i]
+ hs.add(ch)
+ dp1[i] = hs.size
+ }
+ val hm = HashSet()
+ for (i in s.length - 1 downTo 1) {
+ val ch = s[i]
+ hm.add(ch)
+ dp2[i - 1] = hm.size
+ }
+ var count = 0
+ for (i in 0 until s.length - 1) {
+ if (dp1[i] == dp2[i]) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1526_minimum_number_of_increments_on_subarrays_to_form_a_target_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1526_minimum_number_of_increments_on_subarrays_to_form_a_target_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1d827571
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1526_minimum_number_of_increments_on_subarrays_to_form_a_target_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1526\. Minimum Number of Increments on Subarrays to Form a Target Array
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer array `target`. You have an integer array `initial` of the same size as `target` with all elements initially zeros.
+
+In one operation you can choose **any** subarray from `initial` and increment each value by one.
+
+Return _the minimum number of operations to form a_ `target` _array from_ `initial`.
+
+The test cases are generated so that the answer fits in a 32-bit integer.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** target = [1,2,3,2,1]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** We need at least 3 operations to form the target array from the initial array.
+
+[**0,0,0,0,0**] increment 1 from index 0 to 4 (inclusive).
+
+[1,**1,1,1**,1] increment 1 from index 1 to 3 (inclusive).
+
+[1,2,**2**,2,1] increment 1 at index 2.
+
+[1,2,3,2,1] target array is formed.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** target = [3,1,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** [**0,0,0,0**] -> [1,1,1,**1**] -> [**1**,1,1,2] -> [**2**,1,1,2] -> [3,1,1,2]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** target = [3,1,5,4,2]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:** [**0,0,0,0,0**] -> [**1**,1,1,1,1] -> [**2**,1,1,1,1] -> [3,1,**1,1,1**] -> [3,1,**2,2**,2] -> [3,1,**3,3**,2] -> [3,1,**4**,4,2] -> [3,1,5,4,2].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= target.length <= 105
+* 1 <= target[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minNumberOperations(target: IntArray): Int {
+ var operations = target[0]
+ for (i in 1 until target.size) {
+ if (target[i] > target[i - 1]) {
+ operations += target[i] - target[i - 1]
+ }
+ }
+ return operations
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1527_patients_with_a_condition/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1527_patients_with_a_condition/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3f69beda
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1527_patients_with_a_condition/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1527\. Patients With a Condition
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Patients`
+
+ +--------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +--------------+---------+
+ | patient_id | int |
+ | patient_name | varchar |
+ | conditions | varchar |
+ +--------------+---------+
+ patient_id is the primary key for this table.
+ 'conditions' contains 0 or more code separated by spaces.
+ This table contains information of the patients in the hospital.
+
+Write an SQL query to report the patient\_id, patient\_name all conditions of patients who have Type I Diabetes. Type I Diabetes always starts with `DIAB1` prefix
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Patients table:
+ +------------+--------------+--------------+
+ | patient_id | patient_name | conditions |
+ +------------+--------------+--------------+
+ | 1 | Daniel | YFEV COUGH |
+ | 2 | Alice | |
+ | 3 | Bob | DIAB100 MYOP |
+ | 4 | George | ACNE DIAB100 |
+ | 5 | Alain | DIAB201 |
+ +------------+--------------+--------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +------------+--------------+--------------+
+ | patient_id | patient_name | conditions |
+ +------------+--------------+--------------+
+ | 3 | Bob | DIAB100 MYOP |
+ | 4 | George | ACNE DIAB100 |
+ +------------+--------------+--------------+
+
+**Explanation:** Bob and George both have a condition that starts with DIAB1.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+Select patient_id,patient_name,conditions from Patients
+where conditions like '% DIAB1%' or conditions like 'DIAB1%'; -- NOSONAR
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1528_shuffle_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1528_shuffle_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..be166011
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1528_shuffle_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1528\. Shuffle String
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `s` and an integer array `indices` of the **same length**. The string `s` will be shuffled such that the character at the ith position moves to `indices[i]` in the shuffled string.
+
+Return _the shuffled string_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** s = "codeleet", `indices` = [4,5,6,7,0,2,1,3]
+
+**Output:** "leetcode"
+
+**Explanation:** As shown, "codeleet" becomes "leetcode" after shuffling.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abc", `indices` = [0,1,2]
+
+**Output:** "abc"
+
+**Explanation:** After shuffling, each character remains in its position.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `s.length == indices.length == n`
+* `1 <= n <= 100`
+* `s` consists of only lowercase English letters.
+* `0 <= indices[i] < n`
+* All values of `indices` are **unique**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun restoreString(s: String, indices: IntArray): String {
+ val c = CharArray(s.length)
+ for (i in 0 until s.length) {
+ val index = findIndex(indices, i)
+ c[i] = s[index]
+ }
+ return String(c)
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private fun findIndex(indices: IntArray, i: Int): Int {
+ for (j in indices.indices) {
+ if (indices[j] == i) {
+ return j
+ }
+ }
+ return 0
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1529_minimum_suffix_flips/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1529_minimum_suffix_flips/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..07c918ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1529_minimum_suffix_flips/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1529\. Minimum Suffix Flips
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a **0-indexed** binary string `target` of length `n`. You have another binary string `s` of length `n` that is initially set to all zeros. You want to make `s` equal to `target`.
+
+In one operation, you can pick an index `i` where `0 <= i < n` and flip all bits in the **inclusive** range `[i, n - 1]`. Flip means changing `'0'` to `'1'` and `'1'` to `'0'`.
+
+Return _the minimum number of operations needed to make_ `s` _equal to_ `target`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** target = "10111"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Initially, s = "00000".
+
+Choose index i = 2: "00000" -> "00111"
+
+Choose index i = 0: "00111" -> "11000"
+
+Choose index i = 1: "11000" -> "10111"
+
+We need at least 3 flip operations to form target.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** target = "101"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Initially, s = "000".
+
+Choose index i = 0: "000" -> "111"
+
+Choose index i = 1: "111" -> "100"
+
+Choose index i = 2: "100" -> "101"
+
+We need at least 3 flip operations to form target.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** target = "00000"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** We do not need any operations since the initial s already equals target.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == target.length`
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* `target[i]` is either `'0'` or `'1'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minFlips(target: String): Int {
+ var flipCount = target[0].code - 48
+ var prev = target[0]
+ for (ch in target.toCharArray()) {
+ if (ch != prev) {
+ flipCount++
+ prev = ch
+ }
+ }
+ return flipCount
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1530_number_of_good_leaf_nodes_pairs/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1530_number_of_good_leaf_nodes_pairs/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..69157c57
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1530_number_of_good_leaf_nodes_pairs/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1530\. Number of Good Leaf Nodes Pairs
+
+Medium
+
+You are given the `root` of a binary tree and an integer `distance`. A pair of two different **leaf** nodes of a binary tree is said to be good if the length of **the shortest path** between them is less than or equal to `distance`.
+
+Return _the number of good leaf node pairs_ in the tree.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,3,null,4], distance = 3
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The leaf nodes of the tree are 3 and 4 and the length of the shortest path between them is 3. This is the only good pair.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], distance = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The good pairs are [4,5] and [6,7] with shortest path = 2. The pair [4,6] is not good because the length of ther shortest path between them is 4.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** root = [7,1,4,6,null,5,3,null,null,null,null,null,2], distance = 3
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The only good pair is [2,5].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* The number of nodes in the `tree` is in the range [1, 210].
+* `1 <= Node.val <= 100`
+* `1 <= distance <= 10`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode
+
+/*
+ * Example:
+ * var ti = TreeNode(5)
+ * var v = ti.`val`
+ * Definition for a binary tree node.
+ * class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ * var left: TreeNode? = null
+ * var right: TreeNode? = null
+ * }
+ */
+class Solution {
+ fun countPairs(root: TreeNode?, distance: Int): Int {
+ return if (distance < 2) {
+ 0
+ } else pairsAndLeaves(root, distance)[0]
+ }
+
+ private fun pairsAndLeaves(node: TreeNode?, distance: Int): IntArray {
+ val r = IntArray(distance)
+ if (node == null) {
+ return r
+ }
+ if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
+ r[1] = 1
+ return r
+ }
+ val rl = pairsAndLeaves(node.left, distance)
+ val rr = pairsAndLeaves(node.right, distance)
+ for (i in 2 until distance) {
+ r[i] = rl[i - 1] + rr[i - 1]
+ }
+ var pairs = rl[0] + rr[0]
+ for (dist in 2..distance) {
+ for (leftToNodeDist in 1 until dist) {
+ pairs += rl[leftToNodeDist] * rr[dist - leftToNodeDist]
+ }
+ }
+ r[0] = pairs
+ return r
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1531_string_compression_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1531_string_compression_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..124014f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1531_string_compression_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1531\. String Compression II
+
+Hard
+
+[Run-length encoding](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Run-length_encoding) is a string compression method that works by replacing consecutive identical characters (repeated 2 or more times) with the concatenation of the character and the number marking the count of the characters (length of the run). For example, to compress the string `"aabccc"` we replace `"aa"` by `"a2"` and replace `"ccc"` by `"c3"`. Thus the compressed string becomes `"a2bc3"`.
+
+Notice that in this problem, we are not adding `'1'` after single characters.
+
+Given a string `s` and an integer `k`. You need to delete **at most** `k` characters from `s` such that the run-length encoded version of `s` has minimum length.
+
+Find the _minimum length of the run-length encoded version of_ `s` _after deleting at most_ `k` _characters_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aaabcccd", k = 2
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** Compressing s without deleting anything will give us "a3bc3d" of length 6. Deleting any of the characters 'a' or 'c' would at most decrease the length of the compressed string to 5, for instance delete 2 'a' then we will have s = "abcccd" which compressed is abc3d. Therefore, the optimal way is to delete 'b' and 'd', then the compressed version of s will be "a3c3" of length 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aabbaa", k = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** If we delete both 'b' characters, the resulting compressed string would be "a4" of length 2.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aaaaaaaaaaa", k = 0
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Since k is zero, we cannot delete anything. The compressed string is "a11" of length 3.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 100`
+* `0 <= k <= s.length`
+* `s` contains only lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private val dp = Array(101) { IntArray(101) }
+ private fun getLen(cnt: Int): Int {
+ if (cnt == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (cnt == 1) {
+ return 1
+ }
+ if (cnt < 10) {
+ return 2
+ }
+ return if (cnt < 100) {
+ 3
+ } else 4
+ }
+
+ fun getLengthOfOptimalCompression(s: String, k: Int): Int {
+ val sarr = s.toCharArray()
+ for (i in 0..s.length) {
+ for (j in 0..k) {
+ dp[i][j] = -1
+ }
+ }
+ return dfs(sarr, 0, k)
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(sarr: CharArray, pos: Int, k: Int): Int {
+ if (k < 0) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ if (pos == sarr.size || sarr.size - pos <= k) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (dp[pos][k] != -1) {
+ return dp[pos][k]
+ }
+ val cnts = IntArray(26)
+ var most = 0
+ var res = -1
+ for (j in pos until sarr.size) {
+ cnts[sarr[j].code - 'a'.code]++
+ most = Math.max(most, cnts[sarr[j].code - 'a'.code])
+ val cost = dfs(sarr, j + 1, k - (j - pos + 1 - most))
+ if (cost == -1) {
+ continue
+ }
+ res = if (res == -1) {
+ cost + getLen(most)
+ } else {
+ Math.min(res, cost + getLen(most))
+ }
+ }
+ dp[pos][k] = res
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1534_count_good_triplets/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1534_count_good_triplets/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..943e49ab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1534_count_good_triplets/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1534\. Count Good Triplets
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array of integers `arr`, and three integers `a`, `b` and `c`. You need to find the number of good triplets.
+
+A triplet `(arr[i], arr[j], arr[k])` is **good** if the following conditions are true:
+
+* `0 <= i < j < k < arr.length`
+* `|arr[i] - arr[j]| <= a`
+* `|arr[j] - arr[k]| <= b`
+* `|arr[i] - arr[k]| <= c`
+
+Where `|x|` denotes the absolute value of `x`.
+
+Return _the number of good triplets_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [3,0,1,1,9,7], a = 7, b = 2, c = 3
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** There are 4 good triplets: [(3,0,1), (3,0,1), (3,1,1), (0,1,1)].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,1,2,2,3], a = 0, b = 0, c = 1
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** No triplet satisfies all conditions.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `3 <= arr.length <= 100`
+* `0 <= arr[i] <= 1000`
+* `0 <= a, b, c <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countGoodTriplets(arr: IntArray, a: Int, b: Int, c: Int): Int {
+ var count = 0
+ for (i in 0 until arr.size - 2) {
+ for (j in i + 1 until arr.size - 1) {
+ if (Math.abs(arr[i] - arr[j]) <= a) {
+ for (k in j + 1 until arr.size) {
+ if (Math.abs(arr[j] - arr[k]) <= b && Math.abs(arr[i] - arr[k]) <= c) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1535_find_the_winner_of_an_array_game/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1535_find_the_winner_of_an_array_game/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cc31897e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1535_find_the_winner_of_an_array_game/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1535\. Find the Winner of an Array Game
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `arr` of **distinct** integers and an integer `k`.
+
+A game will be played between the first two elements of the array (i.e. `arr[0]` and `arr[1]`). In each round of the game, we compare `arr[0]` with `arr[1]`, the larger integer wins and remains at position `0`, and the smaller integer moves to the end of the array. The game ends when an integer wins `k` consecutive rounds.
+
+Return _the integer which will win the game_.
+
+It is **guaranteed** that there will be a winner of the game.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [2,1,3,5,4,6,7], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** Let's see the rounds of the game:
+
+
+ Round | arr | winner | win_count
+ 1 | [2,1,3,5,4,6,7] | 2 | 1
+ 2 | [2,3,5,4,6,7,1] | 3 | 1
+ 3 | [3,5,4,6,7,1,2] | 5 | 1
+ 4 | [5,4,6,7,1,2,3] | 5 | 2
+
+So we can see that 4 rounds will be played and 5 is the winner because it wins 2 consecutive games.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [3,2,1], k = 10
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** 3 will win the first 10 rounds consecutively.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= arr.length <= 105
+* 1 <= arr[i] <= 106
+* `arr` contains **distinct** integers.
+* 1 <= k <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun getWinner(arr: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ var winner = arr[0]
+ var winTimes = 0
+ for (i in 1 until arr.size) {
+ if (arr[i] > winner) {
+ winner = arr[i]
+ winTimes = 1
+ } else {
+ winTimes++
+ }
+ if (winTimes >= k) {
+ return winner
+ }
+ }
+ return winner
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1536_minimum_swaps_to_arrange_a_binary_grid/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1536_minimum_swaps_to_arrange_a_binary_grid/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5b29a6b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1536_minimum_swaps_to_arrange_a_binary_grid/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1536\. Minimum Swaps to Arrange a Binary Grid
+
+Medium
+
+Given an `n x n` binary `grid`, in one step you can choose two **adjacent rows** of the grid and swap them.
+
+A grid is said to be **valid** if all the cells above the main diagonal are **zeros**.
+
+Return _the minimum number of steps_ needed to make the grid valid, or **\-1** if the grid cannot be valid.
+
+The main diagonal of a grid is the diagonal that starts at cell `(1, 1)` and ends at cell `(n, n)`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[0,0,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0]]
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** All rows are similar, swaps have no effect on the grid.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == grid.length` `== grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= n <= 200`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either `0` or `1`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minSwaps(grid: Array): Int {
+ val len = grid.size
+ var swap = 0
+ val preProcess = IntArray(len)
+ for (i in 0 until len) {
+ preProcess[i] = countRightZeros(grid[i])
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until len) {
+ val minValueRequired = len - i - 1
+ var j = i
+ while (j < len && preProcess[j] < minValueRequired) {
+ j++
+ }
+ if (j == len) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ while (j != i) {
+ swap++
+ val temp = preProcess[j]
+ preProcess[j] = preProcess[j - 1]
+ preProcess[j - 1] = temp
+ j--
+ }
+ }
+ return swap
+ }
+
+ private fun countRightZeros(row: IntArray): Int {
+ var cnt = 0
+ for (i in row.indices.reversed()) {
+ if (row[i] != 0) {
+ break
+ }
+ cnt++
+ }
+ return cnt
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1537_get_the_maximum_score/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1537_get_the_maximum_score/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e6026154
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1537_get_the_maximum_score/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1537\. Get the Maximum Score
+
+Hard
+
+You are given two **sorted** arrays of distinct integers `nums1` and `nums2.`
+
+A **valid path** is defined as follows:
+
+* Choose array `nums1` or `nums2` to traverse (from index-0).
+* Traverse the current array from left to right.
+* If you are reading any value that is present in `nums1` and `nums2` you are allowed to change your path to the other array. (Only one repeated value is considered in the valid path).
+
+The **score** is defined as the sum of uniques values in a valid path.
+
+Return _the maximum score you can obtain of all possible **valid paths**_. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [2,4,5,8,10], nums2 = [4,6,8,9]
+
+**Output:** 30
+
+**Explanation:** Valid paths:
+
+[2,4,5,8,10], [2,4,5,8,9], [2,4,6,8,9], [2,4,6,8,10], (starting from nums1)
+
+[4,6,8,9], [4,5,8,10], [4,5,8,9], [4,6,8,10] (starting from nums2)
+
+The maximum is obtained with the path in green **[2,4,6,8,10]**.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [1,3,5,7,9], nums2 = [3,5,100]
+
+**Output:** 109
+
+**Explanation:** Maximum sum is obtained with the path **[1,3,5,100]**.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [1,2,3,4,5], nums2 = [6,7,8,9,10]
+
+**Output:** 40
+
+**Explanation:** There are no common elements between nums1 and nums2. Maximum sum is obtained with the path [6,7,8,9,10].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 107
+* `nums1` and `nums2` are strictly increasing.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxSum(nums1: IntArray, nums2: IntArray): Int {
+ val mod = 1000000007
+ var result: Long = 0
+ var start1 = 0
+ var start2 = 0
+ var sum1: Long = 0
+ var sum2: Long = 0
+ while (start1 < nums1.size && start2 < nums2.size) {
+ if (nums1[start1] < nums2[start2]) {
+ sum1 += nums1[start1].toLong()
+ start1++
+ } else if (nums1[start1] > nums2[start2]) {
+ sum2 += nums2[start2].toLong()
+ start2++
+ } else {
+ result += Math.max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[start1]
+ start1++
+ start2++
+ sum1 = 0
+ sum2 = 0
+ }
+ }
+ while (start1 < nums1.size) {
+ sum1 += nums1[start1].toLong()
+ start1++
+ }
+ while (start2 < nums2.size) {
+ sum2 += nums2[start2].toLong()
+ start2++
+ }
+ return ((Math.max(sum1, sum2) + result) % mod).toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1539_kth_missing_positive_number/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1539_kth_missing_positive_number/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8a7595f7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1539_kth_missing_positive_number/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1539\. Kth Missing Positive Number
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array `arr` of positive integers sorted in a **strictly increasing order**, and an integer `k`.
+
+_Find the_ kth _positive integer that is missing from this array._
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [2,3,4,7,11], k = 5
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Explanation:** The missing positive integers are [1,5,6,8,9,10,12,13,...]. The 5th missing positive integer is 9.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3,4], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** The missing positive integers are [5,6,7,...]. The 2nd missing positive integer is 6.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= arr.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= arr[i] <= 1000`
+* `1 <= k <= 1000`
+* `arr[i] < arr[j]` for `1 <= i < j <= arr.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findKthPositive(arr: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ var missed = 0
+ for (i in arr.indices) {
+ if (i == 0) {
+ missed += arr[0] - 1
+ if (missed >= k) {
+ return k
+ }
+ } else {
+ missed += arr[i] - arr[i - 1] - 1
+ if (missed >= k) {
+ missed -= arr[i] - arr[i - 1] - 1
+ var result = arr[i - 1]
+ while (missed++ < k) {
+ result++
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ var result = arr[arr.size - 1]
+ while (missed++ < k) {
+ result++
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1540_can_convert_string_in_k_moves/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1540_can_convert_string_in_k_moves/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..92f4145a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1540_can_convert_string_in_k_moves/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1540\. Can Convert String in K Moves
+
+Medium
+
+Given two strings `s` and `t`, your goal is to convert `s` into `t` in `k`moves or less.
+
+During the ith (`1 <= i <= k`) move you can:
+
+* Choose any index `j` (1-indexed) from `s`, such that `1 <= j <= s.length` and `j` has not been chosen in any previous move, and shift the character at that index `i` times.
+* Do nothing.
+
+Shifting a character means replacing it by the next letter in the alphabet (wrapping around so that `'z'` becomes `'a'`). Shifting a character by `i` means applying the shift operations `i` times.
+
+Remember that any index `j` can be picked at most once.
+
+Return `true` if it's possible to convert `s` into `t` in no more than `k` moves, otherwise return `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "input", t = "ouput", k = 9
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** In the 6th move, we shift 'i' 6 times to get 'o'. And in the 7th move we shift 'n' to get 'u'.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abc", t = "bcd", k = 10
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** We need to shift each character in s one time to convert it into t. We can shift 'a' to 'b' during the 1st move. However, there is no way to shift the other characters in the remaining moves to obtain t from s.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aab", t = "bbb", k = 27
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** In the 1st move, we shift the first 'a' 1 time to get 'b'. In the 27th move, we shift the second 'a' 27 times to get 'b'.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length, t.length <= 10^5`
+* `0 <= k <= 10^9`
+* `s`, `t` contain only lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun canConvertString(s: String, t: String, k: Int): Boolean {
+ val len1 = s.length
+ val len2 = t.length
+ if (len1 != len2) {
+ return false
+ }
+ if (s == t) {
+ return true
+ }
+ val freq = IntArray(26)
+ val multiple = k / 26
+ for (i in 0..25) {
+ freq[i] = multiple
+ }
+ val rem = k % 26
+ for (i in 1..rem) {
+ freq[i]++
+ }
+ var movesRemaining = k
+ for (i in 0 until len1) {
+ val ch1 = s[i]
+ val ch2 = t[i]
+ if (ch1 == ch2) {
+ movesRemaining--
+ continue
+ }
+ val diff = (ch2.code - ch1.code + 26) % 26
+ if (freq[diff] > 0) {
+ freq[diff]--
+ movesRemaining--
+ } else {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return movesRemaining >= 0
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1541_minimum_insertions_to_balance_a_parentheses_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1541_minimum_insertions_to_balance_a_parentheses_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..24082cf8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1541_minimum_insertions_to_balance_a_parentheses_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1541\. Minimum Insertions to Balance a Parentheses String
+
+Medium
+
+Given a parentheses string `s` containing only the characters `'('` and `')'`. A parentheses string is **balanced** if:
+
+* Any left parenthesis `'('` must have a corresponding two consecutive right parenthesis `'))'`.
+* Left parenthesis `'('` must go before the corresponding two consecutive right parenthesis `'))'`.
+
+In other words, we treat `'('` as an opening parenthesis and `'))'` as a closing parenthesis.
+
+* For example, `"())"`, `"())(())))"` and `"(())())))"` are balanced, `")()"`, `"()))"` and `"(()))"` are not balanced.
+
+You can insert the characters `'('` and `')'` at any position of the string to balance it if needed.
+
+Return _the minimum number of insertions_ needed to make `s` balanced.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "(()))"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The second '(' has two matching '))', but the first '(' has only ')' matching. We need to to add one more ')' at the end of the string to be "(())))" which is balanced.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "())"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** The string is already balanced.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "))())("
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Add '(' to match the first '))', Add '))' to match the last '('.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s` consists of `'('` and `')'` only.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minInsertions(s: String): Int {
+ var conClosed = 0
+ var opened = 0
+ var total = 0
+ for (i in 0 until s.length) {
+ if (s[i] == ')') {
+ conClosed++
+ if (conClosed == 2) {
+ conClosed = 0
+ if (opened > 0) {
+ opened--
+ } else {
+ total++
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (conClosed == 1) {
+ total += if (opened > 0) {
+ opened--
+ 1
+ } else {
+ 2
+ }
+ conClosed = 0
+ }
+ opened += 1
+ }
+ }
+ if (conClosed == 1) {
+ total += if (opened > 0) {
+ opened--
+ 1
+ } else {
+ 2
+ }
+ }
+ total += opened * 2
+ return total
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1542_find_longest_awesome_substring/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1542_find_longest_awesome_substring/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..72db5a53
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1542_find_longest_awesome_substring/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1542\. Find Longest Awesome Substring
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a string `s`. An **awesome** substring is a non-empty substring of `s` such that we can make any number of swaps in order to make it a palindrome.
+
+Return _the length of the maximum length **awesome substring** of_ `s`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "3242415"
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** "24241" is the longest awesome substring, we can form the palindrome "24142" with some swaps.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "12345678"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "213123"
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** "213123" is the longest awesome substring, we can form the palindrome "231132" with some swaps.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s` consists only of digits.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun longestAwesome(s: String): Int {
+ val n = s.length
+ val idx = IntArray(Math.pow(2.0, 10.0).toInt())
+ idx.fill(Int.MAX_VALUE)
+ idx[0] = -1
+ var mask = 0
+ var ans = 0
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ mask = mask xor (1 shl s[i].code - '0'.code)
+ ans = Math.max(ans, i - idx[mask])
+ for (j in 0..9) {
+ ans = Math.max(ans, i - idx[mask xor (1 shl j)])
+ }
+ idx[mask] = Math.min(idx[mask], i)
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1544_make_the_string_great/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1544_make_the_string_great/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b0aef16d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1544_make_the_string_great/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1544\. Make The String Great
+
+Easy
+
+Given a string `s` of lower and upper case English letters.
+
+A good string is a string which doesn't have **two adjacent characters** `s[i]` and `s[i + 1]` where:
+
+* `0 <= i <= s.length - 2`
+* `s[i]` is a lower-case letter and `s[i + 1]` is the same letter but in upper-case or **vice-versa**.
+
+To make the string good, you can choose **two adjacent** characters that make the string bad and remove them. You can keep doing this until the string becomes good.
+
+Return _the string_ after making it good. The answer is guaranteed to be unique under the given constraints.
+
+**Notice** that an empty string is also good.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "leEeetcode"
+
+**Output:** "leetcode"
+
+**Explanation:** In the first step, either you choose i = 1 or i = 2, both will result "leEeetcode" to be reduced to "leetcode".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abBAcC"
+
+**Output:** ""
+
+**Explanation:** We have many possible scenarios, and all lead to the same answer. For example: "abBAcC" --> "aAcC" --> "cC" --> "" "abBAcC" --> "abBA" --> "aA" --> ""
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "s"
+
+**Output:** "s"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 100`
+* `s` contains only lower and upper case English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Stack
+
+class Solution {
+ fun makeGood(s: String): String {
+ val stack = Stack()
+ for (element in s) {
+ if (stack.isEmpty()) {
+ stack.add(element)
+ } else {
+ if (stack.peek().lowercaseChar() == element.lowercaseChar()) {
+ if (Character.isLowerCase(stack.peek()) && Character.isUpperCase(element)) {
+ stack.pop()
+ } else if (Character.isUpperCase(stack.peek()) && Character.isLowerCase(element)) {
+ stack.pop()
+ } else {
+ stack.add(element)
+ }
+ } else {
+ stack.add(element)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ while (stack.isNotEmpty()) {
+ sb.append(stack.pop())
+ }
+ return sb.reverse().toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1545_find_kth_bit_in_nth_binary_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1545_find_kth_bit_in_nth_binary_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..23aecc6c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1545_find_kth_bit_in_nth_binary_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1545\. Find Kth Bit in Nth Binary String
+
+Medium
+
+Given two positive integers `n` and `k`, the binary string Sn is formed as follows:
+
+* S1 = "0"
+* Si = Si - 1 + "1" + reverse(invert(Si - 1)) for `i > 1`
+
+Where `+` denotes the concatenation operation, `reverse(x)` returns the reversed string `x`, and `invert(x)` inverts all the bits in `x` (`0` changes to `1` and `1` changes to `0`).
+
+For example, the first four strings in the above sequence are:
+
+* S1 = "0"
+* S2 = "0**1**1"
+* S3 = "011**1**001"
+* S4 = "0111001**1**0110001"
+
+Return _the_ kth _bit_ _in_ Sn. It is guaranteed that `k` is valid for the given `n`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, k = 1
+
+**Output:** "0"
+
+**Explanation:** S3 is "**0**111001". The 1st bit is "0".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, k = 11
+
+**Output:** "1"
+
+**Explanation:** S4 is "0111001101**1**0001". The 11th bit is "1".
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 20`
+* 1 <= k <= 2n - 1
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("NAME_SHADOWING", "UNUSED_PARAMETER")
+class Solution {
+ fun findKthBit(n: Int, k: Int): Char {
+ var k = k
+ var flip = false
+ while (k != 1) {
+ val base = floorTwo(k)
+ if (base == k) {
+ return if (flip) '0' else '1'
+ }
+ flip = !flip
+ k = base - (k - base)
+ }
+ return if (flip) '1' else '0'
+ }
+
+ private fun floorTwo(k: Int): Int {
+ var k = k
+ while (k and k - 1 > 0) {
+ k = k and k - 1
+ }
+ return k
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1546_maximum_number_of_non_overlapping_subarrays_with_sum_equals_target/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1546_maximum_number_of_non_overlapping_subarrays_with_sum_equals_target/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a4330dae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1546_maximum_number_of_non_overlapping_subarrays_with_sum_equals_target/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1546\. Maximum Number of Non-Overlapping Subarrays With Sum Equals Target
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array `nums` and an integer `target`, return _the maximum number of **non-empty** **non-overlapping** subarrays such that the sum of values in each subarray is equal to_ `target`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,1,1,1,1], target = 2
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** There are 2 non-overlapping subarrays [**1,1**,1,**1,1**] with sum equals to target(2).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-1,3,5,1,4,2,-9], target = 6
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** There are 3 subarrays with sum equal to 6. ([5,1], [4,2], [3,5,1,4,2,-9]) but only the first 2 are non-overlapping.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
+* 0 <= target <= 106
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxNonOverlapping(nums: IntArray, target: Int): Int {
+ var culSum = 0
+ var res = 0
+ val map: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ map[0] = 0
+ for (num in nums) {
+ culSum += num
+ if (map.containsKey(culSum - target)) {
+ res = Math.max(res, map[culSum - target]!! + 1)
+ }
+ map[culSum] = res
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1547_minimum_cost_to_cut_a_stick/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1547_minimum_cost_to_cut_a_stick/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a6742b27
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1547_minimum_cost_to_cut_a_stick/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1547\. Minimum Cost to Cut a Stick
+
+Hard
+
+Given a wooden stick of length `n` units. The stick is labelled from `0` to `n`. For example, a stick of length **6** is labelled as follows:
+
+
+
+Given an integer array `cuts` where `cuts[i]` denotes a position you should perform a cut at.
+
+You should perform the cuts in order, you can change the order of the cuts as you wish.
+
+The cost of one cut is the length of the stick to be cut, the total cost is the sum of costs of all cuts. When you cut a stick, it will be split into two smaller sticks (i.e. the sum of their lengths is the length of the stick before the cut). Please refer to the first example for a better explanation.
+
+Return _the minimum total cost_ of the cuts.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 7, cuts = [1,3,4,5]
+
+**Output:** 16
+
+**Explanation:** Using cuts order = [1, 3, 4, 5] as in the input leads to the following scenario: 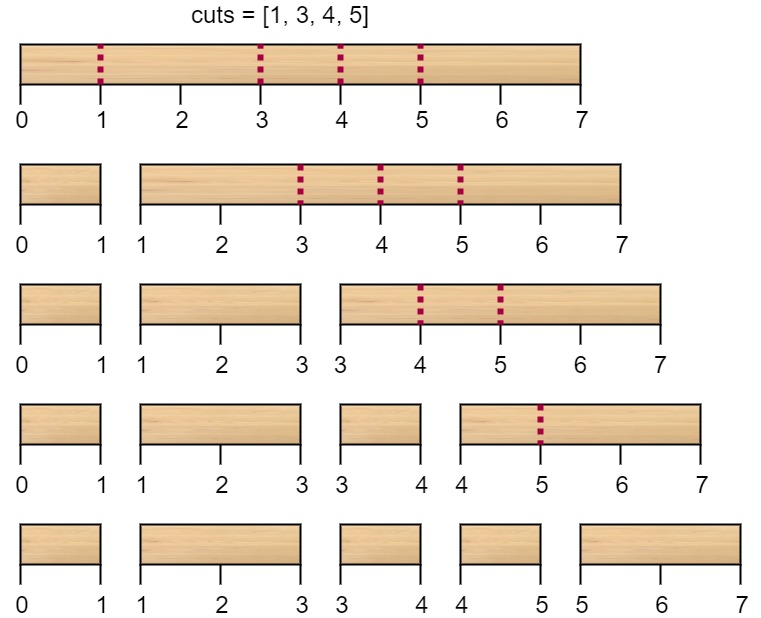
+
+The first cut is done to a rod of length 7 so the cost is 7. The second cut is done to a rod of length 6 (i.e. the second part of the first cut), the third is done to a rod of length 4 and the last cut is to a rod of length 3.
+
+The total cost is 7 + 6 + 4 + 3 = 20.
+
+Rearranging the cuts to be [3, 5, 1, 4] for example will lead to a scenario with total cost = 16 (as shown in the example photo 7 + 4 + 3 + 2 = 16).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 9, cuts = [5,6,1,4,2]
+
+**Output:** 22
+
+**Explanation:** If you try the given cuts ordering the cost will be 25.
+
+There are much ordering with total cost <= 25, for example, the order [4, 6, 5, 2, 1] has total cost = 22 which is the minimum possible.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= n <= 106
+* `1 <= cuts.length <= min(n - 1, 100)`
+* `1 <= cuts[i] <= n - 1`
+* All the integers in `cuts` array are **distinct**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minCost(n: Int, cuts: IntArray): Int {
+ cuts.sort()
+ val m = cuts.size
+ val dp = Array(m + 1) { IntArray(m + 1) }
+ for (i in 1..m) {
+ for (j in 0..m - i) {
+ val k = j + i
+ var min = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ for (p in j until k) {
+ min = Math.min(min, dp[j][p] + dp[p + 1][k])
+ }
+ val len = (if (k == m) n else cuts[k]) - if (j == 0) 0 else cuts[j - 1]
+ dp[j][k] = min + len
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[0][m]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1550_three_consecutive_odds/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1550_three_consecutive_odds/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3d79bc38
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1550_three_consecutive_odds/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1550\. Three Consecutive Odds
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer array `arr`, return `true` if there are three consecutive odd numbers in the array. Otherwise, return `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [2,6,4,1]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** There are no three consecutive odds.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,34,3,4,5,7,23,12]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** [5,7,23] are three consecutive odds.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= arr.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= arr[i] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun threeConsecutiveOdds(arr: IntArray): Boolean {
+ for (i in 0 until arr.size - 2) {
+ if (arr[i] % 2 == 1 && arr[i + 1] % 2 == 1 && arr[i + 2] % 2 == 1) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1551_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1551_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..62bb0b5c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1551_minimum_operations_to_make_array_equal/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1551\. Minimum Operations to Make Array Equal
+
+Medium
+
+You have an array `arr` of length `n` where `arr[i] = (2 * i) + 1` for all valid values of `i` (i.e., `0 <= i < n`).
+
+In one operation, you can select two indices `x` and `y` where `0 <= x, y < n` and subtract `1` from `arr[x]` and add `1` to `arr[y]` (i.e., perform `arr[x] -=1` and `arr[y] += 1`). The goal is to make all the elements of the array **equal**. It is **guaranteed** that all the elements of the array can be made equal using some operations.
+
+Given an integer `n`, the length of the array, return _the minimum number of operations_ needed to make all the elements of arr equal.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** arr = [1, 3, 5] First operation choose x = 2 and y = 0, this leads arr to be [2, 3, 4] In the second operation choose x = 2 and y = 0 again, thus arr = [3, 3, 3].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 6
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(n: Int) = (n - (n % 2)) * (n + (n % 2)) / 4
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1552_magnetic_force_between_two_balls/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1552_magnetic_force_between_two_balls/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fdda6647
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1552_magnetic_force_between_two_balls/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1552\. Magnetic Force Between Two Balls
+
+Medium
+
+In the universe Earth C-137, Rick discovered a special form of magnetic force between two balls if they are put in his new invented basket. Rick has `n` empty baskets, the ith basket is at `position[i]`, Morty has `m` balls and needs to distribute the balls into the baskets such that the **minimum magnetic force** between any two balls is **maximum**.
+
+Rick stated that magnetic force between two different balls at positions `x` and `y` is `|x - y|`.
+
+Given the integer array `position` and the integer `m`. Return _the required force_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+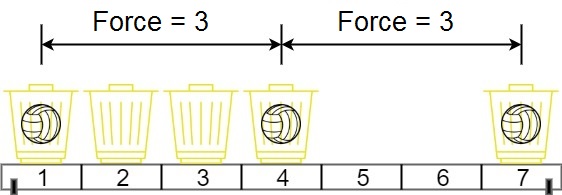
+
+**Input:** position = [1,2,3,4,7], m = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Distributing the 3 balls into baskets 1, 4 and 7 will make the magnetic force between ball pairs [3, 3, 6]. The minimum magnetic force is 3. We cannot achieve a larger minimum magnetic force than 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** position = [5,4,3,2,1,1000000000], m = 2
+
+**Output:** 999999999
+
+**Explanation:** We can use baskets 1 and 1000000000.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == position.length`
+* 2 <= n <= 105
+* 1 <= position[i] <= 109
+* All integers in `position` are **distinct**.
+* `2 <= m <= position.length`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxDistance(position: IntArray, m: Int): Int {
+ position.sort()
+ return binarySearch(position, m)
+ }
+
+ private fun binarySearch(arr: IntArray, m: Int): Int {
+ var low = 0
+ val n = arr.size
+ var high = arr[n - 1]
+ var max = -1
+ while (low <= high) {
+ val mid = low + (high - low) / 2
+ if (check(arr, mid, m)) {
+ if (max < mid) {
+ max = mid
+ }
+ low = mid + 1
+ } else {
+ high = mid - 1
+ }
+ }
+ return max
+ }
+
+ private fun check(arr: IntArray, mid: Int, m: Int): Boolean {
+ var pos = arr[0]
+ var magnet = 1
+ for (i in 1 until arr.size) {
+ if (arr[i] - pos >= mid) {
+ pos = arr[i]
+ magnet += 1
+ if (magnet == m) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1553_minimum_number_of_days_to_eat_n_oranges/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1553_minimum_number_of_days_to_eat_n_oranges/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a6021d4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1553_minimum_number_of_days_to_eat_n_oranges/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1553\. Minimum Number of Days to Eat N Oranges
+
+Hard
+
+There are `n` oranges in the kitchen and you decided to eat some of these oranges every day as follows:
+
+* Eat one orange.
+* If the number of remaining oranges `n` is divisible by `2` then you can eat `n / 2` oranges.
+* If the number of remaining oranges `n` is divisible by `3` then you can eat `2 * (n / 3)` oranges.
+
+You can only choose one of the actions per day.
+
+Given the integer `n`, return _the minimum number of days to eat_ `n` _oranges_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 10
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** You have 10 oranges.
+
+Day 1: Eat 1 orange, 10 - 1 = 9.
+
+Day 2: Eat 6 oranges, 9 - 2\*(9/3) = 9 - 6 = 3. (Since 9 is divisible by 3)
+
+Day 3: Eat 2 oranges, 3 - 2\*(3/3) = 3 - 2 = 1.
+
+Day 4: Eat the last orange 1 - 1 = 0.
+
+You need at least 4 days to eat the 10 oranges.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 6
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** You have 6 oranges.
+
+Day 1: Eat 3 oranges, 6 - 6/2 = 6 - 3 = 3. (Since 6 is divisible by 2).
+
+Day 2: Eat 2 oranges, 3 - 2\*(3/3) = 3 - 2 = 1. (Since 3 is divisible by 3)
+
+Day 3: Eat the last orange 1 - 1 = 0.
+
+You need at least 3 days to eat the 6 oranges.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 2 * 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minDays(n: Int): Int {
+ return eat(n, HashMap())
+ }
+
+ private fun eat(n: Int, cache: MutableMap): Int {
+ if (n <= 1) {
+ return n
+ }
+ val cached = cache[n]
+ if (cached != null) {
+ return cached
+ }
+ val result = (n % 2 + eat(n / 2, cache)).coerceAtMost(n % 3 + eat(n / 3, cache)) + 1
+ cache[n] = result
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1556_thousand_separator/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1556_thousand_separator/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..03198061
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1556_thousand_separator/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1556\. Thousand Separator
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer `n`, add a dot (".") as the thousands separator and return it in string format.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 987
+
+**Output:** "987"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1234
+
+**Output:** "1.234"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 0 <= n <= 231 - 1
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun thousandSeparator(n: Int): String {
+ val str = n.toString()
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ var i = str.length - 1
+ var j = 1
+ while (i >= 0) {
+ sb.append(str[i])
+ j++
+ if (j % 3 == 0) {
+ sb.append(".")
+ }
+ i--
+ j++
+ }
+ var result = sb.reverse().toString()
+ if (result[0] == '.') {
+ result = result.substring(1)
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1557_minimum_number_of_vertices_to_reach_all_nodes/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1557_minimum_number_of_vertices_to_reach_all_nodes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fac968d2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1557_minimum_number_of_vertices_to_reach_all_nodes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1557\. Minimum Number of Vertices to Reach All Nodes
+
+Medium
+
+Given a** directed acyclic graph**, with `n` vertices numbered from `0` to `n-1`, and an array `edges` where edges[i] = [fromi, toi] represents a directed edge from node fromi to node toi.
+
+Find _the smallest set of vertices from which all nodes in the graph are reachable_. It's guaranteed that a unique solution exists.
+
+Notice that you can return the vertices in any order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+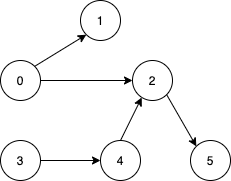
+
+**Input:** n = 6, edges = \[\[0,1],[0,2],[2,5],[3,4],[4,2]]
+
+**Output:** [0,3]
+
+**Explanation:** It's not possible to reach all the nodes from a single vertex. From 0 we can reach [0,1,2,5]. From 3 we can reach [3,4,2,5]. So we output [0,3].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+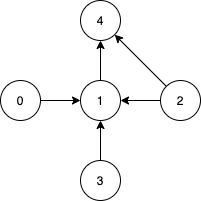
+
+**Input:** n = 5, edges = \[\[0,1],[2,1],[3,1],[1,4],[2,4]]
+
+**Output:** [0,2,3]
+
+**Explanation:** Notice that vertices 0, 3 and 2 are not reachable from any other node, so we must include them. Also any of these vertices can reach nodes 1 and 4.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n <= 10^5`
+* `1 <= edges.length <= min(10^5, n * (n - 1) / 2)`
+* `edges[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= fromi, toi < n
+* All pairs (fromi, toi) are distinct.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findSmallestSetOfVertices(n: Int, edges: List>): List {
+ val indegree = IntArray(n)
+ for (edge in edges) {
+ indegree[edge[1]]++
+ }
+ val ans: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (i in indegree.indices) {
+ if (indegree[i] == 0) {
+ ans.add(i)
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1558_minimum_numbers_of_function_calls_to_make_target_array/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1558_minimum_numbers_of_function_calls_to_make_target_array/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b5ffb821
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1558_minimum_numbers_of_function_calls_to_make_target_array/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1558\. Minimum Numbers of Function Calls to Make Target Array
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`. You have an integer array `arr` of the same length with all values set to `0` initially. You also have the following `modify` function:
+
+
+
+You want to use the modify function to covert `arr` to `nums` using the minimum number of calls.
+
+Return _the minimum number of function calls to make_ `nums` _from_ `arr`.
+
+The test cases are generated so that the answer fits in a **32-bit** signed integer.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,5]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** Increment by 1 (second element): [0, 0] to get [0, 1] (1 operation).
+
+Double all the elements: [0, 1] -> [0, 2] -> [0, 4] (2 operations).
+
+Increment by 1 (both elements) [0, 4] -> [1, 4] -> **[1, 5]** (2 operations).
+
+Total of operations: 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,2]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** Increment by 1 (both elements) [0, 0] -> [0, 1] -> [1, 1] (2 operations).
+
+Double all the elements: [1, 1] -> **[2, 2]** (1 operation).
+
+Total of operations: 2 + 1 = 3.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,2,5]
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:** (initial)[0,0,0] -> [1,0,0] -> [1,0,1] -> [2,0,2] -> [2,1,2] -> [4,2,4] -> **[4,2,5]**(nums).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 0 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var ops = 0
+ for (bit in 0..31) {
+ var nonzero = false
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ ops += nums[i] % 2
+ nums[i] /= 2
+ nonzero = nonzero or (nums[i] > 0)
+ }
+ if (nonzero) {
+ ops++
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return ops
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1559_detect_cycles_in_2d_grid/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1559_detect_cycles_in_2d_grid/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..09dac598
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1559_detect_cycles_in_2d_grid/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1559\. Detect Cycles in 2D Grid
+
+Medium
+
+Given a 2D array of characters `grid` of size `m x n`, you need to find if there exists any cycle consisting of the **same value** in `grid`.
+
+A cycle is a path of **length 4 or more** in the grid that starts and ends at the same cell. From a given cell, you can move to one of the cells adjacent to it - in one of the four directions (up, down, left, or right), if it has the **same value** of the current cell.
+
+Also, you cannot move to the cell that you visited in your last move. For example, the cycle `(1, 1) -> (1, 2) -> (1, 1)` is invalid because from `(1, 2)` we visited `(1, 1)` which was the last visited cell.
+
+Return `true` if any cycle of the same value exists in `grid`, otherwise, return `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\["a","a","a","a"],["a","b","b","a"],["a","b","b","a"],["a","a","a","a"]]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** There are two valid cycles shown in different colors in the image below: 
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\["c","c","c","a"],["c","d","c","c"],["c","c","e","c"],["f","c","c","c"]]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** There is only one valid cycle highlighted in the image below: 
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**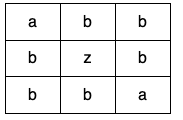**
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\["a","b","b"],["b","z","b"],["b","b","a"]]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 500`
+* `grid` consists only of lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun containsCycle(grid: Array): Boolean {
+ val n = grid.size
+ val m = grid[0].size
+ val visited = Array(n + 1) { BooleanArray(m + 1) }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ for (j in 0 until m) {
+ if (!visited[i][j] && cycle(grid, i, j, visited, grid[i][j])) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ private fun cycle(grid: Array, i: Int, j: Int, visited: Array, cc: Char): Boolean {
+ if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= grid.size || j >= grid[0].size || grid[i][j] != cc) {
+ return false
+ }
+ if (visited[i][j]) {
+ return true
+ }
+ visited[i][j] = true
+ val temp = grid[i][j]
+ grid[i][j] = '*'
+ val ans = (
+ cycle(grid, i + 1, j, visited, cc) ||
+ cycle(grid, i - 1, j, visited, cc) ||
+ cycle(grid, i, j + 1, visited, cc) ||
+ cycle(grid, i, j - 1, visited, cc)
+ )
+ grid[i][j] = temp
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1560_most_visited_sector_in_a_circular_track/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1560_most_visited_sector_in_a_circular_track/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..85e0ece8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1560_most_visited_sector_in_a_circular_track/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1560\. Most Visited Sector in a Circular Track
+
+Easy
+
+Given an integer `n` and an integer array `rounds`. We have a circular track which consists of `n` sectors labeled from `1` to `n`. A marathon will be held on this track, the marathon consists of `m` rounds. The ith round starts at sector `rounds[i - 1]` and ends at sector `rounds[i]`. For example, round 1 starts at sector `rounds[0]` and ends at sector `rounds[1]`
+
+Return _an array of the most visited sectors_ sorted in **ascending** order.
+
+Notice that you circulate the track in ascending order of sector numbers in the counter-clockwise direction (See the first example).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 4, rounds = [1,3,1,2]
+
+**Output:** [1,2]
+
+**Explanation:** The marathon starts at sector 1. The order of the visited sectors is as follows: 1 --> 2 --> 3 (end of round 1) --> 4 --> 1 (end of round 2) --> 2 (end of round 3 and the marathon) We can see that both sectors 1 and 2 are visited twice and they are the most visited sectors. Sectors 3 and 4 are visited only once.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2, rounds = [2,1,2,1,2,1,2,1,2]
+
+**Output:** [2]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 7, rounds = [1,3,5,7]
+
+**Output:** [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n <= 100`
+* `1 <= m <= 100`
+* `rounds.length == m + 1`
+* `1 <= rounds[i] <= n`
+* `rounds[i] != rounds[i + 1]` for `0 <= i < m`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun mostVisited(n: Int, rounds: IntArray): List {
+ val res: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ var start = rounds[0]
+ val end = rounds[rounds.size - 1]
+ val ans = IntArray(n + 1)
+ while (start != end) {
+ ans[start]++
+ start++
+ if (start > n) {
+ start = 1
+ }
+ }
+ ans[end]++
+ for (i in 1..n) {
+ if (ans[i] != 0) {
+ res.add(i)
+ }
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1561_maximum_number_of_coins_you_can_get/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1561_maximum_number_of_coins_you_can_get/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b8e0ff91
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1561_maximum_number_of_coins_you_can_get/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1561\. Maximum Number of Coins You Can Get
+
+Medium
+
+There are `3n` piles of coins of varying size, you and your friends will take piles of coins as follows:
+
+* In each step, you will choose **any** `3` piles of coins (not necessarily consecutive).
+* Of your choice, Alice will pick the pile with the maximum number of coins.
+* You will pick the next pile with the maximum number of coins.
+* Your friend Bob will pick the last pile.
+* Repeat until there are no more piles of coins.
+
+Given an array of integers `piles` where `piles[i]` is the number of coins in the ith pile.
+
+Return the maximum number of coins that you can have.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** piles = [2,4,1,2,7,8]
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Explanation:** Choose the triplet (2, 7, 8), Alice Pick the pile with 8 coins, you the pile with **7** coins and Bob the last one.
+
+Choose the triplet (1, 2, 4), Alice Pick the pile with 4 coins, you the pile with **2** coins and Bob the last one. The maximum number of coins which you can have are: 7 + 2 = 9.
+
+On the other hand if we choose this arrangement (1, **2**, 8), (2, **4**, 7) you only get 2 + 4 = 6 coins which is not optimal.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** piles = [2,4,5]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** piles = [9,8,7,6,5,1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 18
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 3 <= piles.length <= 105
+* `piles.length % 3 == 0`
+* 1 <= piles[i] <= 104
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxCoins(piles: IntArray): Int {
+ piles.sort()
+ var j = 0
+ var coins = 0
+ var i = piles.size - 2
+ while (i > 0) {
+ coins += piles[i]
+ if (++j == piles.size / 3) {
+ return coins
+ }
+ i -= 2
+ }
+ return coins
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1562_find_latest_group_of_size_m/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1562_find_latest_group_of_size_m/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..20729665
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1562_find_latest_group_of_size_m/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1562\. Find Latest Group of Size M
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array `arr` that represents a permutation of numbers from `1` to `n`.
+
+You have a binary string of size `n` that initially has all its bits set to zero. At each step `i` (assuming both the binary string and `arr` are 1-indexed) from `1` to `n`, the bit at position `arr[i]` is set to `1`.
+
+You are also given an integer `m`. Find the latest step at which there exists a group of ones of length `m`. A group of ones is a contiguous substring of `1`'s such that it cannot be extended in either direction.
+
+Return _the latest step at which there exists a group of ones of length **exactly**_ `m`. _If no such group exists, return_ `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [3,5,1,2,4], m = 1
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Step 1: "00100", groups: ["1"]
+
+Step 2: "00101", groups: ["1", "1"]
+
+Step 3: "10101", groups: ["1", "1", "1"]
+
+Step 4: "11101", groups: ["111", "1"]
+
+Step 5: "11111", groups: ["11111"]
+
+The latest step at which there exists a group of size 1 is step 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [3,1,5,4,2], m = 2
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Step 1: "00100", groups: ["1"]
+
+Step 2: "10100", groups: ["1", "1"]
+
+Step 3: "10101", groups: ["1", "1", "1"]
+
+Step 4: "10111", groups: ["1", "111"]
+
+Step 5: "11111", groups: ["11111"]
+
+No group of size 2 exists during any step.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == arr.length`
+* 1 <= m <= n <= 105
+* `1 <= arr[i] <= n`
+* All integers in `arr` are **distinct**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findLatestStep(arr: IntArray, m: Int): Int {
+ val lengthAtIndex = IntArray(arr.size + 2)
+ val countOfLength = IntArray(arr.size + 1)
+ var res = -1
+ var step = 1
+ for (i in arr) {
+ val leftLength = lengthAtIndex[i - 1]
+ val rightLength = lengthAtIndex[i + 1]
+ val newLength = leftLength + rightLength + 1
+ lengthAtIndex[i] = newLength
+ lengthAtIndex[i - leftLength] = newLength
+ lengthAtIndex[i + rightLength] = newLength
+ countOfLength[newLength] += 1
+ countOfLength[leftLength] -= 1
+ countOfLength[rightLength] -= 1
+ if (countOfLength[m] > 0) {
+ res = step
+ }
+ step++
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1563_stone_game_v/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1563_stone_game_v/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d99fa318
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1563_stone_game_v/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1563\. Stone Game V
+
+Hard
+
+There are several stones **arranged in a row**, and each stone has an associated value which is an integer given in the array `stoneValue`.
+
+In each round of the game, Alice divides the row into **two non-empty rows** (i.e. left row and right row), then Bob calculates the value of each row which is the sum of the values of all the stones in this row. Bob throws away the row which has the maximum value, and Alice's score increases by the value of the remaining row. If the value of the two rows are equal, Bob lets Alice decide which row will be thrown away. The next round starts with the remaining row.
+
+The game ends when there is only **one stone remaining**. Alice's is initially **zero**.
+
+Return _the maximum score that Alice can obtain_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** stoneValue = [6,2,3,4,5,5]
+
+**Output:** 18
+
+**Explanation:** In the first round, Alice divides the row to [6,2,3], [4,5,5]. The left row has the value 11 and the right row has value 14. Bob throws away the right row and Alice's score is now 11. In the second round Alice divides the row to [6], [2,3]. This time Bob throws away the left row and Alice's score becomes 16 (11 + 5).
+
+ The last round Alice has only one choice to divide the row which is [2], [3]. Bob throws away the right row and Alice's score is now 18 (16 + 2). The game ends because only one stone is remaining in the row.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** stoneValue = [7,7,7,7,7,7,7]
+
+**Output:** 28
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** stoneValue = [4]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= stoneValue.length <= 500`
+* 1 <= stoneValue[i] <= 106
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun stoneGameV(stoneValue: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = stoneValue.size
+ val ps = IntArray(n)
+ ps[0] = stoneValue[0]
+ for (i in 1 until n) {
+ ps[i] = ps[i - 1] + stoneValue[i]
+ }
+ return gameDP(ps, 0, n - 1, Array>(n) { arrayOfNulls(n) })
+ }
+
+ private fun gameDP(ps: IntArray, i: Int, j: Int, dp: Array>): Int {
+ if (i == j) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (dp[i][j] != null) {
+ return dp[i][j]!!
+ }
+ var max = 0
+ for (k in i + 1..j) {
+ val l = ps[k - 1] - if (i == 0) 0 else ps[i - 1]
+ val r = ps[j] - ps[k - 1]
+ if (2 * Math.min(l, r) < max) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if (l <= r) {
+ max = Math.max(max, l + gameDP(ps, i, k - 1, dp))
+ }
+ if (l >= r) {
+ max = Math.max(max, r + gameDP(ps, k, j, dp))
+ }
+ }
+ dp[i][j] = max
+ return max
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1566_detect_pattern_of_length_m_repeated_k_or_more_times/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1566_detect_pattern_of_length_m_repeated_k_or_more_times/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a224a4b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1566_detect_pattern_of_length_m_repeated_k_or_more_times/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1566\. Detect Pattern of Length M Repeated K or More Times
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array of positive integers `arr`, find a pattern of length `m` that is repeated `k` or more times.
+
+A **pattern** is a subarray (consecutive sub-sequence) that consists of one or more values, repeated multiple times **consecutively** without overlapping. A pattern is defined by its length and the number of repetitions.
+
+Return `true` _if there exists a pattern of length_ `m` _that is repeated_ `k` _or more times, otherwise return_ `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,4,4,4,4], m = 1, k = 3
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** The pattern **(4)** of length 1 is repeated 4 consecutive times. Notice that pattern can be repeated k or more times but not less.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,1,2,1,1,1,3], m = 2, k = 2
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** The pattern **(1,2)** of length 2 is repeated 2 consecutive times. Another valid pattern **(2,1) is** also repeated 2 times.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,1,2,1,3], m = 2, k = 3
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** The pattern (1,2) is of length 2 but is repeated only 2 times. There is no pattern of length 2 that is repeated 3 or more times.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= arr.length <= 100`
+* `1 <= arr[i] <= 100`
+* `1 <= m <= 100`
+* `2 <= k <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun containsPattern(arr: IntArray, m: Int, k: Int): Boolean {
+ for (i in 0 until arr.size - m) {
+ val pattern = arr.copyOfRange(i, i + m)
+ var times = 1
+ var j = i + m
+ while (j < arr.size) {
+ val candidate = arr.copyOfRange(j, Math.min(arr.size, j + m))
+ if (pattern.contentEquals(candidate)) {
+ times++
+ if (times == k) {
+ return true
+ }
+ } else {
+ break
+ }
+ j += m
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1567_maximum_length_of_subarray_with_positive_product/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1567_maximum_length_of_subarray_with_positive_product/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2e7179f9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1567_maximum_length_of_subarray_with_positive_product/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1567\. Maximum Length of Subarray With Positive Product
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of integers `nums`, find the maximum length of a subarray where the product of all its elements is positive.
+
+A subarray of an array is a consecutive sequence of zero or more values taken out of that array.
+
+Return _the maximum length of a subarray with positive product_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,-2,-3,4]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The array nums already has a positive product of 24.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,1,-2,-3,-4]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The longest subarray with positive product is [1,-2,-3] which has a product of 6. Notice that we cannot include 0 in the subarray since that'll make the product 0 which is not positive.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-1,-2,-3,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** The longest subarray with positive product is [-1,-2] or [-2,-3].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun getMaxLen(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ var posLen = 0
+ var negLen = 0
+ var res = 0
+ for (num in nums) {
+ if (num == 0) {
+ posLen = 0
+ negLen = 0
+ } else if (num > 0) {
+ posLen++
+ negLen = if (negLen == 0) 0 else negLen + 1
+ } else {
+ val temp = posLen
+ posLen = if (negLen == 0) 0 else negLen + 1
+ negLen = temp + 1
+ }
+ res = Math.max(res, posLen)
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1568_minimum_number_of_days_to_disconnect_island/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1568_minimum_number_of_days_to_disconnect_island/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0fbe6fab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1568_minimum_number_of_days_to_disconnect_island/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1568\. Minimum Number of Days to Disconnect Island
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an `m x n` binary grid `grid` where `1` represents land and `0` represents water. An **island** is a maximal **4-directionally** (horizontal or vertical) connected group of `1`'s.
+
+The grid is said to be **connected** if we have **exactly one island**, otherwise is said **disconnected**.
+
+In one day, we are allowed to change **any** single land cell `(1)` into a water cell `(0)`.
+
+Return _the minimum number of days to disconnect the grid_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+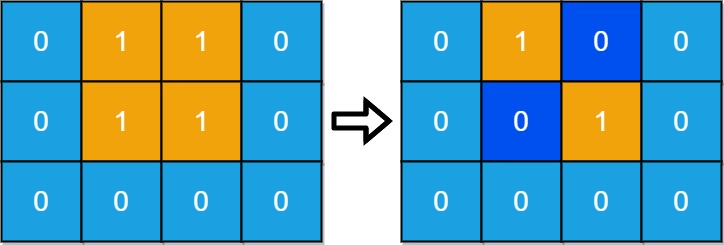
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** We need at least 2 days to get a disconnected grid. Change land grid[1][1] and grid[0][2] to water and get 2 disconnected island.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Grid of full water is also disconnected ([[1,1]] -> [[0,0]]), 0 islands.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 30`
+* `grid[i][j]` is either `0` or `1`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("kotlin:S107")
+class Solution {
+ private val dirs = arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1), intArrayOf(0, -1), intArrayOf(1, 0), intArrayOf(-1, 0))
+ fun minDays(grid: Array): Int {
+ val m = grid.size
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ var numOfIslands = 0
+ var hasArticulationPoint = false
+ var color = 1
+ var minIslandSize = m * n
+ val time = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
+ val low = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in 0 until n) {
+ if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
+ numOfIslands++
+ color++
+ val articulationPoints: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val islandSize = IntArray(1)
+ tarjan(i, j, -1, -1, 0, time, low, grid, articulationPoints, color, islandSize)
+ minIslandSize = Math.min(minIslandSize, islandSize[0])
+ if (articulationPoints.isNotEmpty()) {
+ hasArticulationPoint = true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (numOfIslands >= 2) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (numOfIslands == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (numOfIslands == 1 && minIslandSize == 1) {
+ return 1
+ }
+ return if (hasArticulationPoint) 1 else 2
+ }
+
+ private fun tarjan(
+ x: Int,
+ y: Int,
+ prex: Int,
+ prey: Int,
+ time: Int,
+ times: Array,
+ lows: Array,
+ grid: Array,
+ articulationPoints: MutableList,
+ color: Int,
+ islandSize: IntArray
+ ) {
+ times[x][y] = time
+ lows[x][y] = time
+ grid[x][y] = color
+ islandSize[0]++
+ var children = 0
+ for (dir in dirs) {
+ val nx = x + dir[0]
+ val ny = y + dir[1]
+ if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= grid.size || ny >= grid[0].size) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if (grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
+ children++
+ tarjan(
+ nx,
+ ny,
+ x,
+ y,
+ time + 1,
+ times,
+ lows,
+ grid,
+ articulationPoints,
+ color,
+ islandSize
+ )
+ lows[x][y] = Math.min(lows[x][y], lows[nx][ny])
+ if (prex != -1 && lows[nx][ny] >= time) {
+ articulationPoints.add(x * grid.size + y)
+ }
+ } else if ((nx != prex || ny != prey) && grid[nx][ny] != 0) {
+ lows[x][y] = Math.min(lows[x][y], times[nx][ny])
+ }
+ }
+ if (prex == -1 && children > 1) {
+ articulationPoints.add(x * grid.size + y)
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1569_number_of_ways_to_reorder_array_to_get_same_bst/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1569_number_of_ways_to_reorder_array_to_get_same_bst/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5c3beda9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1569_number_of_ways_to_reorder_array_to_get_same_bst/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1569\. Number of Ways to Reorder Array to Get Same BST
+
+Hard
+
+Given an array `nums` that represents a permutation of integers from `1` to `n`. We are going to construct a binary search tree (BST) by inserting the elements of `nums` in order into an initially empty BST. Find the number of different ways to reorder `nums` so that the constructed BST is identical to that formed from the original array `nums`.
+
+* For example, given `nums = [2,1,3]`, we will have 2 as the root, 1 as a left child, and 3 as a right child. The array `[2,3,1]` also yields the same BST but `[3,2,1]` yields a different BST.
+
+Return _the number of ways to reorder_ `nums` _such that the BST formed is identical to the original BST formed from_ `nums`.
+
+Since the answer may be very large, **return it modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,1,3]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** We can reorder nums to be [2,3,1] which will yield the same BST. There are no other ways to reorder nums which will yield the same BST.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,4,5,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** The following 5 arrays will yield the same BST:
+
+ [3,1,2,4,5]
+ [3,1,4,2,5]
+ [3,1,4,5,2]
+ [3,4,1,2,5]
+ [3,4,1,5,2]
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** There are no other orderings of nums that will yield the same BST.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 1000`
+* `1 <= nums[i] <= nums.length`
+* All integers in `nums` are **distinct**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numOfWays(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val mod: Long = 1000000007
+ val fact = LongArray(1001)
+ fact[0] = 1
+ for (i in 1..1000) {
+ fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i % mod
+ }
+ val root = TreeNode(nums[0])
+ for (i in 1 until nums.size) {
+ addInTree(nums[i], root)
+ }
+ return ((calcPerms(root, fact).perm - 1) % mod).toInt()
+ }
+
+ class Inverse(var x: Long, var y: Long)
+ class TreeInfo(var numOfNodes: Long, var perm: Long)
+ class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
+ var left: TreeNode? = null
+ var right: TreeNode? = null
+ }
+
+ private fun calcPerms(root: TreeNode?, fact: LongArray): TreeInfo {
+ val left: TreeInfo
+ val right: TreeInfo
+ left = if (root!!.left != null) {
+ calcPerms(
+ root.left, fact
+ )
+ } else {
+ TreeInfo(0, 1)
+ }
+ right = if (root.right != null) {
+ calcPerms(
+ root.right, fact
+ )
+ } else {
+ TreeInfo(0, 1)
+ }
+ val mod: Long = 1000000007
+ val totNodes = left.numOfNodes + right.numOfNodes + 1
+ val modDiv = getModDivision(
+ fact[totNodes.toInt() - 1],
+ fact[left.numOfNodes.toInt()],
+ fact[right.numOfNodes.toInt()],
+ mod
+ )
+ val perms = if (totNodes == 1L) 1 else left.perm * right.perm % mod * modDiv % mod
+ left.numOfNodes = totNodes
+ left.perm = perms
+ return left
+ }
+
+ private fun getModDivision(a: Long, b1: Long, b2: Long, m: Long): Long {
+ val b = b1 * b2
+ val inv = getInverse(b, m)
+ return inv * a % m
+ }
+
+ private fun getInverse(b: Long, m: Long): Long {
+ val inv = getInverseExtended(b, m)
+ return (inv.x % m + m) % m
+ }
+
+ private fun getInverseExtended(a: Long, b: Long): Inverse {
+ if (a == 0L) {
+ return Inverse(0, 1)
+ }
+ val inv = getInverseExtended(b % a, a)
+ val x1 = inv.y - b / a * inv.x
+ val y1 = inv.x
+ inv.x = x1
+ inv.y = y1
+ return inv
+ }
+
+ private fun addInTree(x: Int, root: TreeNode?) {
+ if (root!!.`val` > x) {
+ if (root.left != null) {
+ addInTree(x, root.left)
+ } else {
+ root.left = TreeNode(x)
+ }
+ }
+ if (root.`val` < x) {
+ if (root.right != null) {
+ addInTree(x, root.right)
+ } else {
+ root.right = TreeNode(x)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1572_matrix_diagonal_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1572_matrix_diagonal_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7574704f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1572_matrix_diagonal_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1572\. Matrix Diagonal Sum
+
+Easy
+
+Given a square matrix `mat`, return the sum of the matrix diagonals.
+
+Only include the sum of all the elements on the primary diagonal and all the elements on the secondary diagonal that are not part of the primary diagonal.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[**1**,2,**3**],
+ [4,**5**,6],
+ [**7**,8,**9**]]
+
+**Output:** 25
+
+**Explanation:** Diagonals sum: 1 + 5 + 9 + 3 + 7 = 25 Notice that element mat[1][1] = 5 is counted only once.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[**1**,1,1,**1**],
+ [1,**1**,**1**,1],
+ [1,**1**,**1**,1],
+ [**1**,1,1,**1**]]
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[**5**]]
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == mat.length == mat[i].length`
+* `1 <= n <= 100`
+* `1 <= mat[i][j] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun diagonalSum(mat: Array): Int {
+ val m = mat.size
+ val added: MutableSet = HashSet()
+ var sum = 0
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in 0 until m) {
+ if (i == j) {
+ added.add(i * m + j)
+ sum += mat[i][j]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until m) {
+ for (j in m - 1 downTo 0) {
+ if (i + j == m - 1 && added.add(i * m + j)) {
+ sum += mat[i][j]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return sum
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1573_number_of_ways_to_split_a_string/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1573_number_of_ways_to_split_a_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0723c145
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1573_number_of_ways_to_split_a_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1573\. Number of Ways to Split a String
+
+Medium
+
+Given a binary string `s`, you can split `s` into 3 **non-empty** strings `s1`, `s2`, and `s3` where `s1 + s2 + s3 = s`.
+
+Return the number of ways `s` can be split such that the number of ones is the same in `s1`, `s2`, and `s3`. Since the answer may be too large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "10101"
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** There are four ways to split s in 3 parts where each part contain the same number of letters '1'.
+
+"1\|010\|1"
+
+"1\|01\|01"
+
+"10\|10\|1"
+
+"10\|1\|01"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "1001"
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "0000"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** There are three ways to split s in 3 parts.
+
+"0\|0\|00"
+
+"0\|00\|0"
+
+"00\|0\|0"
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 3 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s[i]` is either `'0'` or `'1'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numWays(s: String): Int {
+ var totalOnesCount: Long = 0
+ val mod: Long = 1000000007
+ var waysOfFirstString: Long = 0
+ var waysOfSecondString: Long = 0
+ var onesCount: Long = 0
+ val n = s.length.toLong()
+ for (i in 0 until s.length) {
+ if (s[i] == '1') {
+ totalOnesCount += 1
+ }
+ }
+ if (totalOnesCount % 3 != 0L) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val onesFirstPart = totalOnesCount / 3
+ val onesSecondPart = onesFirstPart * 2
+ if (totalOnesCount == 0L) {
+ return ((n - 1) * (n - 2) / 2 % mod).toInt()
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until s.length) {
+ if (s[i] == '1') {
+ onesCount += 1
+ }
+ if (onesCount == onesFirstPart) {
+ waysOfFirstString += 1
+ } else if (onesCount == onesSecondPart) {
+ waysOfSecondString += 1
+ } else if (onesCount > onesSecondPart) {
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ return (waysOfFirstString * waysOfSecondString % mod).toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1574_shortest_subarray_to_be_removed_to_make_array_sorted/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1574_shortest_subarray_to_be_removed_to_make_array_sorted/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f23bc182
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1574_shortest_subarray_to_be_removed_to_make_array_sorted/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1574\. Shortest Subarray to be Removed to Make Array Sorted
+
+Medium
+
+Given an integer array `arr`, remove a subarray (can be empty) from `arr` such that the remaining elements in `arr` are **non-decreasing**.
+
+Return _the length of the shortest subarray to remove_.
+
+A **subarray** is a contiguous subsequence of the array.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3,10,4,2,3,5]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The shortest subarray we can remove is [10,4,2] of length 3. The remaining elements after that will be [1,2,3,3,5] which are sorted. Another correct solution is to remove the subarray [3,10,4].
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [5,4,3,2,1]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** Since the array is strictly decreasing, we can only keep a single element. Therefore we need to remove a subarray of length 4, either [5,4,3,2] or [4,3,2,1].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** The array is already non-decreasing. We do not need to remove any elements.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= arr.length <= 105
+* 0 <= arr[i] <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun findLengthOfShortestSubarray(arr: IntArray): Int {
+ var left = 0
+ while (left < arr.size - 1 && arr[left] <= arr[left + 1]) {
+ left++
+ }
+ if (left == arr.size - 1) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ var right = arr.size - 1
+ while (right > left && arr[right] >= arr[right - 1]) {
+ right--
+ }
+ if (right == 0) {
+ return arr.size - 1
+ }
+ var result = Math.min(arr.size - left - 1, right)
+ var i = 0
+ var j = right
+ while (i <= left && j < arr.size) {
+ if (arr[j] >= arr[i]) {
+ result = Math.min(result, j - i - 1)
+ i++
+ } else {
+ j++
+ }
+ }
+ return result
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1575_count_all_possible_routes/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1575_count_all_possible_routes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4421cc40
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1575_count_all_possible_routes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1575\. Count All Possible Routes
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an array of **distinct** positive integers locations where `locations[i]` represents the position of city `i`. You are also given integers `start`, `finish` and `fuel` representing the starting city, ending city, and the initial amount of fuel you have, respectively.
+
+At each step, if you are at city `i`, you can pick any city `j` such that `j != i` and `0 <= j < locations.length` and move to city `j`. Moving from city `i` to city `j` reduces the amount of fuel you have by `|locations[i] - locations[j]|`. Please notice that `|x|` denotes the absolute value of `x`.
+
+Notice that `fuel` **cannot** become negative at any point in time, and that you are **allowed** to visit any city more than once (including `start` and `finish`).
+
+Return _the count of all possible routes from_ `start` _to_ `finish`. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** locations = [2,3,6,8,4], start = 1, finish = 3, fuel = 5
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The following are all possible routes, each uses 5 units of fuel:
+
+1 -> 3
+
+1 -> 2 -> 3
+
+1 -> 4 -> 3
+
+1 -> 4 -> 2 -> 3
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** locations = [4,3,1], start = 1, finish = 0, fuel = 6
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** The following are all possible routes:
+
+1 -> 0, used fuel = 1
+
+1 -> 2 -> 0, used fuel = 5
+
+1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 0, used fuel = 5
+
+1 -> 0 -> 1 -> 0, used fuel = 3
+
+1 -> 0 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1 -> 0, used fuel = 5
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** locations = [5,2,1], start = 0, finish = 2, fuel = 3
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** It is impossible to get from 0 to 2 using only 3 units of fuel since the shortest route needs 4 units of fuel.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= locations.length <= 100`
+* 1 <= locations[i] <= 109
+* All integers in `locations` are **distinct**.
+* `0 <= start, finish < locations.length`
+* `1 <= fuel <= 200`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun countRoutes(locations: IntArray, start: Int, finish: Int, fuel: Int): Int {
+ val n = locations.size
+ val cache = Array(n) { IntArray(fuel + 1) }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ cache[i].fill(-1)
+ }
+ return dfsHelper(locations, start, finish, fuel, cache)
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ var MOD = 1000000007
+ private fun dfsHelper(locations: IntArray, start: Int, finish: Int, fuel: Int, cache: Array): Int {
+ if (cache[start][fuel] != -1) {
+ return cache[start][fuel]
+ }
+ if (fuel == 0 && start != finish) {
+ cache[start][fuel] = 0
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (fuel > 0 && Math.abs(locations[start] - locations[finish]) > fuel) {
+ cache[start][fuel] = 0
+ return 0
+ }
+ var cnt = if (start == finish) 1 else 0
+ for (i in locations.indices) {
+ if (i != start) {
+ val need = Math.abs(locations[start] - locations[i])
+ if (need <= fuel) {
+ cnt += dfsHelper(locations, i, finish, fuel - need, cache)
+ cnt %= MOD
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ cache[start][fuel] = cnt
+ return cnt
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1576_replace_all_s_to_avoid_consecutive_repeating_characters/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1576_replace_all_s_to_avoid_consecutive_repeating_characters/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..61bcbaf5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1576_replace_all_s_to_avoid_consecutive_repeating_characters/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1576\. Replace All ?'s to Avoid Consecutive Repeating Characters
+
+Easy
+
+Given a string `s` containing only lowercase English letters and the `'?'` character, convert **all** the `'?'` characters into lowercase letters such that the final string does not contain any **consecutive repeating** characters. You **cannot** modify the non `'?'` characters.
+
+It is **guaranteed** that there are no consecutive repeating characters in the given string **except** for `'?'`.
+
+Return _the final string after all the conversions (possibly zero) have been made_. If there is more than one solution, return **any of them**. It can be shown that an answer is always possible with the given constraints.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "?zs"
+
+**Output:** "azs"
+
+**Explanation:** There are 25 solutions for this problem. From "azs" to "yzs", all are valid. Only "z" is an invalid modification as the string will consist of consecutive repeating characters in "zzs".
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "ubv?w"
+
+**Output:** "ubvaw"
+
+**Explanation:** There are 24 solutions for this problem. Only "v" and "w" are invalid modifications as the strings will consist of consecutive repeating characters in "ubvvw" and "ubvww".
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 100`
+* `s` consist of lowercase English letters and `'?'`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun modifyString(s: String): String {
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ val len = s.length
+ for (i in 0 until len) {
+ val c = s[i]
+ if (c == '?') {
+ var replaceChar = 'a'
+ val leftChar = if (i == 0) s[i] else sb[i - 1]
+ val rightChar = s[Math.min(i + 1, len - 1)]
+ while (replaceChar == leftChar || replaceChar == rightChar) {
+ replaceChar += 1.toChar().code
+ }
+ sb.append(replaceChar)
+ } else {
+ sb.append(c)
+ }
+ }
+ return sb.toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1577_number_of_ways_where_square_of_number_is_equal_to_product_of_two_numbers/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1577_number_of_ways_where_square_of_number_is_equal_to_product_of_two_numbers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5045b242
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1577_number_of_ways_where_square_of_number_is_equal_to_product_of_two_numbers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1577\. Number of Ways Where Square of Number Is Equal to Product of Two Numbers
+
+Medium
+
+Given two arrays of integers `nums1` and `nums2`, return the number of triplets formed (type 1 and type 2) under the following rules:
+
+* Type 1: Triplet (i, j, k) if nums1[i]2 == nums2[j] * nums2[k] where `0 <= i < nums1.length` and `0 <= j < k < nums2.length`.
+* Type 2: Triplet (i, j, k) if nums2[i]2 == nums1[j] * nums1[k] where `0 <= i < nums2.length` and `0 <= j < k < nums1.length`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [7,4], nums2 = [5,2,8,9]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** Type 1: (1, 1, 2), nums1[1]2 = nums2[1] \* nums2[2]. (42 = 2 \* 8).
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [1,1], nums2 = [1,1,1]
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Explanation:** All Triplets are valid, because 12 = 1 \* 1.
+
+Type 1: (0,0,1), (0,0,2), (0,1,2), (1,0,1), (1,0,2), (1,1,2). nums1[i]2 = nums2[j] \* nums2[k].
+
+Type 2: (0,0,1), (1,0,1), (2,0,1). nums2[i]2 = nums1[j] \* nums1[k].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums1 = [7,7,8,3], nums2 = [1,2,9,7]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** There are 2 valid triplets.
+
+Type 1: (3,0,2). nums1[3]2 = nums2[0] \* nums2[2].
+
+Type 2: (3,0,1). nums2[3]2 = nums1[0] \* nums1[1].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 1000`
+* 1 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 105
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numTriplets(nums1: IntArray, nums2: IntArray): Int {
+ nums1.sort()
+ nums2.sort()
+ return count(nums1, nums2) + count(nums2, nums1)
+ }
+
+ fun count(a: IntArray, b: IntArray): Int {
+ val m = b.size
+ var count = 0
+ for (value in a) {
+ val x = value.toLong() * value
+ var j = 0
+ var k = m - 1
+ while (j < k) {
+ val prod = b[j].toLong() * b[k]
+ if (prod < x) {
+ j++
+ } else if (prod > x) {
+ k--
+ } else if (b[j] != b[k]) {
+ var jNew = j
+ var kNew = k
+ while (b[j] == b[jNew]) {
+ jNew++
+ }
+ while (b[k] == b[kNew]) {
+ kNew--
+ }
+ count += (jNew - j) * (k - kNew)
+ j = jNew
+ k = kNew
+ } else {
+ val q = k - j + 1
+ count += q * (q - 1) / 2
+ break
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1578_minimum_time_to_make_rope_colorful/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1578_minimum_time_to_make_rope_colorful/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..16bb7968
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1578_minimum_time_to_make_rope_colorful/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1578\. Minimum Time to Make Rope Colorful
+
+Medium
+
+Alice has `n` balloons arranged on a rope. You are given a **0-indexed** string `colors` where `colors[i]` is the color of the ith balloon.
+
+Alice wants the rope to be **colorful**. She does not want **two consecutive balloons** to be of the same color, so she asks Bob for help. Bob can remove some balloons from the rope to make it **colorful**. You are given a **0-indexed** integer array `neededTime` where `neededTime[i]` is the time (in seconds) that Bob needs to remove the ith balloon from the rope.
+
+Return _the **minimum time** Bob needs to make the rope **colorful**_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** colors = "abaac", neededTime = [1,2,3,4,5]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** In the above image, 'a' is blue, 'b' is red, and 'c' is green.
+
+Bob can remove the blue balloon at index 2. This takes 3 seconds.
+
+There are no longer two consecutive balloons of the same color. Total time = 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** colors = "abc", neededTime = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** The rope is already colorful. Bob does not need to remove any balloons from the rope.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** colors = "aabaa", neededTime = [1,2,3,4,1]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Bob will remove the ballons at indices 0 and 4. Each ballon takes 1 second to remove.
+
+There are no longer two consecutive balloons of the same color. Total time = 1 + 1 = 2.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == colors.length == neededTime.length`
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* 1 <= neededTime[i] <= 104
+* `colors` contains only lowercase English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minCost(colors: String, neededTime: IntArray): Int {
+ val str = colors.toCharArray()
+ var minCost = 0
+ for (i in 1 until str.size) {
+ if (str[i] == str[i - 1]) {
+ // accrue the cost of deletion for the lower duplicate
+ minCost += Math.min(neededTime[i], neededTime[i - 1])
+ // keep the cost of the higher duplicate for next iteration
+ neededTime[i] = Math.max(neededTime[i], neededTime[i - 1])
+ }
+ }
+ return minCost
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1579_remove_max_number_of_edges_to_keep_graph_fully_traversable/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1579_remove_max_number_of_edges_to_keep_graph_fully_traversable/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6511ae6b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1579_remove_max_number_of_edges_to_keep_graph_fully_traversable/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,139 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1579\. Remove Max Number of Edges to Keep Graph Fully Traversable
+
+Hard
+
+Alice and Bob have an undirected graph of `n` nodes and 3 types of edges:
+
+* Type 1: Can be traversed by Alice only.
+* Type 2: Can be traversed by Bob only.
+* Type 3: Can by traversed by both Alice and Bob.
+
+Given an array `edges` where edges[i] = [typei, ui, vi] represents a bidirectional edge of type typei between nodes ui and vi, find the maximum number of edges you can remove so that after removing the edges, the graph can still be fully traversed by both Alice and Bob. The graph is fully traversed by Alice and Bob if starting from any node, they can reach all other nodes.
+
+Return _the maximum number of edges you can remove, or return_ `-1` _if it's impossible for the graph to be fully traversed by Alice and Bob._
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** n = 4, edges = \[\[3,1,2],[3,2,3],[1,1,3],[1,2,4],[1,1,2],[2,3,4]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** If we remove the 2 edges [1,1,2] and [1,1,3]. The graph will still be fully traversable by Alice and Bob. Removing any additional edge will not make it so. So the maximum number of edges we can remove is 2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** n = 4, edges = \[\[3,1,2],[3,2,3],[1,1,4],[2,1,4]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Notice that removing any edge will not make the graph fully traversable by Alice and Bob.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+****
+
+**Input:** n = 4, edges = \[\[3,2,3],[1,1,2],[2,3,4]]
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** In the current graph, Alice cannot reach node 4 from the other nodes. Likewise, Bob cannot reach 1. Therefore it's impossible to make the graph fully traversable.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 10^5`
+* `1 <= edges.length <= min(10^5, 3 * n * (n-1) / 2)`
+* `edges[i].length == 3`
+* `1 <= edges[i][0] <= 3`
+* `1 <= edges[i][1] < edges[i][2] <= n`
+* All tuples (typei, ui, vi) are distinct.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.Arrays
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxNumEdgesToRemove(n: Int, edges: Array): Int {
+ Arrays.sort(edges) { a: IntArray, b: IntArray -> b[0] - a[0] }
+ val alice = IntArray(n + 1)
+ val rankAlice = IntArray(n + 1)
+ val bob = IntArray(n + 1)
+ val rankBob = IntArray(n + 1)
+ for (i in 1..n) {
+ alice[i] = i
+ bob[i] = i
+ }
+ var countAlice = n
+ var countBob = n
+ var remove = 0
+ for (edge in edges) {
+ val type = edge[0]
+ val u = edge[1]
+ val v = edge[2]
+ if (type == 1) {
+ val a = union(u, v, alice, rankAlice)
+ if (a) {
+ countAlice--
+ } else {
+ remove++
+ }
+ } else if (type == 2) {
+ val b = union(u, v, bob, rankBob)
+ if (b) {
+ countBob--
+ } else {
+ remove++
+ }
+ } else {
+ val b = union(u, v, bob, rankBob)
+ val a = union(u, v, alice, rankAlice)
+ if (!a && !b) {
+ remove++
+ }
+ if (a) {
+ countAlice--
+ }
+ if (b) {
+ countBob--
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return if (countAlice != 1 || countBob != 1) {
+ -1
+ } else remove
+ }
+
+ fun union(x: Int, y: Int, arr: IntArray, rank: IntArray): Boolean {
+ val p1 = find(arr[x], arr)
+ val p2 = find(arr[y], arr)
+ if (p1 != p2) {
+ if (rank[p1] > rank[p2]) {
+ arr[p2] = p1
+ } else if (rank[p1] < rank[p2]) {
+ arr[p1] = p2
+ } else {
+ arr[p1] = p2
+ rank[p2]++
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ fun find(x: Int, arr: IntArray): Int {
+ if (arr[x] == x) {
+ return x
+ }
+ val temp = find(arr[x], arr)
+ arr[x] = temp
+ return temp
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1581_customer_who_visited_but_did_not_make_any_transactions/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1581_customer_who_visited_but_did_not_make_any_transactions/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2dccb0d2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1581_customer_who_visited_but_did_not_make_any_transactions/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1581\. Customer Who Visited but Did Not Make Any Transactions
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Visits`
+
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ | visit_id | int |
+ | customer_id | int |
+ +-------------+---------+
+ visit_id is the primary key for this table.
+ This table contains information about the customers who visited the mall.
+
+Table: `Transactions`
+
+ +----------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +----------------+---------+
+ | transaction_id | int |
+ | visit_id | int |
+ | amount | int |
+ +----------------+---------+
+ transaction_id is the primary key for this table.
+ This table contains information about the transactions made during the visit\_id.
+
+Write an SQL query to find the IDs of the users who visited without making any transactions and the number of times they made these types of visits.
+
+Return the result table sorted in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Visits
+ +----------+-------------+
+ | visit_id | customer_id |
+ +----------+-------------+
+ | 1 | 23 |
+ | 2 | 9 |
+ | 4 | 30 |
+ | 5 | 54 |
+ | 6 | 96 |
+ | 7 | 54 |
+ | 8 | 54 |
+ +----------+-------------+
+ Transactions
+ +----------------+----------+--------+
+ | transaction_id | visit_id | amount |
+ +----------------+----------+--------+
+ | 2 | 5 | 310 |
+ | 3 | 5 | 300 |
+ | 9 | 5 | 200 |
+ | 12 | 1 | 910 |
+ | 13 | 2 | 970 |
+ +----------------+----------+--------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +-------------+----------------+
+ | customer_id | count_no_trans |
+ +-------------+----------------+
+ | 54 | 2 |
+ | 30 | 1 |
+ | 96 | 1 |
+ +-------------+----------------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Customer with id = 23 visited the mall once and made one transaction during the visit with id = 12.c
+
+Customer with id = 9 visited the mall once and made one transaction during the visit with id = 13.
+
+Customer with id = 30 visited the mall once and did not make any transactions.
+
+Customer with id = 54 visited the mall three times. During 2 visits they did not make any transactions, and during one visit they made 3 transactions.
+
+Customer with id = 96 visited the mall once and did not make any transactions.
+
+As we can see, users with IDs 30 and 96 visited the mall one time without making any transactions. Also, user 54 visited the mall twice and did not make any transactions.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+select customer_id, COUNT(*) as count_no_trans
+from visits v left join transactions t
+on v.visit_id = t.visit_id
+where transaction_id is null
+group by customer_id
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1582_special_positions_in_a_binary_matrix/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1582_special_positions_in_a_binary_matrix/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3e9ae18a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1582_special_positions_in_a_binary_matrix/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1582\. Special Positions in a Binary Matrix
+
+Easy
+
+Given an `m x n` binary matrix `mat`, return _the number of special positions in_ `mat`_._
+
+A position `(i, j)` is called **special** if `mat[i][j] == 1` and all other elements in row `i` and column `j` are `0` (rows and columns are **0-indexed**).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[1,0,0],[0,0,1],[1,0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** (1, 2) is a special position because mat[1][2] == 1 and all other elements in row 1 and column 2 are 0.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** mat = \[\[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** (0, 0), (1, 1) and (2, 2) are special positions.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == mat.length`
+* `n == mat[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 100`
+* `mat[i][j]` is either `0` or `1`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun numSpecial(mat: Array): Int {
+ var count = 0
+ for (i in mat.indices) {
+ for (j in mat[0].indices) {
+ if (mat[i][j] == 1 && isSpecial(mat, i, j)) {
+ count++
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+
+ private fun isSpecial(mat: Array, row: Int, col: Int): Boolean {
+ for (i in mat.indices) {
+ if (i != row && mat[i][col] == 1) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ for (j in mat[0].indices) {
+ if (j != col && mat[row][j] == 1) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1583_count_unhappy_friends/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1583_count_unhappy_friends/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e17e4ee1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1583_count_unhappy_friends/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1583\. Count Unhappy Friends
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a list of `preferences` for `n` friends, where `n` is always **even**.
+
+For each person `i`, `preferences[i]` contains a list of friends **sorted** in the **order of preference**. In other words, a friend earlier in the list is more preferred than a friend later in the list. Friends in each list are denoted by integers from `0` to `n-1`.
+
+All the friends are divided into pairs. The pairings are given in a list `pairs`, where pairs[i] = [xi, yi] denotes xi is paired with yi and yi is paired with xi.
+
+However, this pairing may cause some of the friends to be unhappy. A friend `x` is unhappy if `x` is paired with `y` and there exists a friend `u` who is paired with `v` but:
+
+* `x` prefers `u` over `y`, and
+* `u` prefers `x` over `v`.
+
+Return _the number of unhappy friends_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, preferences = \[\[1, 2, 3], [3, 2, 0], [3, 1, 0], [1, 2, 0]], pairs = \[\[0, 1], [2, 3]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Friend 1 is unhappy because:
+
+- 1 is paired with 0 but prefers 3 over 0, and
+
+- 3 prefers 1 over 2.
+
+Friend 3 is unhappy because:
+
+- 3 is paired with 2 but prefers 1 over 2, and
+
+- 1 prefers 3 over 0.
+
+Friends 0 and 2 are happy.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2, preferences = \[\[1], [0]], pairs = \[\[1, 0]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Both friends 0 and 1 are happy.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, preferences = \[\[1, 3, 2], [2, 3, 0], [1, 3, 0], [0, 2, 1]], pairs = \[\[1, 3], [0, 2]]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n <= 500`
+* `n` is even.
+* `preferences.length == n`
+* `preferences[i].length == n - 1`
+* `0 <= preferences[i][j] <= n - 1`
+* `preferences[i]` does not contain `i`.
+* All values in `preferences[i]` are unique.
+* `pairs.length == n/2`
+* `pairs[i].length == 2`
+* xi != yi
+* 0 <= xi, yi <= n - 1
+* Each person is contained in **exactly one** pair.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+@Suppress("UNUSED_PARAMETER")
+class Solution {
+ fun unhappyFriends(n: Int, preferences: Array, pairs: Array): Int {
+ var unhappyFriends = 0
+ val assignedPair: MutableMap = HashMap()
+ for (pair in pairs) {
+ assignedPair[pair[0]] = pair[1]
+ assignedPair[pair[1]] = pair[0]
+ }
+ for (pair in pairs) {
+ if (isUnHappy(pair[1], pair[0], preferences, assignedPair)) {
+ unhappyFriends++
+ }
+ if (isUnHappy(pair[0], pair[1], preferences, assignedPair)) {
+ unhappyFriends++
+ }
+ }
+ return unhappyFriends
+ }
+
+ private fun isUnHappy(
+ self: Int,
+ assignedFriend: Int,
+ preferences: Array,
+ assignedPairs: Map
+ ): Boolean {
+ val preference = preferences[self]
+ val assignedFriendPreferenceIndex = findIndex(preference, assignedFriend)
+ for (i in 0..assignedFriendPreferenceIndex) {
+ val preferredFriend = preference[i]
+ val preferredFriendAssignedFriend = assignedPairs[preferredFriend]!!
+ if (preferredFriendAssignedFriend == self) {
+ return false
+ }
+ val candidateAssignedFriendIndex = findIndex(preferences[preferredFriend], preferredFriendAssignedFriend)
+ if (isPreferred(self, preferences[preferredFriend], candidateAssignedFriendIndex)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ private fun isPreferred(self: Int, preference: IntArray, boundary: Int): Boolean {
+ for (i in 0..boundary) {
+ if (self == preference[i]) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ private fun findIndex(preference: IntArray, assignedFriend: Int): Int {
+ for (i in preference.indices) {
+ if (preference[i] == assignedFriend) {
+ return i
+ }
+ }
+ return 0
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1584_min_cost_to_connect_all_points/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1584_min_cost_to_connect_all_points/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..38697a41
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1584_min_cost_to_connect_all_points/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1584\. Min Cost to Connect All Points
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an array `points` representing integer coordinates of some points on a 2D-plane, where points[i] = [xi, yi].
+
+The cost of connecting two points [xi, yi] and [xj, yj] is the **manhattan distance** between them: |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|, where `|val|` denotes the absolute value of `val`.
+
+Return _the minimum cost to make all points connected._ All points are connected if there is **exactly one** simple path between any two points.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** points = \[\[0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0]]
+
+**Output:** 20
+
+**Explanation:** 
+
+We can connect the points as shown above to get the minimum cost of 20.
+
+Notice that there is a unique path between every pair of points.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** points = \[\[3,12],[-2,5],[-4,1]]
+
+**Output:** 18
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= points.length <= 1000`
+* -106 <= xi, yi <= 106
+* All pairs (xi, yi) are distinct.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minCostConnectPoints(points: Array): Int {
+ val v = points.size
+ if (v == 2) {
+ return getDistance(points[0], points[1])
+ }
+ val pq = PriorityQueue(v, Pair())
+ val mst = BooleanArray(v)
+ val dist = IntArray(v)
+ val parent = IntArray(v)
+ dist.fill(1000000)
+ parent.fill(-1)
+ dist[0] = 0
+ parent[0] = 0
+ for (i in 0 until v) {
+ pq.add(Pair(dist[i], i))
+ }
+ constructMST(parent, points, mst, pq, dist)
+ var cost = 0
+ for (i in 1 until parent.size) {
+ cost += getDistance(points[parent[i]], points[i])
+ }
+ return cost
+ }
+
+ private fun constructMST(
+ parent: IntArray,
+ points: Array,
+ mst: BooleanArray,
+ pq: PriorityQueue,
+ dist: IntArray
+ ) {
+ if (!containsFalse(mst)) {
+ return
+ }
+ val newPair = pq.poll()
+ val pointIndex: Int = newPair.v
+ mst[pointIndex] = true
+ for (i in parent.indices) {
+ val d = getDistance(points[pointIndex], points[i])
+ if (!mst[i] && d < dist[i]) {
+ dist[i] = d
+ pq.add(Pair(dist[i], i))
+ parent[i] = pointIndex
+ }
+ }
+ constructMST(parent, points, mst, pq, dist)
+ }
+
+ private fun containsFalse(mst: BooleanArray): Boolean {
+ for (b in mst) {
+ if (!b) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ private fun getDistance(p1: IntArray, p2: IntArray): Int {
+ return Math.abs(p1[0] - p2[0]) + Math.abs(p1[1] - p2[1])
+ }
+
+ class Pair : Comparator {
+ var dis = 0
+ var v = 0
+
+ constructor()
+ constructor(dis: Int, v: Int) {
+ this.dis = dis
+ this.v = v
+ }
+
+ override fun compare(p1: Pair, p2: Pair): Int {
+ return p1.dis - p2.dis
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1585_check_if_string_is_transformable_with_substring_sort_operations/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1585_check_if_string_is_transformable_with_substring_sort_operations/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f72043b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1585_check_if_string_is_transformable_with_substring_sort_operations/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1585\. Check If String Is Transformable With Substring Sort Operations
+
+Hard
+
+Given two strings `s` and `t`, transform string `s` into string `t` using the following operation any number of times:
+
+* Choose a **non-empty** substring in `s` and sort it in place so the characters are in **ascending order**.
+ * For example, applying the operation on the underlined substring in `"14234"` results in `"12344"`.
+
+Return `true` if _it is possible to transform `s` into `t`_. Otherwise, return `false`.
+
+A **substring** is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "84532", t = "34852"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** You can transform s into t using the following sort operations: "84532" (from index 2 to 3) -> "84352" "84352" (from index 0 to 2) -> "34852"
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "34521", t = "23415"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** You can transform s into t using the following sort operations: "34521" -> "23451" "23451" -> "23415"
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "12345", t = "12435"
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `s.length == t.length`
+* 1 <= s.length <= 105
+* `s` and `t` consist of only digits.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun isTransformable(s: String, t: String): Boolean {
+ val n = s.length
+ if (n != t.length) {
+ return false
+ }
+ val cnt = IntArray(10)
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ cnt[s[i].code - '0'.code]++
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ cnt[t[i].code - '0'.code]--
+ }
+ for (i in 0..9) {
+ if (cnt[i] != 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ val sCnt = IntArray(10)
+ val tCnt = IntArray(10)
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ val sAsci = s[i].code - '0'.code
+ val tAsci = t[i].code - '0'.code
+ sCnt[sAsci]++
+ if (tCnt[sAsci] >= sCnt[sAsci] || sAsci == tAsci && tCnt[sAsci] + 1 >= sCnt[sAsci]) {
+ var rem = 0
+ for (j in 0 until sAsci) {
+ if (sCnt[j] - tCnt[j] > 0) {
+ rem++
+ }
+ }
+ if (rem > 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ if (sCnt[tAsci] >= tCnt[tAsci] + 1) {
+ var rem = 0
+ for (j in tAsci..9) {
+ if (tCnt[j] - sCnt[j] > 0) {
+ rem++
+ }
+ }
+ if (rem > 0) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ tCnt[tAsci]++
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1587_bank_account_summary_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1587_bank_account_summary_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0da18be5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1587_bank_account_summary_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1587\. Bank Account Summary II
+
+Easy
+
+SQL Schema
+
+Table: `Users`
+
+ +--------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +--------------+---------+
+ | account | int |
+ | name | varchar |
+ +--------------+---------+
+ account is the primary key for this table.
+ Each row of this table contains the account number of each user in the bank.
+
+Table: `Transactions`
+
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | Column Name | Type |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ | trans_id | int |
+ | account | int |
+ | amount | int |
+ | transacted_on | date |
+ +---------------+---------+
+ trans_id is the primary key for this table.
+ Each row of this table contains all changes made to all accounts.
+ amount is positive if the user received money and negative if they transferred money.
+ All accounts start with a balance of 0.
+
+Write an SQL query to report the name and balance of users with a balance higher than `10000`. The balance of an account is equal to the sum of the amounts of all transactions involving that account.
+
+Return the result table in **any order**.
+
+The query result format is in the following example.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+ Users table:
+ +------------+--------------+
+ | account | name |
+ +------------+--------------+
+ | 900001 | Alice |
+ | 900002 | Bob |
+ | 900003 | Charlie |
+ +------------+--------------+
+ Transactions table:
+ +------------+------------+------------+---------------+
+ | trans_id | account | amount | transacted_on |
+ +------------+------------+------------+---------------+
+ | 1 | 900001 | 7000 | 2020-08-01 |
+ | 2 | 900001 | 7000 | 2020-09-01 |
+ | 3 | 900001 | -3000 | 2020-09-02 |
+ | 4 | 900002 | 1000 | 2020-09-12 |
+ | 5 | 900003 | 6000 | 2020-08-07 |
+ | 6 | 900003 | 6000 | 2020-09-07 |
+ | 7 | 900003 | -4000 | 2020-09-11 |
+ +------------+------------+------------+---------------+
+
+**Output:**
+
+ +------------+------------+
+ | name | balance |
+ +------------+------------+
+ | Alice | 11000 |
+ +------------+------------+
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Alice's balance is (7000 + 7000 - 3000) = 11000.
+
+Bob's balance is 1000.
+
+Charlie's balance is (6000 + 6000 - 4000) = 8000.
+
+## Solution
+
+```sql
+# Write your MySQL query statement below
+select u.name, sum(t.amount) as balance from Users as u join Transactions as t on u.account = t.account group by u.name having balance > 10000
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1588_sum_of_all_odd_length_subarrays/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1588_sum_of_all_odd_length_subarrays/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0e0b365e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1588_sum_of_all_odd_length_subarrays/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1588\. Sum of All Odd Length Subarrays
+
+Easy
+
+Given an array of positive integers `arr`, calculate the sum of all possible odd-length subarrays.
+
+A subarray is a contiguous subsequence of the array.
+
+Return _the sum of all odd-length subarrays of _`arr`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,4,2,5,3]
+
+**Output:** 58
+
+**Explanation:** The odd-length subarrays of arr and their sums are:
+
+[1] = 1
+
+[4] = 4
+
+[2] = 2
+
+[5] = 5
+
+[3] = 3
+
+[1,4,2] = 7
+
+[4,2,5] = 11
+
+[2,5,3] = 10
+
+[1,4,2,5,3] = 15
+
+If we add all these together we get 1 + 4 + 2 + 5 + 3 + 7 + 11 + 10 + 15 = 58
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [1,2]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** There are only 2 subarrays of odd length, [1] and [2]. Their sum is 3.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** arr = [10,11,12]
+
+**Output:** 66
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= arr.length <= 100`
+* `1 <= arr[i] <= 1000`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun sumOddLengthSubarrays(arr: IntArray): Int {
+ val len = arr.size
+ var sum = 0
+ for (i in 0..len - 1) {
+ sum = sum + ((i + 1) * (len - i) + 1) / 2 * arr[i]
+ }
+ return sum
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1589_maximum_sum_obtained_of_any_permutation/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1589_maximum_sum_obtained_of_any_permutation/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..323625c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1589_maximum_sum_obtained_of_any_permutation/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1589\. Maximum Sum Obtained of Any Permutation
+
+Medium
+
+We have an array of integers, `nums`, and an array of `requests` where requests[i] = [starti, endi]. The ith request asks for the sum of nums[starti] + nums[starti + 1] + ... + nums[endi - 1] + nums[endi]. Both starti and endi are _0-indexed_.
+
+Return _the maximum total sum of all requests **among all permutations** of_ `nums`.
+
+Since the answer may be too large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4,5], requests = \[\[1,3],[0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 19
+
+**Explanation:** One permutation of nums is [2,1,3,4,5] with the following result:
+
+requests[0] -> nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] = 1 + 3 + 4 = 8
+
+requests[1] -> nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 1 = 3
+
+Total sum: 8 + 3 = 11.
+
+A permutation with a higher total sum is [3,5,4,2,1] with the following result:
+
+requests[0] -> nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] = 5 + 4 + 2 = 11
+
+requests[1] -> nums[0] + nums[1] = 3 + 5 = 8
+
+Total sum: 11 + 8 = 19, which is the best that you can do.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6], requests = \[\[0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 11
+
+**Explanation:** A permutation with the max total sum is [6,5,4,3,2,1] with request sums [11].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3,4,5,10], requests = \[\[0,2],[1,3],[1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 47
+
+**Explanation:** A permutation with the max total sum is [4,10,5,3,2,1] with request sums [19,18,10].
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == nums.length`
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* 0 <= nums[i] <= 105
+* 1 <= requests.length <= 105
+* `requests[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= starti <= endi < n
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxSumRangeQuery(nums: IntArray, requests: Array): Int {
+ nums.sort()
+ val l = nums.size
+ val tempArr = IntArray(l)
+ // requests[i][0] incrementing index element by 1 and for requests[i][1]+1 decrementing by 1
+ // this will help me get the freq of occurrence of each index of array 'nums' in
+ // all 'requests' intervals when I compute the sum array of tempArr.
+ for (request in requests) {
+ val a = request[0]
+ val b = request[1] + 1
+ tempArr[a]++
+ if (b < l) {
+ tempArr[b]--
+ }
+ }
+ var prev = 0
+ for (i in 0 until l) {
+ tempArr[i] += prev
+ prev = tempArr[i]
+ }
+ tempArr.sort()
+ var index = l - 1
+ var ans: Long = 0
+ while (index >= 0) {
+ if (tempArr[index] == 0) {
+ break
+ }
+ val x = (tempArr[index] % 1000000007).toLong()
+ val y = (nums[index] % 1000000007).toLong()
+ index--
+ ans += x * y
+ }
+ return (ans % 1000000007).toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1590_make_sum_divisible_by_p/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1590_make_sum_divisible_by_p/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..077efa0b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1590_make_sum_divisible_by_p/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1590\. Make Sum Divisible by P
+
+Medium
+
+Given an array of positive integers `nums`, remove the **smallest** subarray (possibly **empty**) such that the **sum** of the remaining elements is divisible by `p`. It is **not** allowed to remove the whole array.
+
+Return _the length of the smallest subarray that you need to remove, or_ `-1` _if it's impossible_.
+
+A **subarray** is defined as a contiguous block of elements in the array.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,1,4,2], p = 6
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** The sum of the elements in nums is 10, which is not divisible by 6. We can remove the subarray [4], and the sum of the remaining elements is 6, which is divisible by 6.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [6,3,5,2], p = 9
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** We cannot remove a single element to get a sum divisible by 9. The best way is to remove the subarray [5,2], leaving us with [6,3] with sum 9.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,3], p = 3
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Here the sum is 6. which is already divisible by 3. Thus we do not need to remove anything.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 109
+* 1 <= p <= 109
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minSubarray(nums: IntArray, p: Int): Int {
+ val hmp = HashMap()
+ val n = nums.size
+ var target = 0
+ var sum = 0
+ for (num in nums) {
+ target = (num + target) % p
+ }
+ if (target == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ hmp[0] = -1
+ var ans = n
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ sum = (sum + nums[i]) % p
+ val key = (sum - target + p) % p
+ if (hmp.containsKey(key)) {
+ ans = Math.min(ans, i - hmp[key]!!)
+ }
+ hmp[sum % p] = i
+ }
+ return if (ans < n) {
+ ans
+ } else {
+ -1
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1591_strange_printer_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1591_strange_printer_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1969a543
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1591_strange_printer_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1591\. Strange Printer II
+
+Hard
+
+There is a strange printer with the following two special requirements:
+
+* On each turn, the printer will print a solid rectangular pattern of a single color on the grid. This will cover up the existing colors in the rectangle.
+* Once the printer has used a color for the above operation, **the same color cannot be used again**.
+
+You are given a `m x n` matrix `targetGrid`, where `targetGrid[row][col]` is the color in the position `(row, col)` of the grid.
+
+Return `true` _if it is possible to print the matrix_ `targetGrid`_,_ _otherwise, return_ `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+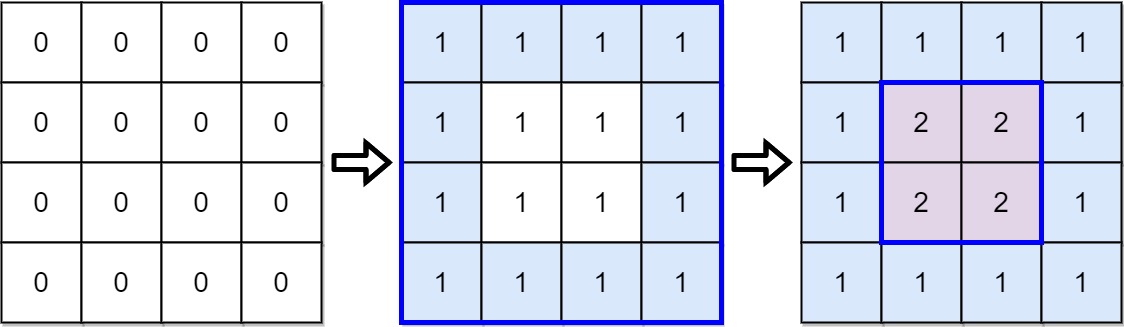
+
+**Input:** targetGrid = \[\[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,1],[1,2,2,1],[1,1,1,1]]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+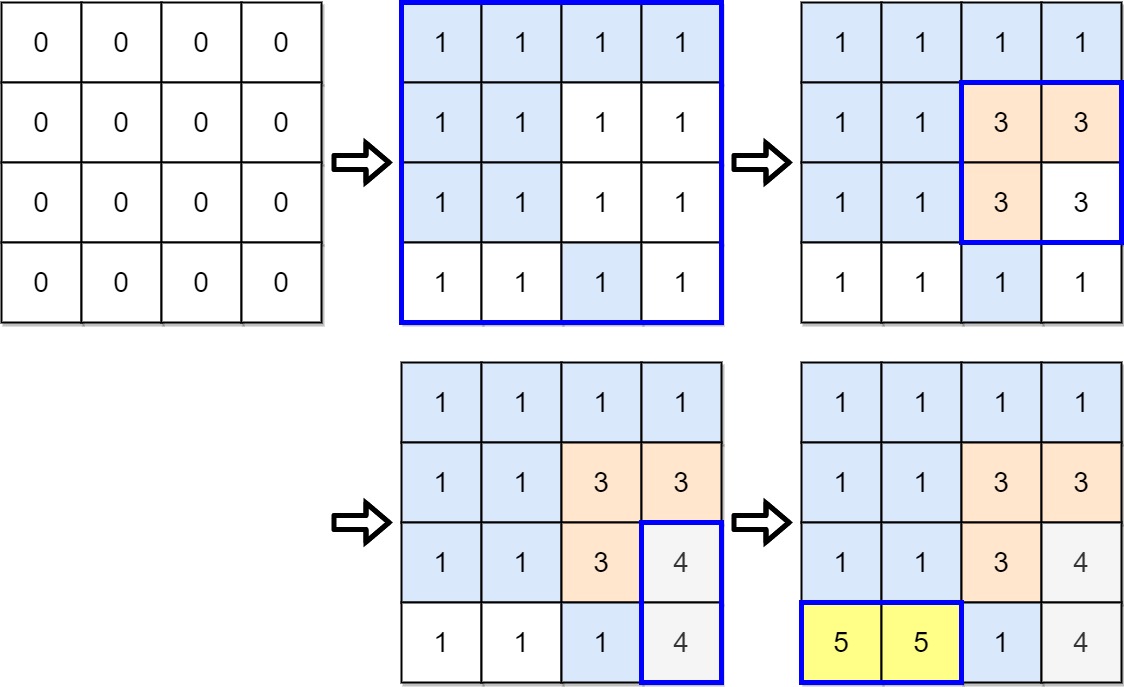
+
+**Input:** targetGrid = \[\[1,1,1,1],[1,1,3,3],[1,1,3,4],[5,5,1,4]]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** targetGrid = \[\[1,2,1],[2,1,2],[1,2,1]]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** It is impossible to form targetGrid because it is not allowed to print the same color in different turns.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == targetGrid.length`
+* `n == targetGrid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 60`
+* `1 <= targetGrid[row][col] <= 60`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun isPrintable(targetGrid: Array): Boolean {
+ val colorBound = Array(61) { IntArray(4) }
+ val colors: MutableSet = HashSet()
+ // prepare colorBound with Max and Min integer for later compare
+ for (i in colorBound.indices) {
+ for (j in colorBound[0].indices) {
+ if (j == 0 || j == 1) {
+ colorBound[i][j] = Int.MAX_VALUE
+ } else {
+ colorBound[i][j] = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // find the color range for each color
+ // each color i has a colorBound[i] with {min_i, min_j, max_i, max_j}
+ for (i in targetGrid.indices) {
+ for (j in targetGrid[0].indices) {
+ colorBound[targetGrid[i][j]][0] = Math.min(colorBound[targetGrid[i][j]][0], i)
+ colorBound[targetGrid[i][j]][1] = Math.min(colorBound[targetGrid[i][j]][1], j)
+ colorBound[targetGrid[i][j]][2] = Math.max(colorBound[targetGrid[i][j]][2], i)
+ colorBound[targetGrid[i][j]][3] = Math.max(colorBound[targetGrid[i][j]][3], j)
+ colors.add(targetGrid[i][j])
+ }
+ }
+ val printed = BooleanArray(61)
+ val visited = Array(targetGrid.size) { BooleanArray(targetGrid[0].size) }
+ // DFS all the colors, skip the color already be printed
+ for (color in colors) {
+ if (printed[color]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ if (!dfs(targetGrid, printed, colorBound, visited, color)) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ // if all color has been printed, then return true
+ return true
+ }
+
+ private fun dfs(
+ targetGrid: Array,
+ printed: BooleanArray,
+ colorBound: Array,
+ visited: Array,
+ color: Int
+ ): Boolean {
+ printed[color] = true
+ for (i in colorBound[color][0]..colorBound[color][2]) {
+ for (j in colorBound[color][1]..colorBound[color][3]) {
+ // if i, j is already visited, skip
+ if (visited[i][j]) {
+ continue
+ }
+ // if we find a different color, then check if the color is already printed, if so,
+ // return false
+ // otherwise, dfs the range of the new color
+ if (targetGrid[i][j] != color) {
+ if (printed[targetGrid[i][j]]) {
+ return false
+ }
+ if (!dfs(targetGrid, printed, colorBound, visited, targetGrid[i][j])) {
+ return false
+ }
+ }
+ visited[i][j] = true
+ }
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1592_rearrange_spaces_between_words/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1592_rearrange_spaces_between_words/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..55ef6a0d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1592_rearrange_spaces_between_words/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1592\. Rearrange Spaces Between Words
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `text` of words that are placed among some number of spaces. Each word consists of one or more lowercase English letters and are separated by at least one space. It's guaranteed that `text` **contains at least one word**.
+
+Rearrange the spaces so that there is an **equal** number of spaces between every pair of adjacent words and that number is **maximized**. If you cannot redistribute all the spaces equally, place the **extra spaces at the end**, meaning the returned string should be the same length as `text`.
+
+Return _the string after rearranging the spaces_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** text = " this is a sentence "
+
+**Output:** "this is a sentence"
+
+**Explanation:** There are a total of 9 spaces and 4 words. We can evenly divide the 9 spaces between the words: 9 / (4-1) = 3 spaces.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** text = " practice makes perfect"
+
+**Output:** "practice makes perfect "
+
+**Explanation:** There are a total of 7 spaces and 3 words. 7 / (3-1) = 3 spaces plus 1 extra space. We place this extra space at the end of the string.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= text.length <= 100`
+* `text` consists of lowercase English letters and `' '`.
+* `text` contains at least one word.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun reorderSpaces(text: String): String {
+ var spaceCount = 0
+ for (c in text.toCharArray()) {
+ if (c == ' ') {
+ spaceCount++
+ }
+ }
+ val words = text.trim { it <= ' ' }.split("\\s+".toRegex()).dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()
+ if (words.size == 1) {
+ val sb = StringBuilder(words[0])
+ for (i in 0 until spaceCount) {
+ sb.append(" ")
+ }
+ return sb.toString()
+ }
+ val trailingSpaces = spaceCount % (words.size - 1)
+ val newSpaces = spaceCount / (words.size - 1)
+ val sb = StringBuilder()
+ for (j in words.indices) {
+ sb.append(words[j])
+ if (j < words.size - 1) {
+ for (i in 0 until newSpaces) {
+ sb.append(" ")
+ }
+ } else {
+ for (i in 0 until trailingSpaces) {
+ sb.append(" ")
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return sb.toString()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1593_split_a_string_into_the_max_number_of_unique_substrings/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1593_split_a_string_into_the_max_number_of_unique_substrings/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5527a46d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1593_split_a_string_into_the_max_number_of_unique_substrings/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1593\. Split a String Into the Max Number of Unique Substrings
+
+Medium
+
+Given a string `s`, return _the maximum number of unique substrings that the given string can be split into_.
+
+You can split string `s` into any list of **non-empty substrings**, where the concatenation of the substrings forms the original string. However, you must split the substrings such that all of them are **unique**.
+
+A **substring** is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "ababccc"
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:** One way to split maximally is ['a', 'b', 'ab', 'c', 'cc']. Splitting like ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'cc'] is not valid as you have 'a' and 'b' multiple times.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aba"
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** One way to split maximally is ['a', 'ba'].
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aa"
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:** It is impossible to split the string any further.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 16`
+
+* `s` contains only lower case English letters.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun maxUniqueSplit(s: String): Int {
+ var lo = 1
+ var hi = s.length
+ // binary search
+ while (lo < hi) {
+ val mid = lo + hi + 1 shr 1
+ if (ok(0, mid, 0, s, HashSet())) {
+ lo = mid
+ } else {
+ hi = mid - 1
+ }
+ }
+ return lo
+ }
+
+ private fun ok(depth: Int, end: Int, curLen: Int, s: String, seen: MutableSet): Boolean {
+ if (depth == end) {
+ return true
+ }
+ for (j in curLen until s.length) {
+ // not enough length remains to reach the end.
+ if (s.length - j < end - depth) {
+ break
+ }
+ val cur = s.substring(curLen, j + 1)
+ if (seen.add(cur)) {
+ if (ok(depth + 1, end, j + 1, s, seen)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ seen.remove(cur)
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1594_maximum_non_negative_product_in_a_matrix/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1594_maximum_non_negative_product_in_a_matrix/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..eb99e7e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1594_maximum_non_negative_product_in_a_matrix/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1594\. Maximum Non Negative Product in a Matrix
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a `m x n` matrix `grid`. Initially, you are located at the top-left corner `(0, 0)`, and in each step, you can only **move right or down** in the matrix.
+
+Among all possible paths starting from the top-left corner `(0, 0)` and ending in the bottom-right corner `(m - 1, n - 1)`, find the path with the **maximum non-negative product**. The product of a path is the product of all integers in the grid cells visited along the path.
+
+Return the _maximum non-negative product **modulo**_ 109 + 7. _If the maximum product is **negative**, return_ `-1`.
+
+Notice that the modulo is performed after getting the maximum product.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[-1,-2,-3],[-2,-3,-3],[-3,-3,-2]]
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** It is not possible to get non-negative product in the path from (0, 0) to (2, 2), so return -1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,-2,1],[1,-2,1],[3,-4,1]]
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:** Maximum non-negative product is shown (1 \* 1 \* -2 \* -4 \* 1 = 8).
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+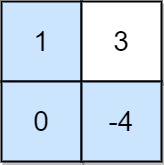
+
+**Input:** grid = \[\[1,3],[0,-4]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:** Maximum non-negative product is shown (1 \* 0 \* -4 = 0).
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 15`
+* `-4 <= grid[i][j] <= 4`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private class Tuple(var max: Long, var min: Long)
+
+ fun maxProductPath(grid: Array?): Int {
+ // DP
+ if (grid == null || grid.size == 0 || grid[0] == null || grid[0]!!.size == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val rows = grid.size
+ val cols = grid[0]!!.size
+ val dp = Array(rows) { arrayOfNulls(cols) }
+ for (i in 0 until rows) {
+ for (j in 0 until cols) {
+ dp[i][j] = Tuple(1, 1)
+ }
+ }
+ // Init first row and column
+ dp[0][0]!!.max = grid[0]!![0].toLong()
+ dp[0][0]!!.min = grid[0]!![0].toLong()
+ for (i in 1 until rows) {
+ dp[i][0]!!.max = grid[i]!![0] * dp[i - 1][0]!!.max
+ dp[i][0]!!.min = grid[i]!![0] * dp[i - 1][0]!!.min
+ }
+ for (i in 1 until cols) {
+ dp[0][i]!!.max = grid[0]!![i] * dp[0][i - 1]!!.max
+ dp[0][i]!!.min = grid[0]!![i] * dp[0][i - 1]!!.min
+ }
+ // DP
+ for (i in 1 until rows) {
+ for (j in 1 until cols) {
+ val up1 = dp[i - 1][j]!!.max * grid[i]!![j]
+ val up2 = dp[i - 1][j]!!.min * grid[i]!![j]
+ val left1 = dp[i][j - 1]!!.max * grid[i]!![j]
+ val left2 = dp[i][j - 1]!!.min * grid[i]!![j]
+ dp[i][j]!!.max = Math.max(up1, Math.max(up2, Math.max(left1, left2)))
+ dp[i][j]!!.min = Math.min(up1, Math.min(up2, Math.min(left1, left2)))
+ }
+ }
+ return if (dp[rows - 1][cols - 1]!!.max < 0) {
+ -1
+ } else (dp[rows - 1][cols - 1]!!.max % (1e9 + 7)).toInt()
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1595_minimum_cost_to_connect_two_groups_of_points/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1595_minimum_cost_to_connect_two_groups_of_points/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ec5e095c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1595_minimum_cost_to_connect_two_groups_of_points/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1595\. Minimum Cost to Connect Two Groups of Points
+
+Hard
+
+You are given two groups of points where the first group has size1 points, the second group has size2 points, and size1 >= size2.
+
+The `cost` of the connection between any two points are given in an size1 x size2 matrix where `cost[i][j]` is the cost of connecting point `i` of the first group and point `j` of the second group. The groups are connected if **each point in both groups is connected to one or more points in the opposite group**. In other words, each point in the first group must be connected to at least one point in the second group, and each point in the second group must be connected to at least one point in the first group.
+
+Return _the minimum cost it takes to connect the two groups_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** cost = \[\[15, 96], [36, 2]]
+
+**Output:** 17
+
+**Explanation:** The optimal way of connecting the groups is:
+
+1--A
+
+2--B
+
+This results in a total cost of 17.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** cost = \[\[1, 3, 5], [4, 1, 1], [1, 5, 3]]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:** The optimal way of connecting the groups is:
+
+1--A
+
+2--B
+
+2--C
+
+3--A
+
+This results in a total cost of 4.
+
+Note that there are multiple points connected to point 2 in the first group and point A in the second group.
+
+This does not matter as there is no limit to the number of points that can be connected. We only care about the minimum total cost.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** cost = \[\[2, 5, 1], [3, 4, 7], [8, 1, 2], [6, 2, 4], [3, 8, 8]]
+
+**Output:** 10
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* size1 == cost.length
+* size2 == cost[i].length
+* 1 <= size1, size2 <= 12
+* size1 >= size2
+* `0 <= cost[i][j] <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun connectTwoGroups(cost: List>): Int {
+ // size of set 1
+ val m = cost.size
+ // size of set 2
+ val n = cost[0].size
+ val mask = 1 shl m
+ // min cost to connect nodes in set 1 (of different states);
+ var record = IntArray(mask)
+ record.fill(Int.MAX_VALUE)
+ // since we use record to get the min cost of connecting nodes in set 1
+ // we shall go through nodes in set 2 one by one, to make sure they are connected
+ // base case:
+ record[0] = 0
+ for (col in 0 until n) {
+ val tmpRecord = IntArray(mask)
+ tmpRecord.fill(Int.MAX_VALUE)
+ // try connection with each of the node in set 1
+ for (row in 0 until m) {
+ for (msk in 0 until mask) {
+ // the new min cost should be based on the cost record of connecting previous
+ // node in set 2;
+ val newMask = msk or (1 shl row)
+ if (record[msk] != Int.MAX_VALUE) {
+ tmpRecord[newMask] = Math.min(tmpRecord[newMask], record[msk] + cost[row][col])
+ }
+ // if row nodes in this state has not been connected yet, and the msk is
+ // achievable by connecting the current node
+ // then check whether connect the current node multiple times will benefit the
+ // cost
+ if (msk and (1 shl row) == 0 && tmpRecord[msk] != Int.MAX_VALUE) {
+ tmpRecord[newMask] = Math.min(
+ tmpRecord[newMask],
+ tmpRecord[msk] + cost[row][col]
+ )
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // use tmpRecord to update record
+ record = tmpRecord
+ }
+ return record[(1 shl m) - 1]
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1598_crawler_log_folder/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1598_crawler_log_folder/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b9dd136a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1598_crawler_log_folder/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1598\. Crawler Log Folder
+
+Easy
+
+The Leetcode file system keeps a log each time some user performs a _change folder_ operation.
+
+The operations are described below:
+
+* `"../"` : Move to the parent folder of the current folder. (If you are already in the main folder, **remain in the same folder**).
+* `"./"` : Remain in the same folder.
+* `"x/"` : Move to the child folder named `x` (This folder is **guaranteed to always exist**).
+
+You are given a list of strings `logs` where `logs[i]` is the operation performed by the user at the ith step.
+
+The file system starts in the main folder, then the operations in `logs` are performed.
+
+Return _the minimum number of operations needed to go back to the main folder after the change folder operations._
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** logs = ["d1/","d2/","../","d21/","./"]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:** Use this change folder operation "../" 2 times and go back to the main folder.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+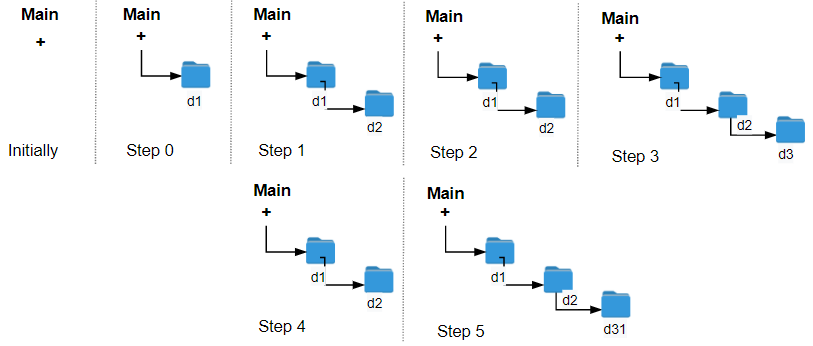
+
+**Input:** logs = ["d1/","d2/","./","d3/","../","d31/"]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** logs = ["d1/","../","../","../"]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= logs.length <= 103
+* `2 <= logs[i].length <= 10`
+* `logs[i]` contains lowercase English letters, digits, `'.'`, and `'/'`.
+* `logs[i]` follows the format described in the statement.
+* Folder names consist of lowercase English letters and digits.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(logs: Array): Int {
+ var steps = 0
+ for (log in logs) {
+ if (log == "../") {
+ if (steps > 0) {
+ steps--
+ }
+ } else if (log != "./") {
+ steps++
+ }
+ }
+ return steps
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1599_maximum_profit_of_operating_a_centennial_wheel/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1599_maximum_profit_of_operating_a_centennial_wheel/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..53d2f2c6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1599_maximum_profit_of_operating_a_centennial_wheel/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1599\. Maximum Profit of Operating a Centennial Wheel
+
+Medium
+
+You are the operator of a Centennial Wheel that has **four gondolas**, and each gondola has room for **up** **to** **four people**. You have the ability to rotate the gondolas **counterclockwise**, which costs you `runningCost` dollars.
+
+You are given an array `customers` of length `n` where `customers[i]` is the number of new customers arriving just before the ith rotation (0-indexed). This means you **must rotate the wheel** `i` **times before the** `customers[i]` **customers arrive**. **You cannot make customers wait if there is room in the gondola**. Each customer pays `boardingCost` dollars when they board on the gondola closest to the ground and will exit once that gondola reaches the ground again.
+
+You can stop the wheel at any time, including **before** **serving** **all** **customers**. If you decide to stop serving customers, **all subsequent rotations are free** in order to get all the customers down safely. Note that if there are currently more than four customers waiting at the wheel, only four will board the gondola, and the rest will wait **for the next rotation**.
+
+Return _the minimum number of rotations you need to perform to maximize your profit._ If there is **no scenario** where the profit is positive, return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+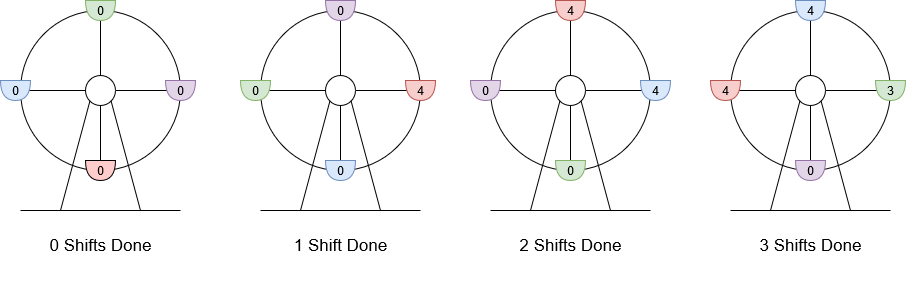
+
+**Input:** customers = [8,3], boardingCost = 5, runningCost = 6
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:** The numbers written on the gondolas are the number of people currently there.
+
+1. 8 customers arrive, 4 board and 4 wait for the next gondola, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 4 \* $5 - 1 \* $6 = $14.
+
+2. 3 customers arrive, the 4 waiting board the wheel and the other 3 wait, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 8 \* $5 - 2 \* $6 = $28.
+
+3. The final 3 customers board the gondola, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 11 \* $5 - 3 \* $6 = $37. The highest profit was $37 after rotating the wheel 3 times.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** customers = [10,9,6], boardingCost = 6, runningCost = 4
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+1. 10 customers arrive, 4 board and 6 wait for the next gondola, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 4 \* $6 - 1 \* $4 = $20.
+
+2. 9 customers arrive, 4 board and 11 wait (2 originally waiting, 9 newly waiting), the wheel rotates. Current profit is 8 \* $6 - 2 \* $4 = $40.
+
+3. The final 6 customers arrive, 4 board and 13 wait, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 12 \* $6 - 3 \* $4 = $60.
+
+4. 4 board and 9 wait, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 16 \* $6 - 4 \* $4 = $80.
+
+5. 4 board and 5 wait, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 20 \* $6 - 5 \* $4 = $100.
+
+6. 4 board and 1 waits, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 24 \* $6 - 6 \* $4 = $120.
+
+7. 1 boards, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 25 \* $6 - 7 \* $4 = $122.
+
+The highest profit was $122 after rotating the wheel 7 times.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** customers = [3,4,0,5,1], boardingCost = 1, runningCost = 92
+
+**Output:** -1
+
+**Explanation:** 1. 3 customers arrive, 3 board and 0 wait, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 3 \* $1 - 1 \* $92 = -$89. 2. 4 customers arrive, 4 board and 0 wait, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 7 \* $1 - 2 \* $92 = -$177. 3. 0 customers arrive, 0 board and 0 wait, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 7 \* $1 - 3 \* $92 = -$269. 4. 5 customers arrive, 4 board and 1 waits, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 11 \* $1 - 4 \* $92 = -$357. 5. 1 customer arrives, 2 board and 0 wait, the wheel rotates. Current profit is 13 \* $1 - 5 \* $92 = -$447. The profit was never positive, so return -1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == customers.length`
+* 1 <= n <= 105
+* `0 <= customers[i] <= 50`
+* `1 <= boardingCost, runningCost <= 100`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperationsMaxProfit(customers: IntArray, boardingCost: Int, runningCost: Int): Int {
+ if (runningCost >= 4 * boardingCost) return -1
+ var maxProfit = 0
+ var currentProfit = 0
+ var queue = 0
+ var rotation = 0
+ for (i in customers.indices) {
+ queue += customers[i]
+ val current = Math.min(queue, 4)
+ queue -= current
+ currentProfit += current * boardingCost - runningCost
+ if (currentProfit > maxProfit) {
+ maxProfit = currentProfit
+ rotation = i + 1
+ }
+ }
+ val mod = queue / 4
+ if (mod > 0) {
+ currentProfit += mod * (4 * boardingCost - runningCost)
+ if (currentProfit > maxProfit) {
+ maxProfit = currentProfit
+ rotation = customers.size + mod
+ }
+ }
+ val div = queue % 4
+ if (div > 0) {
+ currentProfit += div * boardingCost - runningCost
+ if (currentProfit > maxProfit) {
+ maxProfit = currentProfit
+ rotation = customers.size + mod + 1
+ }
+ }
+ return if (maxProfit > 0) rotation else -1
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1600_throne_inheritance/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1600_throne_inheritance/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..45f80ef6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1501_1600/s1600_throne_inheritance/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1600\. Throne Inheritance
+
+Medium
+
+A kingdom consists of a king, his children, his grandchildren, and so on. Every once in a while, someone in the family dies or a child is born.
+
+The kingdom has a well-defined order of inheritance that consists of the king as the first member. Let's define the recursive function `Successor(x, curOrder)`, which given a person `x` and the inheritance order so far, returns who should be the next person after `x` in the order of inheritance.
+
+Successor(x, curOrder): if x has no children or all of x's children are in curOrder: if x is the king return null else return Successor(x's parent, curOrder) else return x's oldest child who's not in curOrder
+
+For example, assume we have a kingdom that consists of the king, his children Alice and Bob (Alice is older than Bob), and finally Alice's son Jack.
+
+1. In the beginning, `curOrder` will be `["king"]`.
+2. Calling `Successor(king, curOrder)` will return Alice, so we append to `curOrder` to get `["king", "Alice"]`.
+3. Calling `Successor(Alice, curOrder)` will return Jack, so we append to `curOrder` to get `["king", "Alice", "Jack"]`.
+4. Calling `Successor(Jack, curOrder)` will return Bob, so we append to `curOrder` to get `["king", "Alice", "Jack", "Bob"]`.
+5. Calling `Successor(Bob, curOrder)` will return `null`. Thus the order of inheritance will be `["king", "Alice", "Jack", "Bob"]`.
+
+Using the above function, we can always obtain a unique order of inheritance.
+
+Implement the `ThroneInheritance` class:
+
+* `ThroneInheritance(string kingName)` Initializes an object of the `ThroneInheritance` class. The name of the king is given as part of the constructor.
+* `void birth(string parentName, string childName)` Indicates that `parentName` gave birth to `childName`.
+* `void death(string name)` Indicates the death of `name`. The death of the person doesn't affect the `Successor` function nor the current inheritance order. You can treat it as just marking the person as dead.
+* `string[] getInheritanceOrder()` Returns a list representing the current order of inheritance **excluding** dead people.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input**
+
+["ThroneInheritance", "birth", "birth", "birth", "birth", "birth", "birth", "getInheritanceOrder", "death", "getInheritanceOrder"]
+
+[["king"], ["king", "andy"], ["king", "bob"], ["king", "catherine"], ["andy", "matthew"], ["bob", "alex"], ["bob", "asha"], [null], ["bob"], [null]]
+
+**Output:** [null, null, null, null, null, null, null, ["king", "andy", "matthew", "bob", "alex", "asha", "catherine"], null, ["king", "andy", "matthew", "alex", "asha", "catherine"]]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ThroneInheritance t= new ThroneInheritance("king"); // order: **king**
+
+t.birth("king", "andy"); // order: king > **andy**
+
+t.birth("king", "bob"); // order: king > andy > **bob**
+
+t.birth("king", "catherine"); // order: king > andy > bob > **catherine**
+
+t.birth("andy", "matthew"); // order: king > andy > **matthew** > bob > catherine
+
+t.birth("bob", "alex"); // order: king > andy > matthew > bob > **alex** > catherine
+
+t.birth("bob", "asha"); // order: king > andy > matthew > bob > alex > **asha** > catherine
+
+t.getInheritanceOrder(); // return ["king", "andy", "matthew", "bob", "alex", "asha", "catherine"]
+
+t.death("bob"); // order: king > andy > matthew > **bob** > alex > asha > catherine t.getInheritanceOrder(); // return ["king", "andy", "matthew", "alex", "asha", "catherine"]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= kingName.length, parentName.length, childName.length, name.length <= 15`
+* `kingName`, `parentName`, `childName`, and `name` consist of lowercase English letters only.
+* All arguments `childName` and `kingName` are **distinct**.
+* All `name` arguments of `death` will be passed to either the constructor or as `childName` to `birth` first.
+* For each call to `birth(parentName, childName)`, it is guaranteed that `parentName` is alive.
+* At most 105 calls will be made to `birth` and `death`.
+* At most `10` calls will be made to `getInheritanceOrder`.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class ThroneInheritance(private val king: String) {
+ private val graph: HashMap>
+ private val isDead: HashSet
+
+ init {
+ graph = HashMap()
+ isDead = HashSet()
+ graph[king] = LinkedHashSet()
+ }
+
+ fun birth(parentName: String, childName: String) {
+ graph.putIfAbsent(parentName, LinkedHashSet())
+ graph[parentName]!!.add(childName)
+ }
+
+ fun death(name: String) {
+ isDead.add(name)
+ }
+
+ fun getInheritanceOrder(): List {
+ val inheritance: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val visited = HashSet()
+ dfs(graph, king, inheritance, visited)
+ return inheritance
+ }
+
+ fun dfs(
+ graph: Map>,
+ src: String,
+ l: MutableList,
+ visited: MutableSet
+ ) {
+ visited.add(src)
+ if (!isDead.contains(src)) {
+ l.add(src)
+ }
+ if (!graph.containsKey(src)) {
+ return
+ }
+ for (s in graph[src]!!) {
+ if (!visited.contains(s)) {
+ dfs(graph, s, l, visited)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+/*
+ * Your ThroneInheritance object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * var obj = ThroneInheritance(kingName)
+ * obj.birth(parentName,childName)
+ * obj.death(name)
+ * var param_3 = obj.getInheritanceOrder()
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1601_maximum_number_of_achievable_transfer_requests/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1601_maximum_number_of_achievable_transfer_requests/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a5bde41e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1601_maximum_number_of_achievable_transfer_requests/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1601\. Maximum Number of Achievable Transfer Requests
+
+Hard
+
+We have `n` buildings numbered from `0` to `n - 1`. Each building has a number of employees. It's transfer season, and some employees want to change the building they reside in.
+
+You are given an array `requests` where requests[i] = [fromi, toi] represents an employee's request to transfer from building fromi to building toi.
+
+**All buildings are full**, so a list of requests is achievable only if for each building, the **net change in employee transfers is zero**. This means the number of employees **leaving** is **equal** to the number of employees **moving in**. For example if `n = 3` and two employees are leaving building `0`, one is leaving building `1`, and one is leaving building `2`, there should be two employees moving to building `0`, one employee moving to building `1`, and one employee moving to building `2`.
+
+Return _the maximum number of achievable requests_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+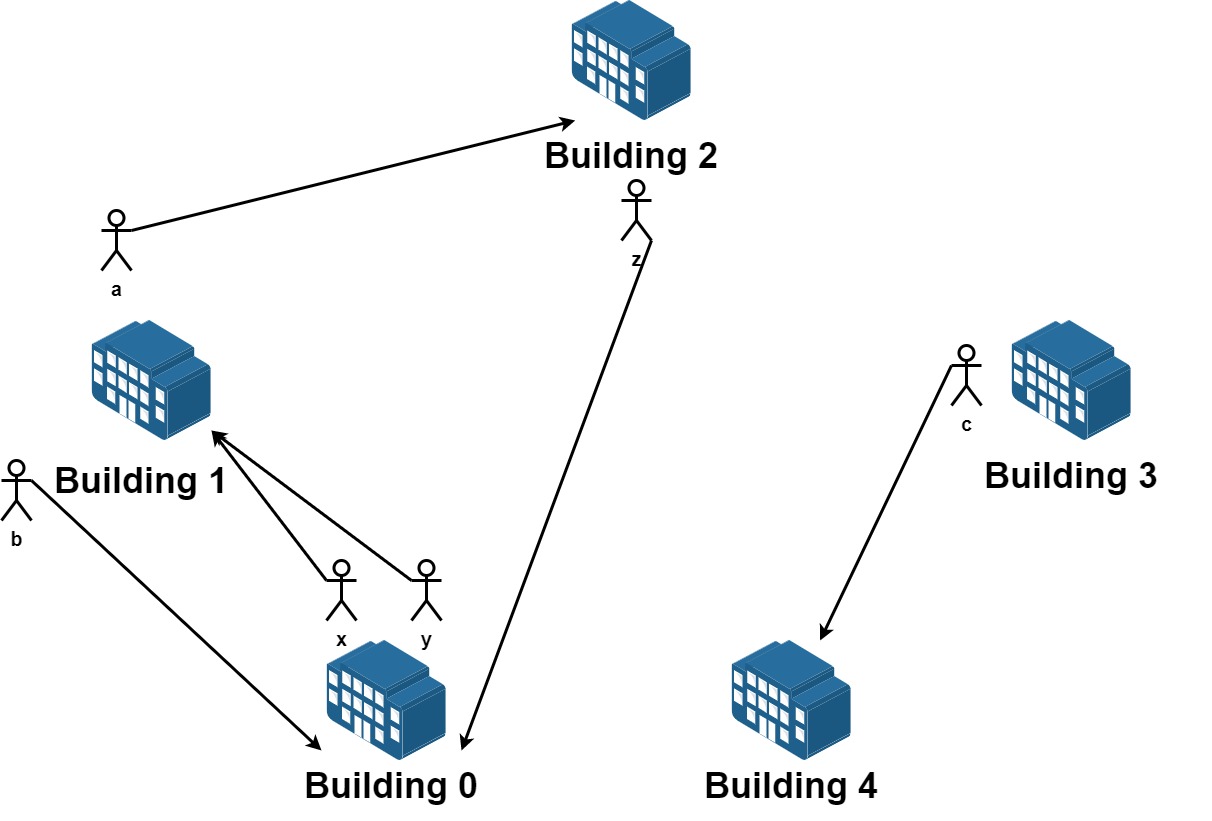
+
+**Input:** n = 5, requests = \[\[0,1],[1,0],[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[3,4]]
+
+**Output:** 5 **Explantion:** Let's see the requests:
+
+From building 0 we have employees x and y and both want to move to building 1.
+
+From building 1 we have employees a and b and they want to move to buildings 2 and 0 respectively.
+
+From building 2 we have employee z and they want to move to building 0.
+
+From building 3 we have employee c and they want to move to building 4.
+
+From building 4 we don't have any requests.
+
+We can achieve the requests of users x and b by swapping their places.
+
+We can achieve the requests of users y, a and z by swapping the places in the 3 buildings.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+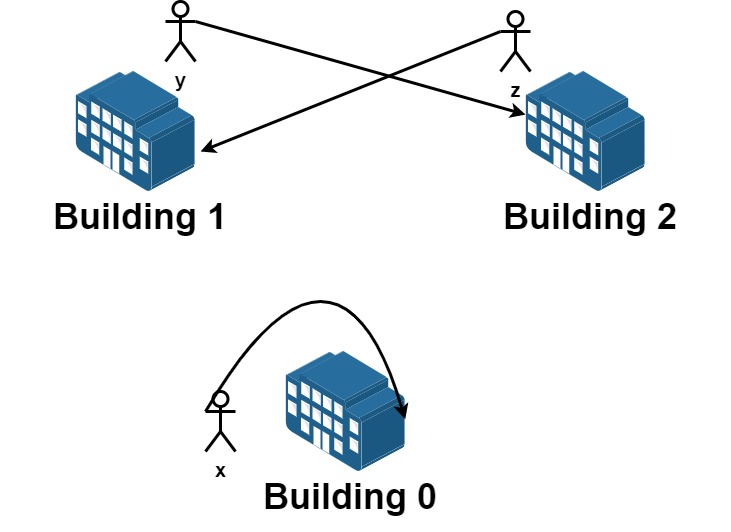
+
+**Input:** n = 3, requests = \[\[0,0],[1,2],[2,1]]
+
+**Output:** 3 **Explantion:** Let's see the requests:
+
+From building 0 we have employee x and they want to stay in the same building 0.
+
+From building 1 we have employee y and they want to move to building 2.
+
+From building 2 we have employee z and they want to move to building 1.
+
+We can achieve all the requests.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, requests = \[\[0,3],[3,1],[1,2],[2,0]]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 20`
+* `1 <= requests.length <= 16`
+* `requests[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= fromi, toi < n
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ private var max = 0
+
+ fun maximumRequests(n: Int, requests: Array): Int {
+ helper(requests, 0, IntArray(n), 0)
+ return max
+ }
+
+ private fun helper(requests: Array, index: Int, count: IntArray, num: Int) {
+ if (index == requests.size) {
+ for (i in count) {
+ if (0 != i) {
+ return
+ }
+ }
+ max = Math.max(max, num)
+ return
+ }
+ count[requests[index][0]]++
+ count[requests[index][1]]--
+ helper(requests, index + 1, count, num + 1)
+ count[requests[index][0]]--
+ count[requests[index][1]]++
+ helper(requests, index + 1, count, num)
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1603_design_parking_system/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1603_design_parking_system/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7416b337
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1603_design_parking_system/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1603\. Design Parking System
+
+Easy
+
+Design a parking system for a parking lot. The parking lot has three kinds of parking spaces: big, medium, and small, with a fixed number of slots for each size.
+
+Implement the `ParkingSystem` class:
+
+* `ParkingSystem(int big, int medium, int small)` Initializes object of the `ParkingSystem` class. The number of slots for each parking space are given as part of the constructor.
+* `bool addCar(int carType)` Checks whether there is a parking space of `carType` for the car that wants to get into the parking lot. `carType` can be of three kinds: big, medium, or small, which are represented by `1`, `2`, and `3` respectively. **A car can only park in a parking space of its** `carType`. If there is no space available, return `false`, else park the car in that size space and return `true`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input** ["ParkingSystem", "addCar", "addCar", "addCar", "addCar"] [[1, 1, 0], [1], [2], [3], [1]]
+
+**Output:** [null, true, true, false, false]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+ParkingSystem parkingSystem = new ParkingSystem(1, 1, 0);
+
+parkingSystem.addCar(1); // return true because there is 1 available slot for a big car
+
+parkingSystem.addCar(2); // return true because there is 1 available slot for a medium car
+
+parkingSystem.addCar(3); // return false because there is no available slot for a small car
+
+parkingSystem.addCar(1); // return false because there is no available slot for a big car. It is already occupied.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= big, medium, small <= 1000`
+* `carType` is `1`, `2`, or `3`
+* At most `1000` calls will be made to `addCar`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class ParkingSystem(big: Int, medium: Int, small: Int) {
+ private val slots = IntArray(3)
+
+ init {
+ slots[0] = big
+ slots[1] = medium
+ slots[2] = small
+ }
+
+ fun addCar(carType: Int): Boolean {
+ return if (carType == 1) {
+ if (slots[0] > 0) {
+ slots[0]--
+ true
+ } else {
+ false
+ }
+ } else if (carType == 2) {
+ if (slots[1] > 0) {
+ slots[1]--
+ true
+ } else {
+ false
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (slots[2] > 0) {
+ slots[2]--
+ true
+ } else {
+ false
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+/*
+ * Your ParkingSystem object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * var obj = ParkingSystem(big, medium, small)
+ * var param_1 = obj.addCar(carType)
+ */
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1604_alert_using_same_key_card_three_or_more_times_in_a_one_hour_period/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1604_alert_using_same_key_card_three_or_more_times_in_a_one_hour_period/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2be5c1d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1604_alert_using_same_key_card_three_or_more_times_in_a_one_hour_period/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1604\. Alert Using Same Key-Card Three or More Times in a One Hour Period
+
+Medium
+
+LeetCode company workers use key-cards to unlock office doors. Each time a worker uses their key-card, the security system saves the worker's name and the time when it was used. The system emits an **alert** if any worker uses the key-card **three or more times** in a one-hour period.
+
+You are given a list of strings `keyName` and `keyTime` where `[keyName[i], keyTime[i]]` corresponds to a person's name and the time when their key-card was used **in a** **single day**.
+
+Access times are given in the **24-hour time format "HH:MM"**, such as `"23:51"` and `"09:49"`.
+
+Return a _list of unique worker names who received an alert for frequent keycard use_. Sort the names in **ascending order alphabetically**.
+
+Notice that `"10:00"` - `"11:00"` is considered to be within a one-hour period, while `"22:51"` - `"23:52"` is not considered to be within a one-hour period.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** keyName = ["daniel","daniel","daniel","luis","luis","luis","luis"], keyTime = ["10:00","10:40","11:00","09:00","11:00","13:00","15:00"]
+
+**Output:** ["daniel"]
+
+**Explanation:** "daniel" used the keycard 3 times in a one-hour period ("10:00","10:40", "11:00").
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** keyName = ["alice","alice","alice","bob","bob","bob","bob"], keyTime = ["12:01","12:00","18:00","21:00","21:20","21:30","23:00"]
+
+**Output:** ["bob"]
+
+**Explanation:** "bob" used the keycard 3 times in a one-hour period ("21:00","21:20", "21:30").
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= keyName.length, keyTime.length <= 105
+* `keyName.length == keyTime.length`
+* `keyTime[i]` is in the format **"HH:MM"**.
+* `[keyName[i], keyTime[i]]` is **unique**.
+* `1 <= keyName[i].length <= 10`
+* `keyName[i] contains only lowercase English letters.`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun alertNames(keyName: Array, keyTime: Array): List {
+ val map = HashMap>()
+ for (i in keyName.indices) {
+ map.putIfAbsent(keyName[i], ArrayList())
+ map[keyName[i]]!!.add(keyTime[i])
+ }
+ val soln: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for ((key, timeStamps) in map) {
+ timeStamps.sort()
+ var i = 0
+ while (i + 2 < timeStamps.size) {
+ val first = timeStamps[i].split(":").dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()
+ val third = timeStamps[i + 2].split(":").dropLastWhile { it.isEmpty() }.toTypedArray()
+ val hourDiff = third[0].toInt() - first[0].toInt()
+ val minDiff = third[1].toInt() - first[1].toInt()
+ if (hourDiff == 0 || hourDiff == 1 && minDiff <= 0) {
+ soln.add(key)
+ break
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ }
+ soln.sort()
+ return soln
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1605_find_valid_matrix_given_row_and_column_sums/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1605_find_valid_matrix_given_row_and_column_sums/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fc6bab80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1605_find_valid_matrix_given_row_and_column_sums/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1605\. Find Valid Matrix Given Row and Column Sums
+
+Medium
+
+You are given two arrays `rowSum` and `colSum` of non-negative integers where `rowSum[i]` is the sum of the elements in the ith row and `colSum[j]` is the sum of the elements of the jth column of a 2D matrix. In other words, you do not know the elements of the matrix, but you do know the sums of each row and column.
+
+Find any matrix of **non-negative** integers of size `rowSum.length x colSum.length` that satisfies the `rowSum` and `colSum` requirements.
+
+Return _a 2D array representing **any** matrix that fulfills the requirements_. It's guaranteed that **at least one** matrix that fulfills the requirements exists.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** rowSum = [3,8], colSum = [4,7]
+
+**Output:** [[3,0], [1,7]]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+0th row: 3 + 0 = 3 == rowSum[0]
+
+1st row: 1 + 7 = 8 == rowSum[1]
+
+0th column: 3 + 1 = 4 == colSum[0]
+
+1st column: 0 + 7 = 7 == colSum[1]
+
+The row and column sums match, and all matrix elements are non-negative.
+
+Another possible matrix is: [[1,2],
+ [3,5]]
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** rowSum = [5,7,10], colSum = [8,6,8]
+
+**Output:** [[0,5,0], [6,1,0], [2,0,8]]
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= rowSum.length, colSum.length <= 500`
+* 0 <= rowSum[i], colSum[i] <= 108
+* `sum(rows) == sum(columns)`
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+class Solution {
+ fun restoreMatrix(rowSum: IntArray, colSum: IntArray): Array {
+ val ans = Array(rowSum.size) { IntArray(colSum.size) }
+ for (i in rowSum.indices) {
+ for (j in colSum.indices) {
+ if (rowSum[i] != 0 && colSum[j] != 0) {
+ ans[i][j] = Math.min(rowSum[i], colSum[j])
+ rowSum[i] -= ans[i][j]
+ colSum[j] -= ans[i][j]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1606_find_servers_that_handled_most_number_of_requests/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1606_find_servers_that_handled_most_number_of_requests/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1e7c7c3c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g1601_1700/s1606_find_servers_that_handled_most_number_of_requests/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin)
+[](https://github.com/javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin/fork)
+
+## 1606\. Find Servers That Handled Most Number of Requests
+
+Hard
+
+You have `k` servers numbered from `0` to `k-1` that are being used to handle multiple requests simultaneously. Each server has infinite computational capacity but **cannot handle more than one request at a time**. The requests are assigned to servers according to a specific algorithm:
+
+* The ith (0-indexed) request arrives.
+* If all servers are busy, the request is dropped (not handled at all).
+* If the (i % k)th server is available, assign the request to that server.
+* Otherwise, assign the request to the next available server (wrapping around the list of servers and starting from 0 if necessary). For example, if the ith server is busy, try to assign the request to the (i+1)th server, then the (i+2)th server, and so on.
+
+You are given a **strictly increasing** array `arrival` of positive integers, where `arrival[i]` represents the arrival time of the ith request, and another array `load`, where `load[i]` represents the load of the ith request (the time it takes to complete). Your goal is to find the **busiest server(s)**. A server is considered **busiest** if it handled the most number of requests successfully among all the servers.
+
+Return _a list containing the IDs (0-indexed) of the **busiest server(s)**_. You may return the IDs in any order.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** k = 3, arrival = [1,2,3,4,5], load = [5,2,3,3,3]
+
+**Output:** [1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+All of the servers start out available.
+
+The first 3 requests are handled by the first 3 servers in order.
+
+Request 3 comes in. Server 0 is busy, so it's assigned to the next available server, which is 1.
+
+Request 4 comes in. It cannot be handled since all servers are busy, so it is dropped.
+
+Servers 0 and 2 handled one request each, while server 1 handled two requests. Hence server 1 is the busiest server.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** k = 3, arrival = [1,2,3,4], load = [1,2,1,2]
+
+**Output:** [0]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The first 3 requests are handled by first 3 servers.
+
+Request 3 comes in. It is handled by server 0 since the server is available.
+
+Server 0 handled two requests, while servers 1 and 2 handled one request each. Hence server 0 is the busiest server.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** k = 3, arrival = [1,2,3], load = [10,12,11]
+
+**Output:** [0,1,2]
+
+**Explanation:** Each server handles a single request, so they are all considered the busiest.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= k <= 105
+* 1 <= arrival.length, load.length <= 105
+* `arrival.length == load.length`
+* 1 <= arrival[i], load[i] <= 109
+* `arrival` is **strictly increasing**.
+
+## Solution
+
+```kotlin
+import java.util.PriorityQueue
+import java.util.TreeSet
+
+class Solution {
+ internal class Server(val id: Int, val busyTime: Int)
+
+ fun busiestServers(k: Int, arrival: IntArray, load: IntArray): List {
+ val available = TreeSet()
+ val busy = PriorityQueue({ a: Server, b: Server -> a.busyTime.compareTo(b.busyTime) })
+ val requestCount = IntArray(k)
+ val n = arrival.size
+ for (id in 0 until k) {
+ available.add(id)
+ }
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ val defaultServer = i % k
+ while (busy.isNotEmpty() && busy.peek().busyTime <= arrival[i]) {
+ val top = busy.poll()
+ available.add(top.id)
+ }
+ if (available.isEmpty()) {
+ continue
+ }
+ var nextServer = available.ceiling(defaultServer)
+ nextServer = nextServer ?: available.ceiling(0)
+ val requestEnd = arrival[i] + load[i]
+ available.remove(nextServer)
+ busy.add(Server(nextServer, requestEnd))
+ requestCount[nextServer]++
+ }
+ var maxRequests = Int.MIN_VALUE
+ val busiestServers: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (id in 0 until k) {
+ maxRequests = Math.max(maxRequests, requestCount[id])
+ }
+ for (id in 0 until k) {
+ if (requestCount[id] == maxRequests) {
+ busiestServers.add(id)
+ }
+ }
+ return busiestServers
+ }
+}
+```
\ No newline at end of file